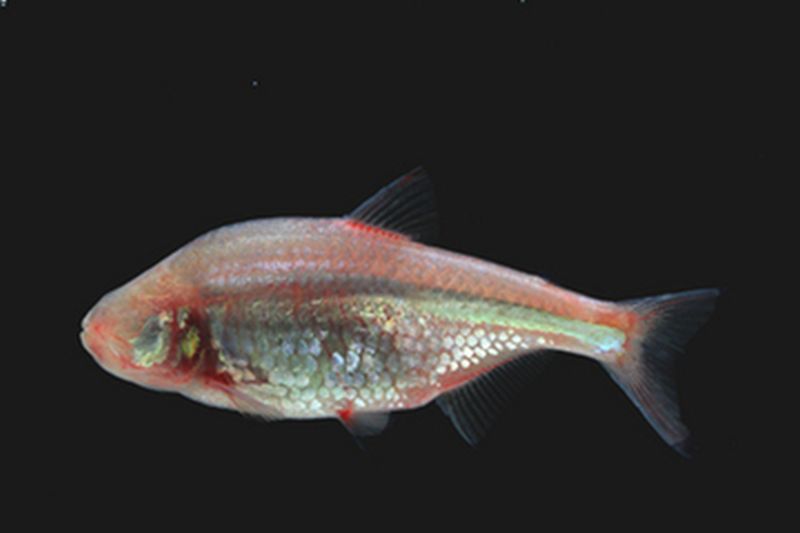
When it comes to visualizing environment, eyes play an important role. But there are other ways of navigation such as echolocation used by bats and dolphins. Recently, researchers studying Mexican blind cavefish (Astyanax fasciatus), have found a unique and new method of navigation. These fishes spend their entire life in the deep sea or dark caves, which are devoid of any source of light and so as the name suggests, their eyes are rendered useless and over the time the fish losses their eyeballs.
Read MoreAuthor: Neha Shukla
Tactile Stimulation and Reproduction go Hand in Hand Amongst Female Cockroaches
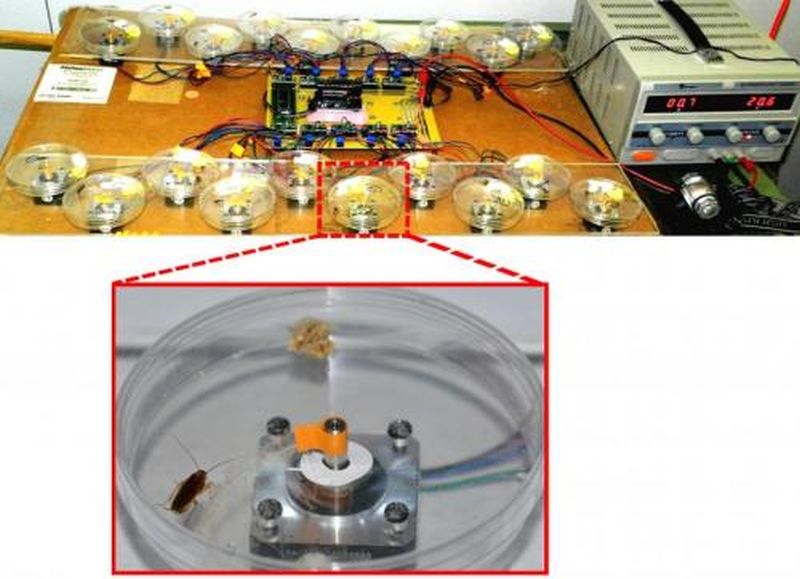
Generally, the antenna, key sensory organ of insects is known to aid insects in perceiving information about its surroundings such as availability of food, danger of predator, obstacles and potential mates and so on. They have many sensory receptors for audition, olfaction, balance, stability, gustation, graviception, thermo, hygro and mechanoreception, to name a few. They also play an important role during social interactions. In German cockroaches (Blattella germanica), during such social interaction, antennal contact alters juvenile hormone production which leads to an increase in female reproduction rate. In short the…
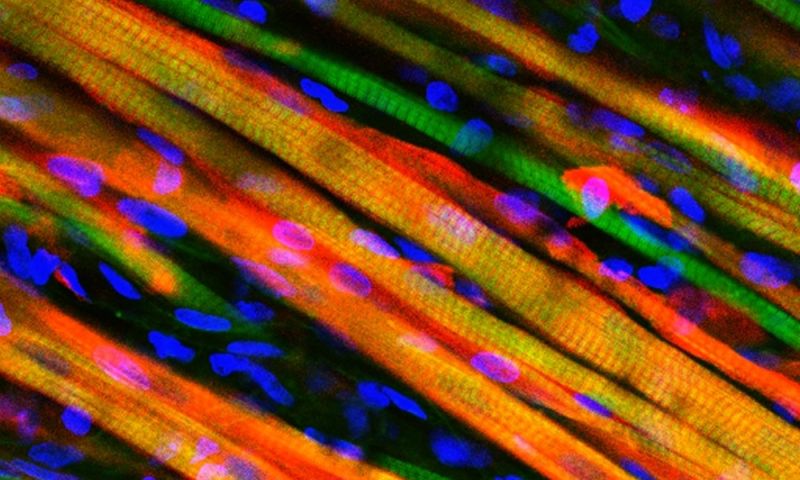
Read MoreBioengineered Self Healing Muscle, Successfully Grown in Laboratory
Biomedical engineers have finally achieved success in growing skeletal muscle under a laboratory conditions. These laboratory grown muscles, similar to real muscle are capable of contracting and expanding quickly. Most important breakthrough in the research is that the muscles when implanted in mice were capable of healing itself from any injuries, which was not possible till now.
Read MoreWater Free Robotic Cleaning System Takes Over The Ketura Sun Solar Park
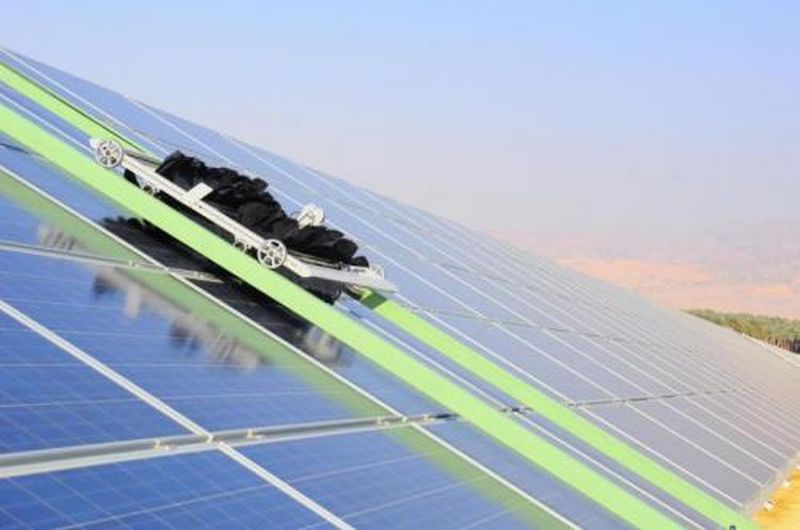
The increasing consumption of electricity, due to rise in population and limited availability of natural resources, countries have been focusing on generating energy from alternative sources. Sun energy in one among them and is widely preferreddue to its long hours availability at no cost at all. Though its conversion technology involves crystalline panels and other components, the panels require a regular look after to sustain effectively for years and decades. The large capacity solar plants consisting huge number of these panels suffer some difficulty in smooth operations as dust, sand…
Read MoreSniffing Web Pheromones Helps Male St. Andrew’s Cross Spiders Determine Female Availability
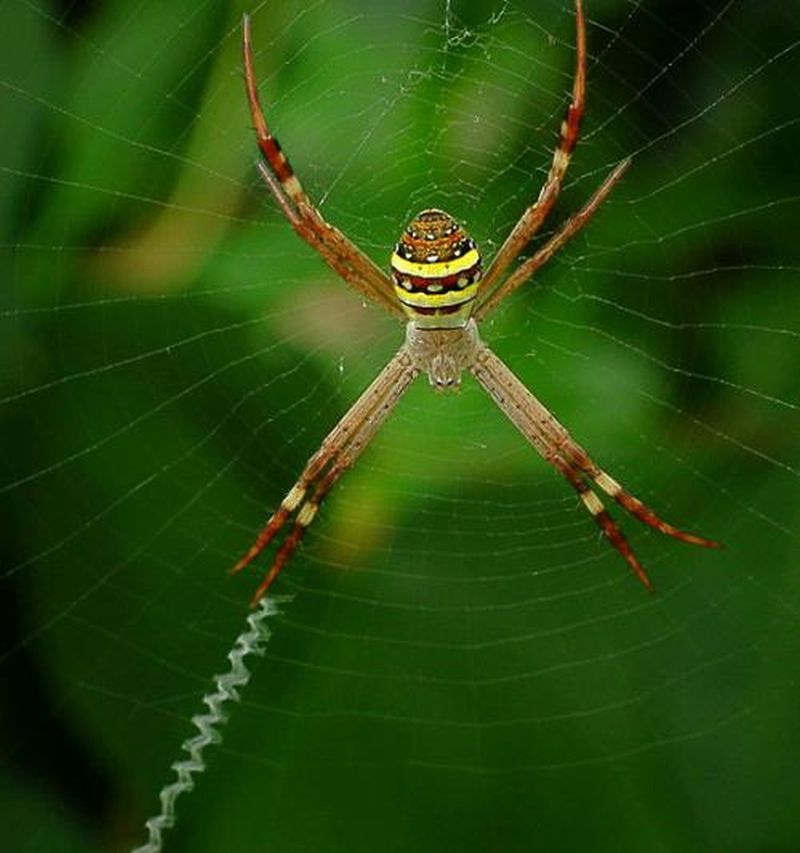
Researchers from the University of Hamburg, Germany and Macquarie University in Australia, studying St. Andrew’s Cross spiders, have found that male spiders looking for suitable mates, smell the webs woven by females and determine the females are ready for mating. The researchers observed several specimens of the species and conducted numerous experiment in their laboratory and finally concluded that smelling the pheromones present on the female web, male spider make a decision whether to move closer to the female for mating or not.
Read MorePlants Uses Chemical Weapons and Employ Insect Armies to Defend Themselves
When we encounter a danger, the first thing that strikes in our mind is to run away and hide (though many of us might choose to give a fight). But the article is in the context of animals and plants. Animals when encounter any danger of being attacked, the first instinct is to escape from the danger is to run. Unfortunately, the plants cannot do that. Rather, plants in order to defend themselves from their predators have evolved various defense techniques such as chemical weapons and insect armies.
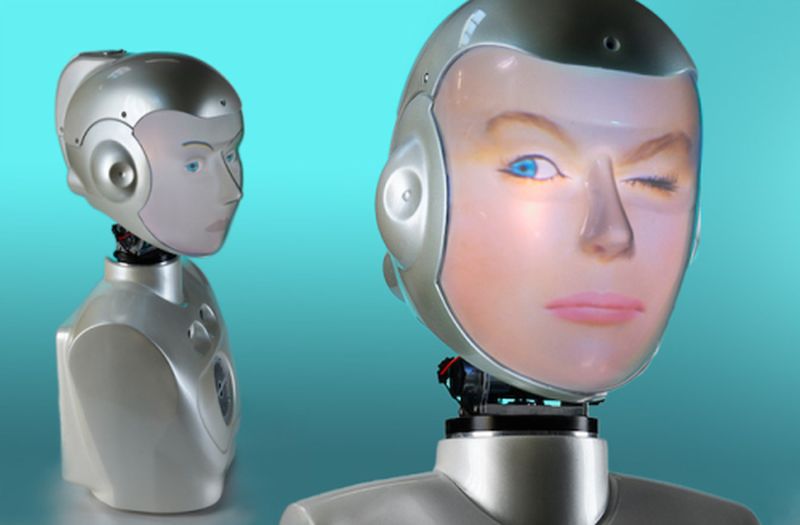
Read MoreSociBot-Mini Reacts to Expressions by Displaying Various Moods
Will Jackson and his team of researchers at Engineered Arts in Penryn, UK, have developed an interactive, one of its kind bot known as SociBot-Mini. The robot distinctive attribute is its face that is capable of displaying distinct moods and can react to expressions of individuals looking at it.
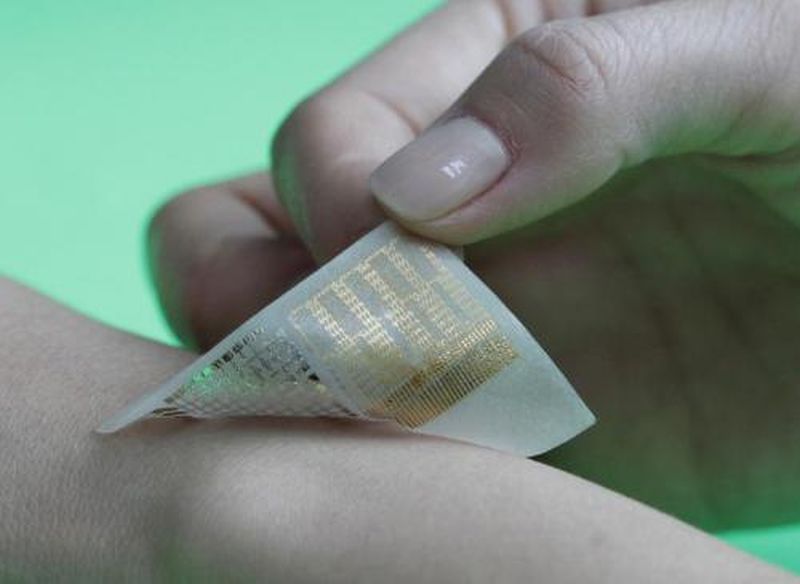
Read MorePlaster to Release Medicine Below the Skin
A team of medical engineers from South Korean have developed a plaster which, when applied to the patient’s skin similar to regular band aids, discharge medicine below the skin. But unlike the normal band aid used for minor cuts and bruises, the plaster engages more complex and advanced technology, which enables it to monitor the activities of the muscle and accordingly discharges the required quantity of medicine and even decide when it is needed to stop.
Read MoreDark Plumage helps in Flushing out Toxic Metals
Just like humans, animals living in urban areas are constantly prone to metal intoxication. In France, a team of researchers studying the level of metal intoxication in birds have found a strange relation between the color of the plumage and the level of metal toxin in the bird’s body. They observed that the birds with dark shade plumage were better at getting rid of metal toxin from their bloodstream.
Read MorePandas Have A Functional Sweet Taste Receptor
The popular known fact that bamboo is the only food that panda exclusively feeds on, is not true. Researchers from the Monell Center have found that the panda has also liking for sweet food. The research, based on panda behavior and molecular genetics reveals the presence of taste receptors and confirms that the panda has a strong liking for natural sweeteners as fructose and sucrose.
Read MoreGoat’s Intelligence Was Underestimated
When we talk about intelligence in the animal kingdom, animals like chimpanzees, dolphins or crows are the first one to come across our minds. But it’s time to get over them, because as per the latest research, common goats are way more intelligent than formerly believed.
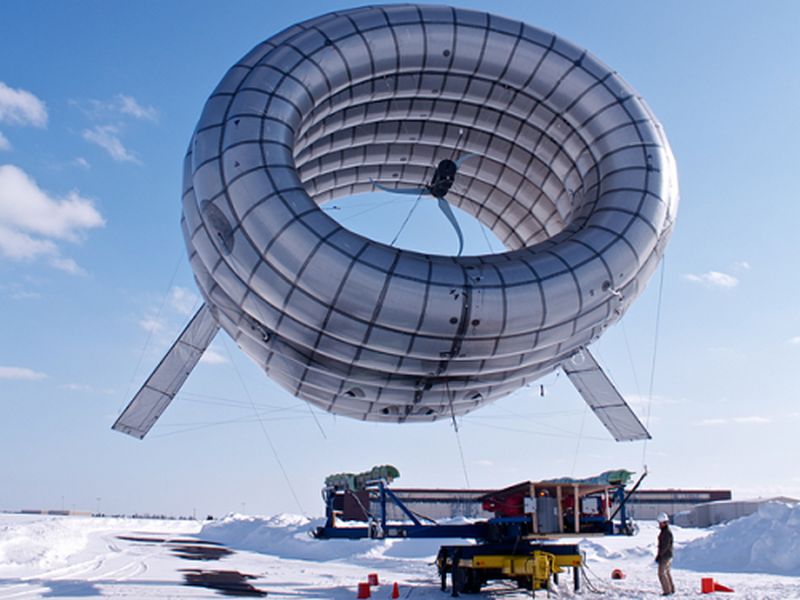
Read MoreAltaeros’ Buoyant Airborne Turbine: Floats at High Altitude
We visualize wind turbine as tall tower with a huge fan mounted on it and fixed at some distant place. But we might have never imagined a wind turbine that floats in the air. Does it sound like a sci-fi movie subject? Surprisingly, it’s a reality being developed by MIT startup Altaeros Energies and will be seen floating in the sky above the city of Fairbanks and the power so generated will be used to power remote military sites and families residing off the grid that usually depend on expensive…
Read MoreBrain Mechanics Still a Debatable Issue
Humans in their entire life come across thousands of people. And they relatively recognize and remember all of these individual faces, thanks to the extraordinary brain for the same. But the mechanism behind this ability of the brain is still an issue for debate among the scientists. There are two hypotheses proposed by the researchers explaining how humans acquired this ability. One group of researchers suggests that the brain has specialized mechanism, exclusively for faces. Whereas the other group put forward the belief (expertise hypothesis) that the identification of any…
Read MoreFAT10 Gene in Mice Associated to Body Fat And Ageing
In a latest research, scientists have identified a gene which synchronizes the immune system and metabolism of the body. And the study conducted on mice shows that eliminating the gene results in increased longevity and less body mass.
Read MoreClimate Change Slowing The Deep Ocean Currents
We recently covered an article explaining the vital role of the oceans in the global carbon cycle and the process in which oceans accumulate, transport and convert carbon molecules. But according to a recent research carried by Irina Marinov and Raffaele Bernardello from University of Pennsylvania and colleagues from McGill University, says that climate change is slowing down the deep ocean currents and can adversely influence the climate in the future.
Read More