Study of human brain is one of the most remarkable subjects of all times. The more we learn, the more questions we have, this holds true for the wide network of neurons that we all carry above our head, literally.
Even experts agree that there is still more to understand. Our knowledge regarding the most complex manifestation of intelligence is very limited than we currently do know.
Brain is one of the most intricate and fascinating organs in our body. We have tried to come up with ten brain facts, a food for thought.
1) Brain feels no pain
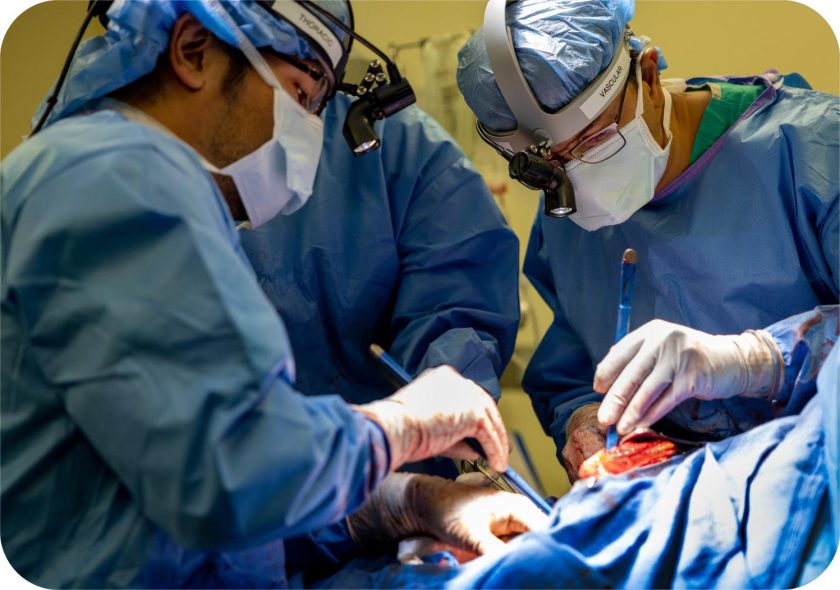
Brain has no pain receptors. Brain surgeries are generally done when patients are awake of course under the influence of local anaesthesia. Awake brain surgery is also called craniotomy.
Craniotomy is performed to treat neurological conditions, like brain tumors and epileptic seizures. It is done to lower the risk of damage to functional areas which are directly related to vision, movement or speech.
2) Brain composes of nearly 80% water
Hydration is critical to its health. Dehydration directly affects the brain as it may lead to memory impairment. Therefore, it is very important to drink at least 2-3 litres of water daily.
Consuming good amount of water not only enhances memory functions, rather it also helps in other areas, like:
- Improvement in concentration and cognition
- Assists in balancing mood and emotions
- Elevates blood flow and oxygen level to brain
- Averts and help in relieving headaches
- Reduce stress
3) Brain never rests (even during sleep)
Sleeping is not that easy as it sounds. It is an incredibly complex process. During sleep, cerebrospinal fluid flushes away harmful waste proteins that gets accumulated between neurons during waking hours. Thus, good sleep is directly proportional to an optimal function of body during waking hours.
When it comes to sleep, brain generates two types of patterns:
I) Slow-wave sleep (SWS), also called as deep sleep. It is characterized by high-amplitude, low-frequency brain waves, relaxed muscles and deep breathing. Generally, intense prolonged exercise and body heating (due to hot bath or sauna) results in SWS. Nearly, 95% production of growth hormones via pituitary gland occurs in body during this stage.
Deep sleep boosts glucose metabolism in the brain. It is because of the neurons, brain is the most energy-demanding organ, it nearly requires one-half of all the sugar energy in the body. Hence, deep sleep supports short-term and long-term memory and overall learning abilities.
II) Rapid eye movement (REM), also called dreaming sleep. As the name suggests, the eyes move rapidly in various directions. REM sleep triggers most of the dream events.
During this stage, the activities of the brain show similar patterns to that during waking hours. Also, breathing becomes fast and irregular.
Lack of REM sleep leads to:
Migraines: Not getting enough sleep is one of the major factors that is linked with migraines and hyper tension.
Excess weight in children and adolescents: Studies have associated sleep deprivation is linked to higher chances of obesity, cardiovascular disease and behavioural problems.
Reduced coping skills: An old research suggests, REM sleep deprivation induces abnormalities in coping and defensive responses in threatening situations.
Therefore, sleep helps to rewire of neural network, boost immune system and activate memory.
4) Neural networks can be rewired at any age
Brain has the capacity to rewire itself. This process is called, plasticity or neuroplasticity. Practising any new activity, fires new connections in neural network. Consistency makes the new connections efficient, robust and self-sustaining.
Typically, neurocircuitry displays, three main principles:
- Use it or lose it: any skill can be acquired all it takes is persistence
- Neurons that fire together, wire together: behaviour can change mental framework
- Survival of the busiest: we become what we think consistently
Although, change does not occur immediately. Like any other biological process, neuroplasticity takes time.
Developing new hobbies and un-learning both take some amount of effort and time. However, taking one step at a time does lay the groundwork for new connections to take place. And accordingly, it helps in developing new cognitive perceptions as well.
5) Music activates entire brain
Music is not only limited to the auditory areas but affects the wide networks in brain, including motor actions, emotions and creativity.
As per Finnish researchers, musical pulse replenishes motor areas in the brain. No wonder, music and dance/movement/foot tapping are closely intertwined.
Also, music is profoundly linked to personal memories. Limbic areas of the brain, known to be associated with emotions, were found to be involved in rhythm and tone of music. That is why certain songs triggers strong memories while still others make us nostalgia.
The act of creating new music or involved in any form of musical activity leads to high levels of cognitive function. Some of them are complex problem solving, logical reasoning and conceptual tasks.
6) Brain freeze is body’s way of putting on the brakes
Brain freeze occurs when we are in the process of eating or drinking anything that is cold at a fast pace. It could be ice cream, ice pops, slushy drink, freezing cold water and cold drinks. It is also called as ice cream headache and cold stimulus headache.
It is caused by the sphenopalatine ganglioneuralgia nerves (SPG), which is a group of nerves near the trigeminal nerve in the brain.
Reasons behind brain freeze:
- Cold stimulus clogs up the sinuses, causing pain and pressure. The sinuses are a connected system of hollow cavities in the skull. Cooling of many tiny blood vessels of the sinuses also results in vasoconstriction, that is, narrowing of the blood vessels.
- Local changes in brain blood flow at times leads to brain freeze. A quick re-warming – to bring back to a state of warmth after being cooled – by introducing warm stimulus such as (hot) air leads to vasodilation, that is widening of the blood vessels.
- Rapid changes in sensitive nerves, such as trigeminal nerve, which runs through the upper palate of the mouth, also create sensations of brain freeze.
Although, brain freeze lasts for few seconds to minutes but the two major nerves responsible – sphenopalatine ganglioneuralgia nerves and trigeminal nerve – also triggers phases of migraines.
7) Alternate nostril breathing improves brain functions
The technique of alternate breathing through nose gives boost to the both sides of cerebral hemispheres as it provides equal amounts of oxygen to left and right hemispheres.
Taking more oxygen through natural process reduces the brain bound free radicals, relaxes neurons, reduce anxiety, improves memory and cognition. Also, it has immediate advantages to the other vital organs in the body, such as the heart and lungs.
Brain and spinal cord are the main centres in the central nervous system (CNS) that are responsible for generating energy and flow of electricity within the entire body. Good flow means that the nerves are in sturdy and good shape. While, less amount of flow means, nerves are deteriorating. Hence, by alternate breathing techniques, the nerve centres are stimulated, which in turn improves the overall functioning of entire nervous system.
8) Brain can store trillions of bytes of information
Cerebral cortex alone has 125 trillion synapses. It is the outermost layer of the brain and often referred to as grey matter due to the collection of neural cell bodies.
Neurons are the true cells of CNS. They are concerned with communication signals and releasing neurotransmitters. Synapses is a junction between two nerve cells, which carry the transmitted messages. 1 synapse can store 4.7 bits of information.
As per the calculations:
(125 trillion synapses) (4.7 bits of information) / 8 (1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024) = 67 TB (Terabyte)
This storage capacity is an amount over 67 Terabytes. And this figure is just in the cerebral cortex alone.
To put this in perspective, our smart phones memory capacity is in “gigabytes” (16GB, 64GB, 128GB). And 1024 GB = 1 TB.
Scientific American reported that memory capacity of the human brain is equal to 2.5 petabytes. To make it simpler, 1 petabyte = 1024 terabytes or a million gigabytes.
This means, adult human brain has the capacity to hold somewhere around 2.5 million gigabytes of digital memory.
9) Body’s posture and expressions influence brain
Brain uses facial expressions and body’s posture as cues to feel emotions. That is why smiling for no reason can actually makes us feel better.
A study using MRI postulates that facial expressions not only reflect what people are feeling, they influence it too. Studies have linked that when people make an angry face, or give frowning expression, they exhibit less activity in regions of the cerebral cortex. The area is associated with empathy and decision making.
Walking, sitting or standing tall with confidence gives boost to neural activity too. After all, body language and posture can temporarily change the chemistry of our body.
Amy Cuddy in her TED talk showed how power posing actually changes the chemistry within brain.
10) Brain cells cannibalize themselves
When we don’t eat body’s required amount of food, hunger-inducing neurons cannibalize themselves to ward off starvation. Although, it is an act of natural balance in cell’s life cycle. However, it was thought that brain (neurons) do not display such behaviour.
According to Cell Press, like any other cell, neurons too appear to self-cannibalize when a body becomes starved for sustenance.
Hypothalamus, that sits above the brain stem is responsible for regulating functions like including sleep, body temperature, thirst and hunger. Researchers observed that neurons in the hypothalamus started consuming their own organelles and proteins to maintain cellular homeostasis, which was disturbed because of lack of food.
Once the autophagy starts off, it releases fatty acids, resulting in the release of hunger signals, telling the brain that more food was required.

The takeaway
As mentioned before, there’s a lot about the brain, what the scientists and doctors are yet to find out. For instance, what is consciousness and how it enters and leaves the body. Is the consciousness or awareness the by-product of neural network? How does it originate? Questions like these boggles the scientists and that is why they call it the “hard problem of consciousness.”