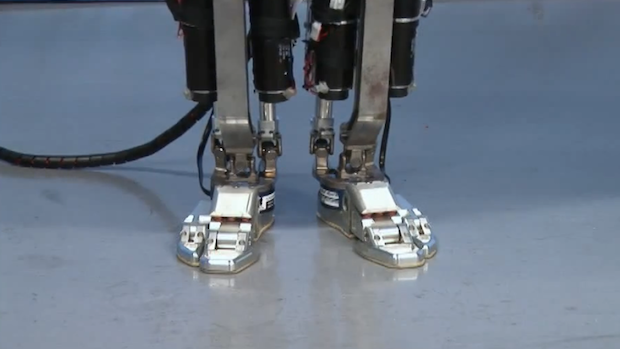
Inspired from living organisms, researchers try to create robots that can simulate living creatures mechanically or chemically. This field of science is named as Biorobotics. A team of researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Campaign has made a miniature walking bio-bots that derive its power from living muscle cells. And their movement can be regulated externally using electrical pulses.
Muscle Cell Powered Bio-Bots
The research team wanted to create a robot based on muscle-tendon-bone complex as seen in nature. Lead author and head of bio-engineering Rashid Bashir and his team, designed the bio-bots that use rat muscle cells to maneuver around. The muscle cells encase flexible 3D printed hydrogel that behave as the backbone of the robot. The backbone is strong and gives structure to the bot, as well as flexible that can bend like a joint. The bot also consists of two posts that help in securing the muscles on the backbone (just like tendons binds muscles on the bones), apart from serving as the feet of the bio-bot.
When these tiny bots are stimulated using electric pulses, the muscle contracts and making bot move forward. The use of skeletal muscle gave researchers unprecedented control of the bot’s movement. The bot movement can be increased or decreased by changing the frequency of electric pulses. High frequency leads to faster muscle contraction and increasing the bio-bot’s speed.
Heart Cell Powered Bio-Bots
In certain other research, heart cells from rats were used to power bio–bots to walk. But researchers could not control the robot’s movement as the heart cells contract constantly. To overcome this drawback, researchers used a strip of skeletal muscle cells that can be stimulated by an electric pulse to power the new generation of bio-bots. Bio-engineers can now create customized bio-bots for specific applications.
Skeletal muscle cells can be easily controlled using external signals and so are very helpful while creating such bio-bots, said Bashir. Using skeletal muscle, bio-engineers can create robots that can be programmed to start functioning when triggered by a chemical or any other signal. It also gives researchers the flexibility to turn it off or on or change its rate of movement as required.
Facilitating Implantation & Drug delivery within Body
The research serves as a step towards designing and controlling biological machines that can be triggered, programmed or trained to perform the task assigned. Bio-engineers believe that further improvement in the system will lead to advanced biological machines which would be used in areas like drug delivery, smart implants, surgical robotics, mobile environmental analyzers and so on.
Researchers aiming to gain more control over the locomotion, are planning to introduce neurons in these bio-bots. Such bots will act as autonomous sensors and can be guided using chemical or light acting as stimuli to start functioning. And hydrogel backbone can be refined to provide the bot with extra flexibility and enable the bio-bot to move in different directions depending on different stimuli.
In the future, these bio-bots can be used for delivery of drugs to specific site, inside the human body, along with various other medical applications.
Source: University of Illinois
Image: dailymail.co.uk, dailymail.co.uk