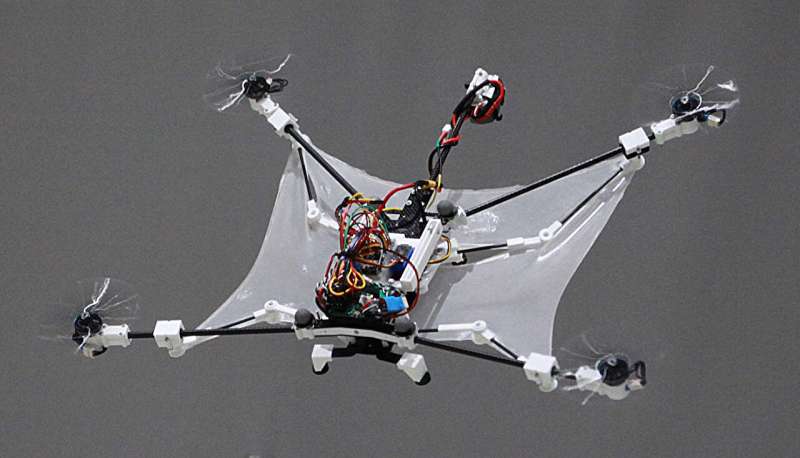
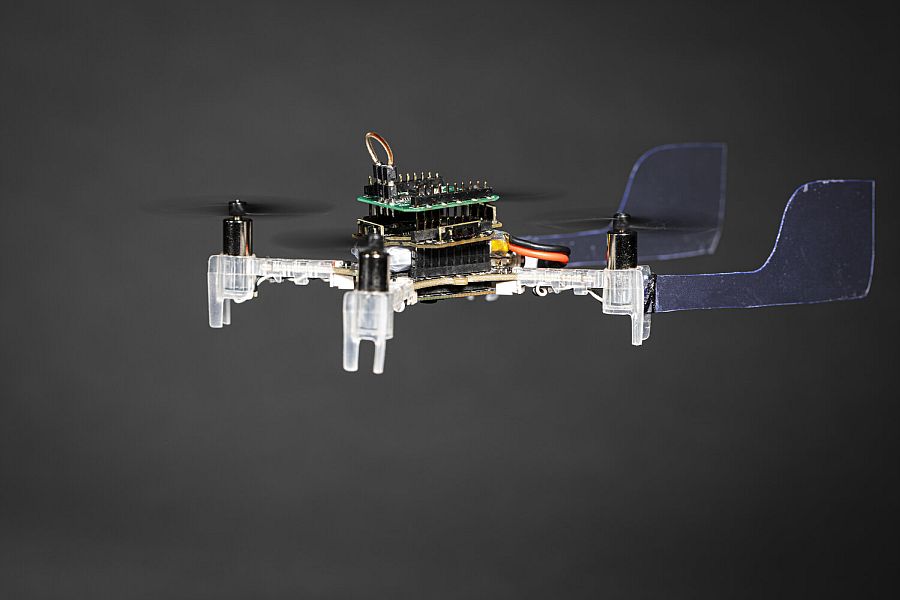
Drones that we see today are very well equipped with focusing systems that allow for high-resolution imaging, precise navigation, and advanced object tracking capabilities. However, when it comes to executing sharp turns, a key limitation of today’s drones, the tech is still in its early stages of development.
Search Results for: biomimicry
Biomimicry: Mantis-Inspired Biomimetic Vision System
A self-driving car approaches a street with a parked car and a cyclist waiting to cross. The car detects the cyclist moving but has difficulty judging the distance and speed of both the stationary parked car and the slow-moving cyclist, leading it to miscalculate the necessary response and causing a collision. This is similar to how some insects see the world: their eyes are good at noticing movement and seeing a lot at once, but they struggle to tell how far away things are. However, this is not the case…
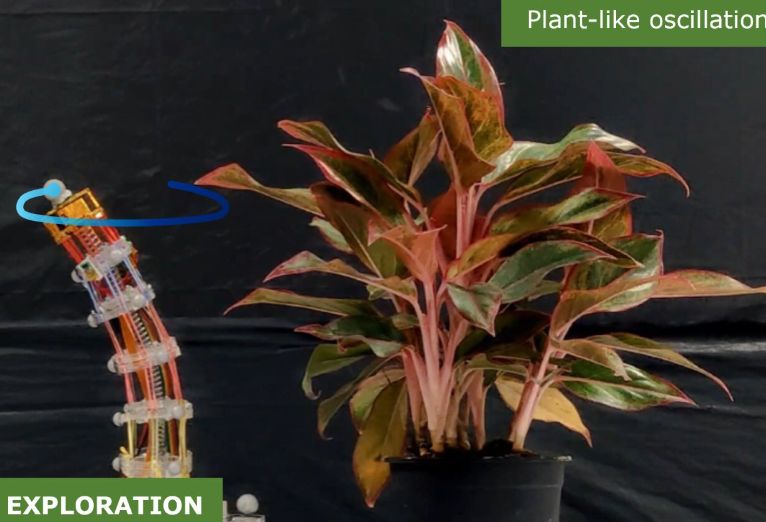
Plant-inspired Controller for Robotic Arms: Biomimicry
Biomimicry is the practice of imitating biological systems and processes. So far, it has been a valuable approach in robotics. By copying animals’ designs, engineers have tried to replicate billions of years of evolution. It has resulted in highly efficient and adaptable designs that nature has already passed on to. For instance, energy-efficient walking patterns inspired by animal gaits or bio inspired vision systems or lizard inspired four-legged robot.
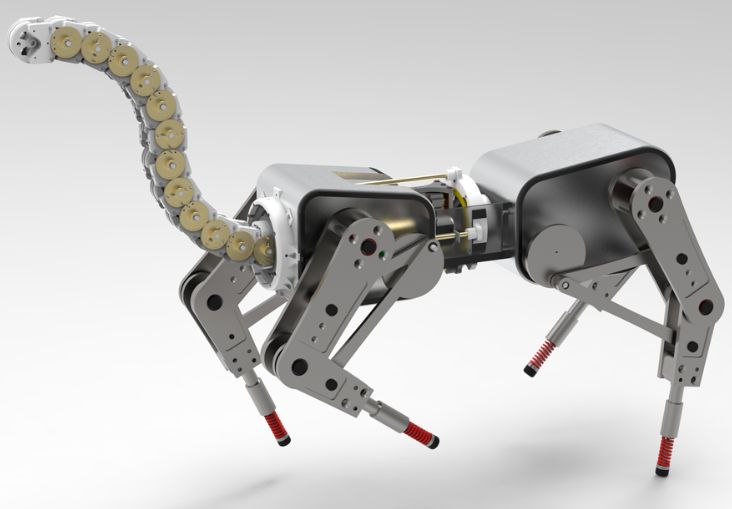
A Quadruped Robot with Proprioception and a Tail: Biomimicry
Nature has always inspired philosophers, scientists, and researchers alike. When it comes to solve human problems or create innovative products and technologies, studying nature’s designs and processes lead to more sustainable and efficient solutions. Afterall, nature has had millions of years to develop solutions to problems. These solutions have been honed through the process of natural selection. Learning and getting inspired from nature’s solutions, is called biomimicry. Designers, engineers, and scientists are inspired from nature to create more sustainable and efficient products and systems.
Lizard Inspired Four-legged Robot: Biomimicry
Technological advancement has opened-up exciting possibilities for research in space and celestial bodies beyond the Earth’s atmosphere. The use of robots in space exploration has greatly increased our understanding of other planets, especially Mars, and its possibility for supporting life. The exploration of Mars and its surface for extra-terrestrial life has always been a fascinating undertaking for astronomers. Additionally, the discovery of resources on Mars, such as water and minerals, could be an asset in future human missions.
Butterfly Robots with Bistable Wings: Biomimicry
In an effort to create faster and more energy-efficient soft robots, researchers at North Carolina State University have created a prototype of swimming soft robots based on manta rays. The team got inspired from the biomechanics of the marine animal. Rate of swimming for most of the (swimming) soft robot is one body length per second, manta rays, however, glide at much faster rate. Their swimming efficiency triggered the scientists to look into the potentiality of creating a similar robot, biomechanically.
Crab Inspired all weather Vision System: Biomimicry
To improve the imaging component in robotics, researchers have been trying to create various types of highly performing cameras, sensors and artificial vision systems. Most of the vision systems are bio-inspired that is, they have been emulated from the systems and elements of nature including humans, animals, insects and fish. These systems, however, have their own restrictions because they operate in limited environment respectively. For instance, majority of (bio-inspired) existing sensors and cameras works either one of the following scenarios: on the ground like biomimetic eye with a hemispherical…
New Microbot Scuttle like a Crab: Biomimicry
Engineers at Northwestern University have developed nano-scale robots that scuttle like small peekytoe crab. The tiny crab-bots measure around half-millimeter wide. Like the decapod crustaceans, the bot can bend, twist, crawl, walk, turn and even jump. Not only the nano crab like devices, engineers have also created same sized robotic inchworms, crickets and beetles. Researchers envision that their technology will explore practical tasks inside tightly confined spaces.
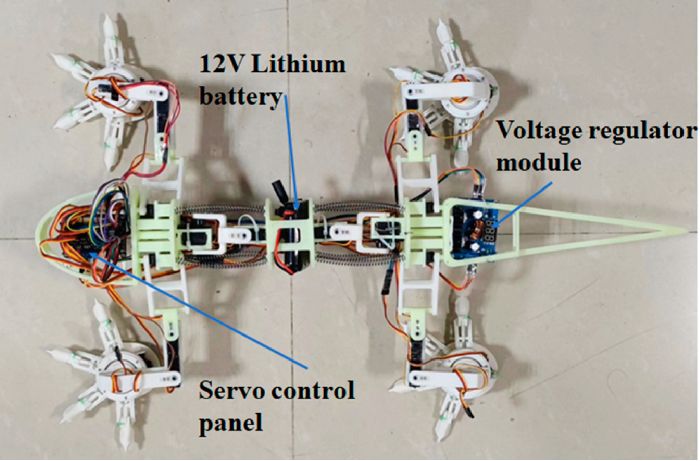
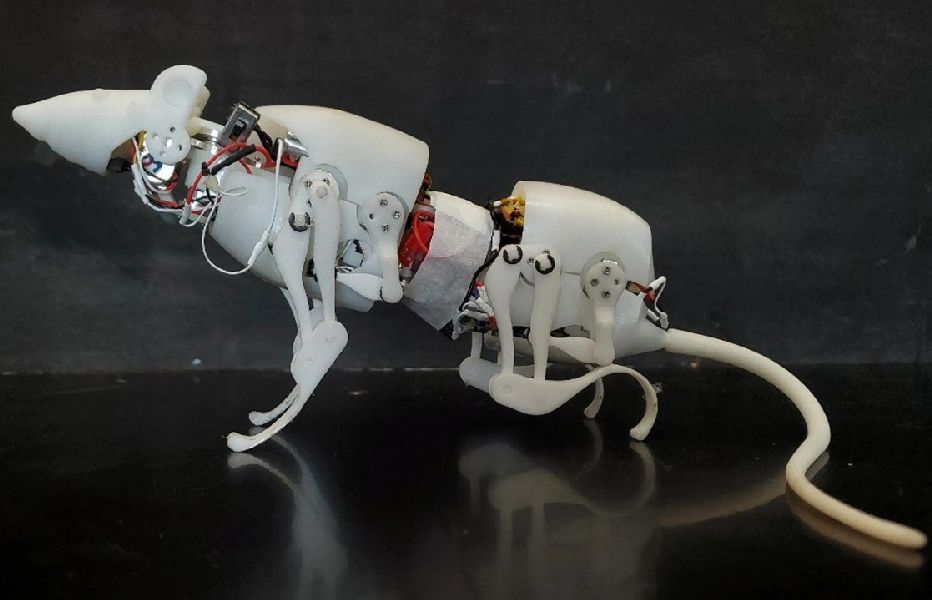
SQuRO, Quadruped Robotic Rat: Biomimicry
Nature has always inspired robotics engineers to design bots with the same agility and efficiency. And this is also one of the reasons why researchers look up to biomimicry to solve human design challenges. When it comes to navigate tight and congested arenas wouldn’t rodents be the best options to design a device? Researchers at Beijing Institute of Technology (BIT) thought the same. According to Qing Shi, a Professor at BIT, legged robots have limitations when operating in narrow spaces. Micro quadruped robots too can face performance issues due to…
Biomimicry: LEONARDO, the Bipedal Robot can Walk and Fly
Nature not only inspire poets, artists, painters but also engineers. In an attempt to simulate the locomotion of birds, researchers at Caltech have developed a bipedal robot that has a movement that is between walking and flying.
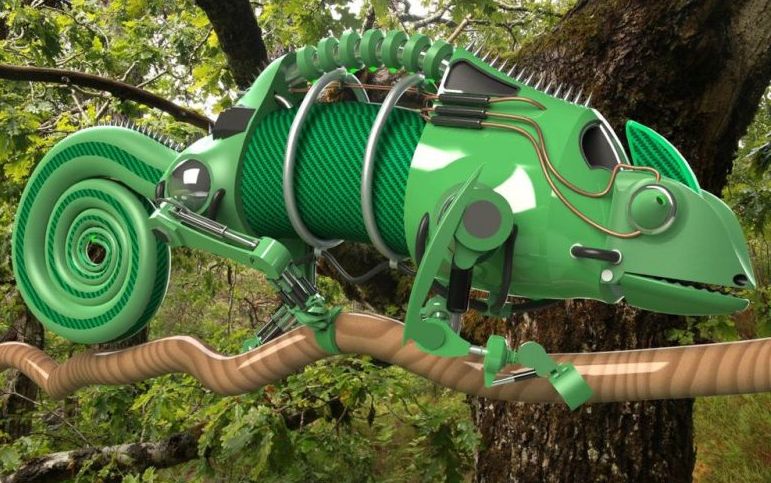
Chameleon Inspired Next-Generation Artificial Camouflage: Biomimicry
To depict natural camouflage characteristics via artificial camouflage at device level has remained a challenge since decades. However, researchers at Seoul National University have developed an artificial camouflage that can adapt and blend with its surroundings. A defense strategy as seen in the case of chameleon that changes its appearance to avoid predators.
Fruitflies Inspired Tiny Drones To Locate Gas Leak Source: Biomimicry
Biomimicry is not only shaping sustainable designs but it’s also revolutionizing the robotic technology. Researchers today are picking up learning from animal and insect kingdom to develop locomotion and structures in their labs.
Smellicopter uses Antennae from Anesthetized Moths: Biomimicry
We as humans have a huge legacy of evolution yet we always fall short in front of nature. Nature has its own rate of progression and it never fails.
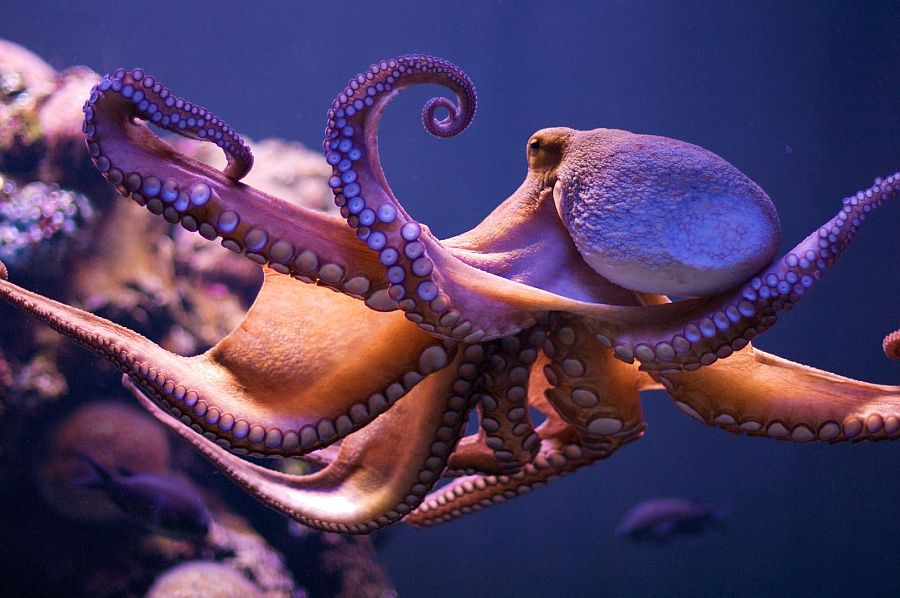
Octopus Inspired Device For Transferring Delicate Implants: Biomimicry
Researchers at University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and collaborators have come with up an innovative way to surgical grip the fragile tissue grafts. Generally, during the ultra-thin tissue grafts, the grip leads to the collapse of structural integrity and functionality of soft tissues transplants. It has always been a challenge to preserve them during grafting and transferring process.
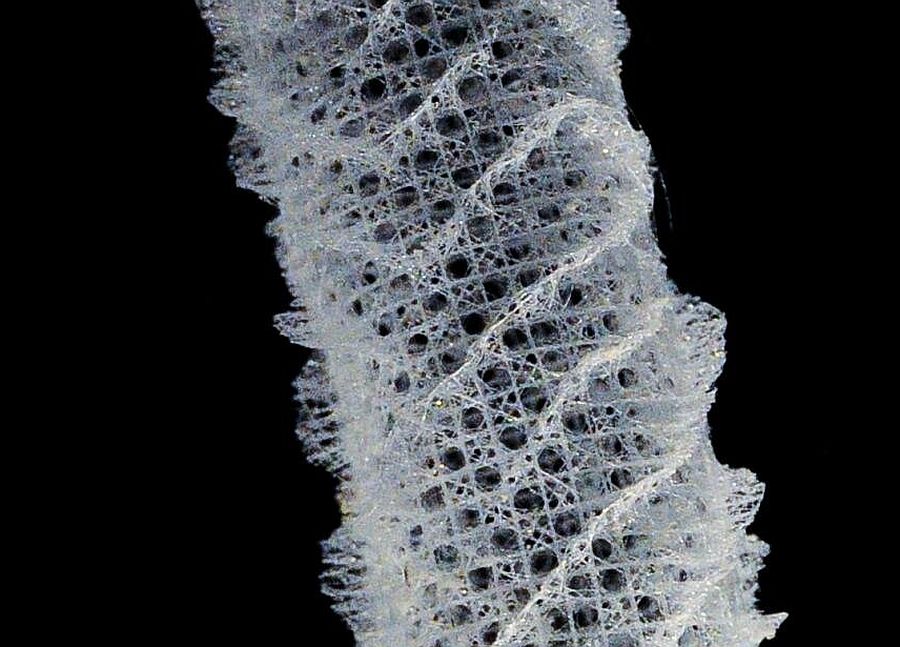
Sponge Inspired Lattice Geometry: Biomimicry
Evolutionary process creates the most efficient mechanical as well as architectural designs. Most of the times, engineers take inspiration and try to replicate such resourcefulness in their designs. Of course, with the help of equations and computer algorithms, engineers try to fabricate bio inspired designs as bio-inspired engineering is a multi-step process.