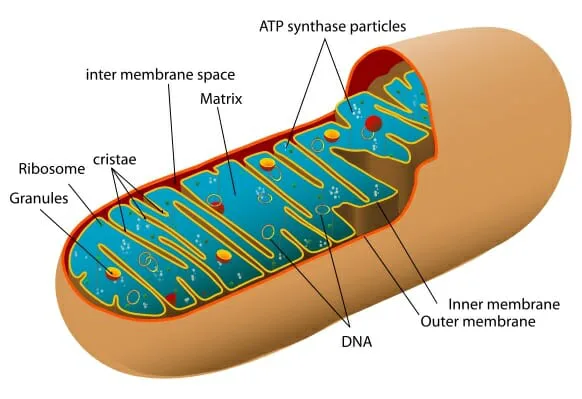
If you’ve ever tried to remember where you parked your car while also keeping track of your grocery list, you’ve felt the limits of working memory. A new study from researchers at NYU and Ohio State digs into how the brain decides what to hold onto more carefully and most importantly, how it does it.
Read MoreTag: neuroscience
Infomorphic Neurons: Self-Learning AI Inspired by Biology
Imagine if artificial neurons could learn like the ones in our brains, adapting, making decisions on their own, and figuring things out without needing a central command. That’s exactly what scientists are working on with a new kind of artificial neuron called infomorphic neurons. Unlike traditional artificial neural networks, these neurons don’t need an external system to guide their learning. Instead, they learn in a self-organized way, just like biological neurons do.
Read MoreHow Your Brain Filters Information: The Science of Excitation and Inhibition
Neurons in our brain are constantly taking in and distributing information, be it sound, sight or touch, everything is getting processed in the real time. But how exactly does this work? Recent research sheds light on how groups of neurons work together to encode and process information. The study has surfaced some interesting insights about the balance between excitation and inhibition in the brain.
Read MorePsychedelics Stimulate Hippocampal Cells to Alleviate Anxiety
When I first read “DMT: The Spirit Molecule” by Dr. Rick Strassman, I thought developing psychedelic inspired drugs without any “hallucinating” side-effects to cure anxiety related problems could be a game changer. Interestingly, I came across research by Cornell University, where researchers did come up with psychedelics to excite cells in hippocampus to reduce anxiety.
Read MoreNew Pathway Discovery: Could Block Glioblastoma Spread
An international team of researchers from the academia of Canada and the U.S., has uncovered a new way that cancer cells use to invade the brain. Interestingly, the research team led by the Singh Lab at McMaster University has also found a new therapy that looks promising for blocking and killing these tumors.
Read MoreCAMs: Key Players in Modulating Post-Stroke Immune Responses
When a blood clot blocks an artery, it leads to an ischemic stroke. The blockage or ischemic stroke prevents blood and oxygen from reaching areas of the brain. This gives rise to one of the following symptoms: According to the statistics, the older one gets, the higher the risk of experiencing ischemic strokes. Although, neuroscience has helped us understand what happens in the body during a stroke. However, we have no idea how the immune system helps with recovery after a stroke.
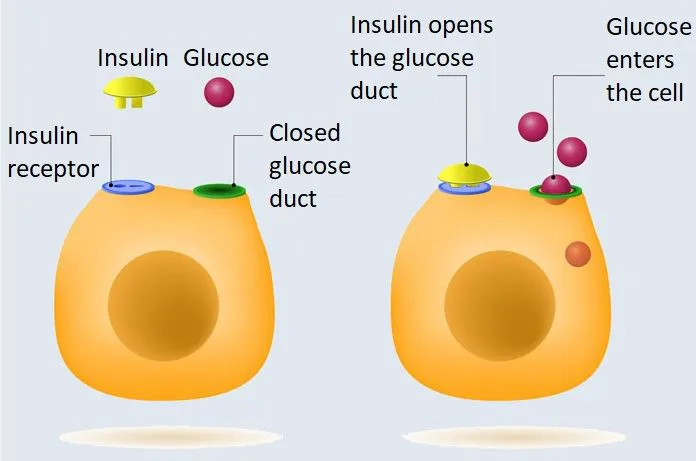
Read MoreInsulin Resistance: Ketones Found to Revive Neuron Function
Recent research conducted by the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester focused on understanding how ketones affect the brain’s hippocampal network. The hippocampus is a crucial brain region involved in memory formation and spatial navigation.
Read MoreNanoparticles Break Blood-Brain Barrier for Cancer Treatment: Targeting Metabolic Adaptability
Scientists at the Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, part of the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, have crafted a tiny particle capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier. The team envision to tackle both primary breast cancer tumors and brain metastases in a single treatment. Their investigations indicate that this approach can reduce the size of both breast and brain tumors in lab experiments.
Read MoreMitochondrial Energy Crisis: Unraveling the Alzheimer’s Puzzle
Brain cells crave immense energy to survive and communicate through connections known as synapses. These cells are like energy enthusiasts, which are busy in making way through synapses. But, in the Alzheimer’s scenario, it’s like they’re facing an energy crisis. This messes up their power production. And so, it leads to crumbling down of the synapses and consequently, our fresh memories slowly slip away.
Read MoreLactate Enriches Neurogenesis: Neuronal Differentiation
Scientists at Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan made an exciting discovery regarding cellular mechanisms that assist in developing our brains. They discovered that lactate plays an important role in helping neural stem cells become specialized neurons. Lactate happens to be the by-product of exercise and metabolism. Researchers even gave this process a fancy name: neuronal differentiation.
Read MoreOmega-3 Slow ALS Progression: Fatty Acid has Neuroprotective Effects
Recent study led by Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health suggests that a diet high in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) may have potential benefits for individuals with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). ALS is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects nerve cells responsible for controlling muscle movement.
Read MoreTargeting Folate Receptors in Gliomas: A New Way to Detect Brain Tumors
Recent research conducted by Maxwell Miner from the University of Turku in Finland, working at the Turku PET Centre, sheds light on the potential of folate receptors as a valuable tool in the field of brain tumor imaging and treatment. Folate-based radiopharmaceuticals are a type of medical imaging agent that combines folate – a form of vitamin B9 – with a radioactive substance.
Read MoreDistinct Activation Patterns of Projection Neurons: Cortical Dynamics
Cerebral cortex is the outer layer of cerebrum, that is the largest part of the brain. All kinds of higher-level processes such as language, memory, and decision-making are performed in this region. The complex, densely packed structure is saturated with various types of neurons. It is extremely difficult to image its neuronal dynamics with the necessary spatial and temporal resolution. So far, fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) technique is widely used for studying brain activity. However, when it comes down to examine neural circuitry at the point of a single…
Read MoreAstrocytes are the Information Regulators: Brain Pathology
Astrocytes are the non-neuronal cells that provide support and maintenance to neurons in the brain and spinal cord. They have a star-shaped morphology, with multiple branching processes that extend out from the cell body. They form specialized junctions with blood vessels for regulating the transport of nutrients and other molecules between the brain and the bloodstream.
Read MoreNeuro-Stack to records Single Neuron Activity: Brain Mechanisms of Movement
New technologies have revolutionized many fields, including medicine and neuroscience. Advances in engineering, materials science, and computer technology have enabled the development of increasingly sophisticated devices for recording and analysing biological signals, such as brain activity, with unprecedented precision and accuracy. For instance, electroencephalography (EEG) is a non-invasive technique that measures electrical activity in the brain using electrodes placed on the scalp. With the advancement in electronics and computing the EEG signals can now be recorded with greater precision and resolution.
Read More