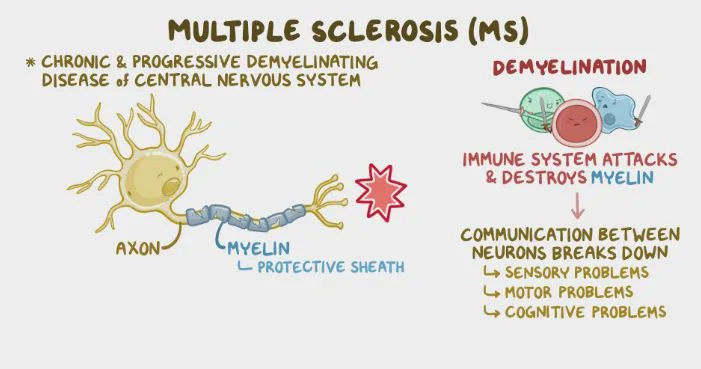
To achieve a holistic understanding of multiple sclerosis, an international team of scientists led by the Department of Medicine and Life Sciences (MELIS) at Pompeu Fabra University, has devised a computational biology instrument. This innovation also holds potential for probing into other intricate illnesses, like various forms of dementia. Understanding multiple sclerosis is not that easy. It’s an autoimmune condition. In such a situation, the immune system mistakenly attacks the brain and spinal cord. Gaining insights as to why it happens is slightly tricky, as it involves everything, from genes…
Read MoreAuthor: Pooja Kashyap
Evolution of Life’s Molecular Systems: Insights into the Rise of Nanomachines
Researchers at Université de Montréal (UdeM) have made a significant discovery regarding the evolution of molecular systems crucial to the development of life. Through the linking of molecules, they have uncovered insights into the emergence of intricate self-regulating mechanisms. Alexis Vallée-Bélisle, a professor at UdeM and the lead researcher of the investigation, explained that life’s sustenance on our planet stems from myriad nanostructures. These nanomachines have undergone evolution over countless years.
Read MoreBook Review: Harrison Bergeron by Kurt Vonnegut
Writers, let me be more specific, science fiction writers are visionaries. Pick up any sci-fi classic, isn’t the themes and repercussions hint at some kind of inevitability? Every science fiction novel that I have read so far has given us a peek into the future and help us understand where our current choices might lead us. Within this genre, themes and repercussions often serve as cautionary tales or reflections of contemporary societal issues. For me, Kurt Vonnegut is one of the names that fall into the category of absolute literary…
Read MoreBook Review: Never Let Me Go by Kazuo Ishiguro
Lately, I’ve been exploring the dystopian genre, relying on recommendations from Goodreads since I’m not very familiar with it. “Never Let Me Go” by Kazuo Ishiguro is my first foray into his work, and it’s a masterpiece of literary fiction. Interestingly, it also evokes comparisons to my favorite author, Margaret Atwood and Lois Lowry. I’ll delve into that connection shortly, but first, let me share my thoughts on this captivating novel. “Never Let Me Go” is an interesting science fiction novel written by British author Kazuo Ishiguro, published in 2005.…
Read MoreBiofilm Microstructure Could Enhance Pathogenic Infection Control: Microbial Ecology
Generally, bacteria are envisioned as tiny, single-cell organisms scattered thinly on surfaces or floating in liquids. However, in various settings, bacteria prefer to grow in clusters known as biofilms. The formation of biofilms provides certain advantages to bacteria. In these clusters, bacteria can collaborate and create a protective environment that enhances their survival and growth. Biofilms, while aiding in kombucha tea production, present a challenge by complicating the control of bacterial growth. When bacteria form a biofilm, it acts like a protective shield, making the cells resistant to antibiotics.
Read MoreInterview: Professor Roberto Maiolino, an Astrophysicist at Cavendish Lab, UK
I am honored to introduce Professor Roberto Maiolino, an esteemed figure in the field of Experimental Astrophysics. Currently holding the position of Professor at the Department of Physics (Cavendish Laboratory) and the Kavli Institute for Cosmology, University of Cambridge, Dr. Maiolino also serves as an Honorary Professor at University College London and holds the prestigious title of Royal Society Research Professor. With a primary focus on the exploration of galaxy formation and the evolution of supermassive black holes, Professor Maiolino employs a diverse array of observing facilities to unravel the…
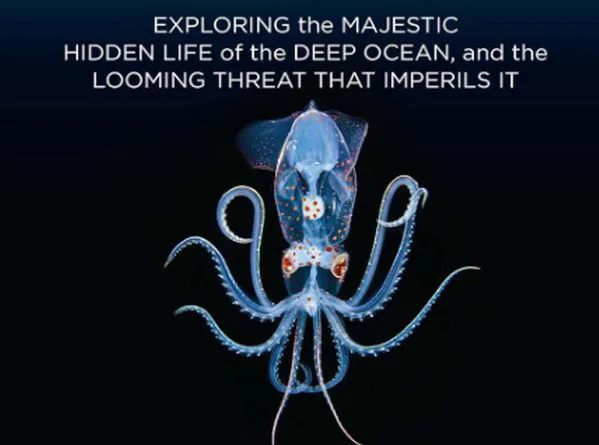
Read MoreBook Review: The Brilliant Abyss by Dr. Helen Scales
“The Brilliant Abyss: Exploring the Majestic Hidden Life of the Deep Ocean and the Looming Threat that Imperils It” is an awesome work by Dr. Helen Scales. The book was first published in 2021. Dr. Scales is a distinguished marine biologist, accomplished writer, and captivating broadcaster. With an impressive repertoire of books exploring the wonders of the ocean, including the Guardian bestseller “Spirals in Time” and the New York Times top summer read “The Brilliant Abyss,” Dr. Scales has established herself as a leading voice in marine literature.
Read MoreElectron Dance: Creating Robust Continuous Time Crystals
Researchers at TU Dortmund University have achieved a breakthrough by creating a remarkably resilient time crystal. It exceeds the temporal stability observed in previous trials by millions of times. This accomplishment not only validates a captivating phenomenon proposed by Nobel Prize laureate Frank Wilczek approximately a decade ago but also echoes themes that have fascinated science fiction enthusiasts. The intriguing findings have been officially documented in the prestigious journal Nature Physics.
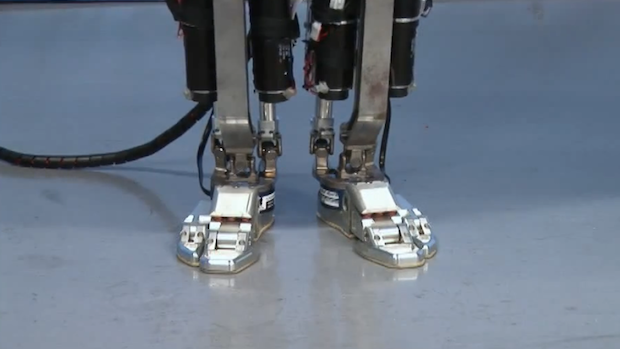
Read MoreBiohybrid Bipedal: Muscle-Powered Two-Legged Robot
Unlike robots, our bodies are super flexible and can make delicate moves effortlessly. Components like muscles, joints, and nerves work in tandem and allow us to make precise and delicate movements with ease. Robots, on the other hand, rely on rigid structures and predefined movements; in contrast, our bodies can adapt and respond dynamically to various situations.
Read MoreBook Review: Twilight of Idols and Anti-Christ by Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche
Friedrich Nietzsche’s ” Twilight of Idols and Anti-Christ” sharply criticizes the dominant values, institutions, and beliefs of his era. Accordingly, this bold work encourages readers to challenge their own assumptions and fearlessly explore long-accepted traditional ideas. “Twilight of the Idols” was penned in 1888, while “The Anti-Christ”, was composed shortly after in the same year. And Nietzsche’s mental breakdown occurred in early January 1889, just a short time after completing these works.
Read MoreMitochondrial Energy Crisis: Unraveling the Alzheimer’s Puzzle
Brain cells crave immense energy to survive and communicate through connections known as synapses. These cells are like energy enthusiasts, which are busy in making way through synapses. But, in the Alzheimer’s scenario, it’s like they’re facing an energy crisis. This messes up their power production. And so, it leads to crumbling down of the synapses and consequently, our fresh memories slowly slip away.
Read MoreBook Review: The Idiot by Fyodor Dostoevsky
In this fascinating literary journey, Dostoevsky takes a deep dive into the complex world of human nature and psychology. Initially released in serialized form, “The Idiot” made its debut in The Russian Messenger during 1868–69. In my opinion, Dostoevsky’s firsthand experiences with corruption, imprisonment, and solitude permeate in nearly all his main characters. The protagonist in the “The Idiot” comes back to his “old city” but he is taken aback as he steps into the refurbished glittering scene of Russian high society. Things here are definitely not what they seem…
Read MoreCosmic Conundrum in the Milky Way: Lightest Black Hole or Heaviest Neutron Star
Exciting news from the cosmos! Astronomers from around the world, including the brains at The University of Manchester and the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy in Germany, have stumbled upon an unknown object in the Milky Way. The newly discovered object is heavier than the heaviest neutron stars we know. And lighter than the lightest black holes we’ve seen. The team used the MeerKAT Radio Telescope, to spot this mysterious object. This celestial entity is in orbit around a high-speed millisecond pulsar, situated around 40,000 light years away in…
Read MoreDecoding Quasicrystal Magnetism: Unveiling a Fresh Magnetic Blueprint
Quasicrystals are interesting materials since they defy regular atomic pattern. It’s non-repeating structure captivates researchers. Since, it leads to extraordinary properties. Thus, the exotic traits not only challenge the traditional material science views but the same also inspire countless innovations. However, there is a rebel in the family of quasicrystals, the Tsai-type icosahedral quasicrystal (iQC). It is a specific variant of quasicrystal with a unique atomic arrangement characterized by icosahedral symmetry. The symmetry involves a structure that resembles a 20-sided polyhedron.
Read MoreBook Review: Nostromo by Joseph Conrad
“Nostromo: A Tale of the Seaboard” is a novel penned by Joseph Conrad in 1904. Many consider it one of Conrad’s finest works of extended fiction. The book explores how money and economics influence what people believe and how they live. The sad part is that both good and bad things are bound to happen because of these big changes.
Read More