Recent research conducted by Maxwell Miner from the University of Turku in Finland, working at the Turku PET Centre, sheds light on the potential of folate receptors as a valuable tool in the field of brain tumor imaging and treatment.
Folate-based radiopharmaceuticals are a type of medical imaging agent that combines folate – a form of vitamin B9 – with a radioactive substance.
These radiopharmaceuticals are used in positron emission tomography (PET) imaging to detect specific folate receptors in the body. These receptors are proteins found on the surface of certain cells, including cancer cells.
This discovery of folate receptors and their potential use in brain tumor detection is a ground-breaking finding in the field of medical research.
Higher folate receptor levels in gliomas
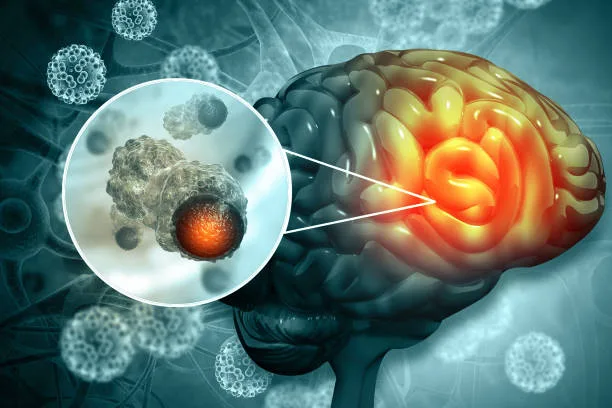
Lately, researchers have identified that gliomas have higher levels of folate receptor as compared to the surrounding healthy brain tissue.
Glioma is a type of brain tumor. It is known to be serious and difficult to treat.
When researchers studied the samples taken from actual human brain tumors, they observed that the tumors were saturated with folate receptors.
Before this discovery, the presence of folate receptors and their increased expression in gliomas was not recognized.
This also implies that folate receptors had not been used for imaging or treatment purposes in relation to brain tumors.
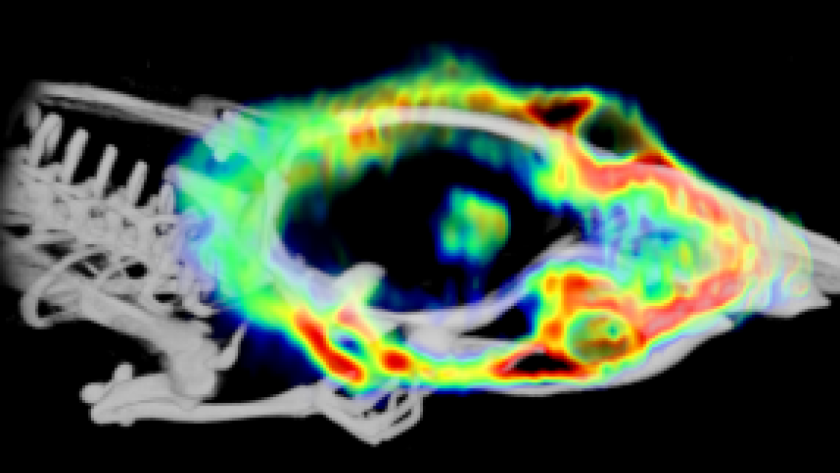
Targeting folate receptors in gliomas
By specifically targeting the folate receptors found in gliomas, medical professionals will have the potential to enhance several aspects of patient care, such as:
Improved Diagnosis: Folate-based radiopharmaceuticals can be used in PET imaging to accurately detect and visualize the presence and location of gliomas.
This targeted approach will provide accurate info about the extent and characteristics of the tumor. Consequently, it’ll aid in the initial diagnosis and guiding further diagnostic tests and procedures.
Enhanced Treatment Planning: Understanding the distribution and expression of folate receptors in gliomas can help doctors in planning the most effective treatment strategies.
Once doctors are able to identify the folate receptor expression, they would be in a better position to tailor following treatment approaches without damaging any healthy surrounding tissue.
- surgery
- radiation therapy
- targeted therapies
Monitoring Treatment Response: Folate receptors can serve as biomarkers for monitoring treatment response in glioma patients.
Medical professionals can assess changes in the folate receptor expression by regularly conducting PET imaging and track the tumor’s response to therapy. This will allow for timely adjustments to treatment plans. Thus, ensuring the most optimal outcomes for patients.
Takeaway
This new development has the potential to revolutionize how to detect and manage brain tumors. It will, thus, provide doctors with more precise and effective tools for patient care.
Further research and exploration of folate-based radiopharmaceuticals hold promise for improving the diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors. Consequently, benefiting patients and advancing the field of medical imaging.
Via: University of Turku