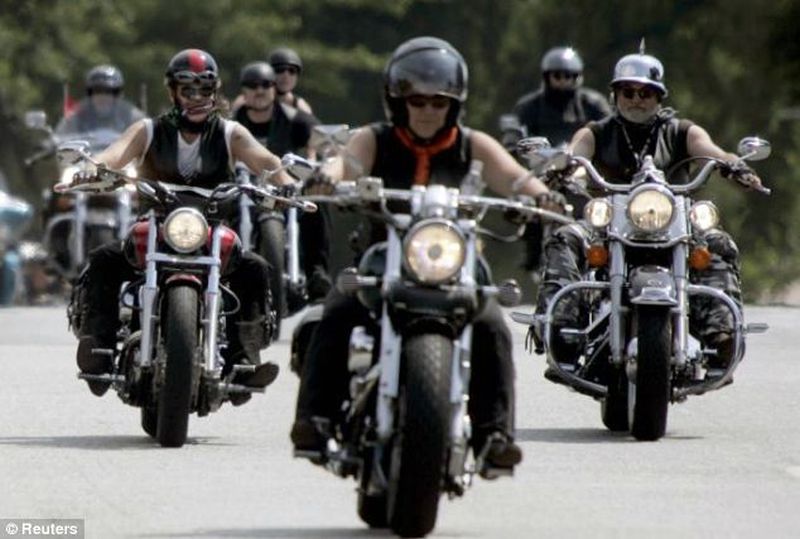
Today we have giant companies Like Tesla, Honda and BMW, investing in research for creating advanced electric cars. But when it comes to electric bikes, the market is limited with just a few options of low powered electric bikes or scooters which surely does not appeal to motorcycle lovers. However, this perception of electric bikes seems to change, as the king of motorcycle, Harley Davidson has announced their project LiveWire to roll out first ever electric bike.
Read MoreCategory: Futuretech Tonics
Polymer for a Shatterproof Smartphone Touchscreen: Copper-based Flexible Display
Polymer scientists at University of Akron have developed an electrode, which is transparent in nature. Researchers aim to create shatterproof screens for smartphones with this newly fabricated layer of electrode. It’s been quite some time now since, researchers were looking for alternatives to conventional indium-tin oxide, the ITO technology used for making the touchscreen. Brittleness is one of the major flaws with smartphone screens made up of ITO technology. Another equally important reason for looking at its alternative is its scarcity. Moreover, escalation of smartphone and tablet market is fueling…
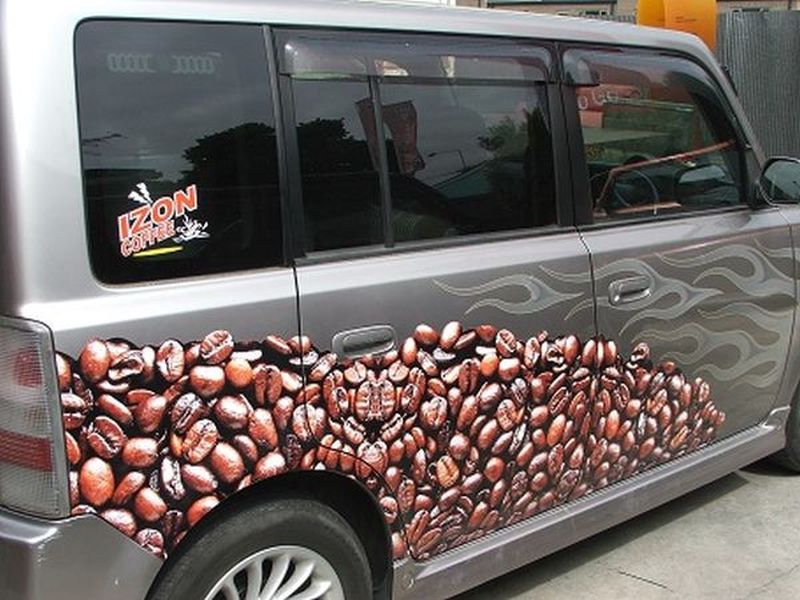
Read MoreBiofuel from Waste Coffee Grounds: Car running on Coffee
Recycling industrial or household waste is very imperative for keeping the environment clean. Recently, researchers from the University of Bath have demonstrated an effective method of generating biofuel from waste coffee grounds that can power vehicles.
Read MoreFully Autonomous Vehicles: Profit Center for Chipmakers
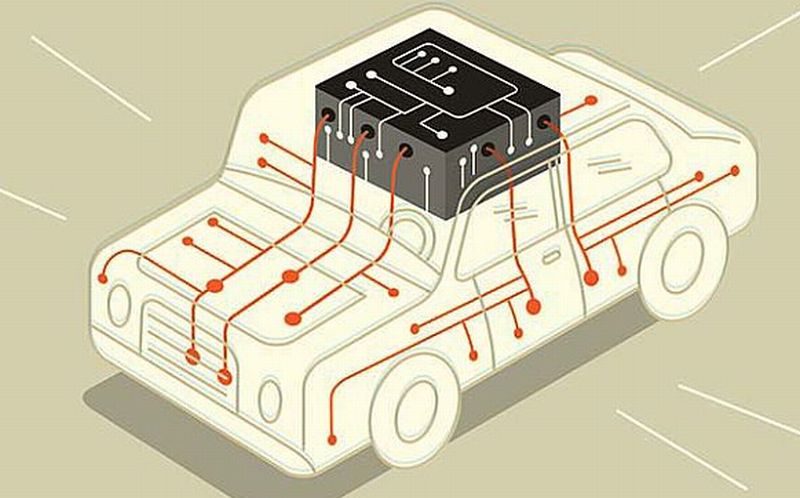
IHS Technology envision that market for MCUs and processor units would touch half a billion dollars by 2020. Similarly, revenues from optical sensors would escalate 7 times by the same year. Google has already rolled in its driverless car and by the end of 2014 we would be witnessing more such autonomous vehicles from robot manufacturers as well, as in robocars. As of now, these cars are not functioning as fully autonomous vehicles and they do require human intervention, especially to avoid unanticipated events. In fact, they are being operated…
Read MoreStenocara beetle Inspired Hygroscopic Scaffold: Nanotubes for Storing Water
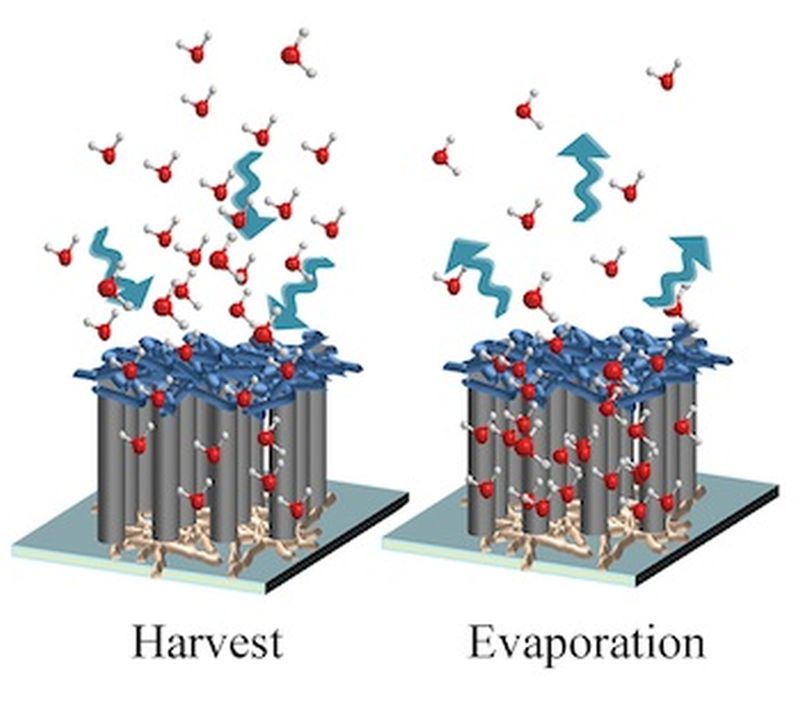
Water is essential for survival of almost all kinds of lives on Earth, hence it is imperative to conserve it at any cost. Researchers from around the world are working to find new and innovative methods to conserve water, especially in areas which are short of water resources. Inspired from an insect, researchers from Rice University have come up with an innovation method of water collection.
Read MoreMindRider: Brain Monitoring Systems for Mapping Mental Experience
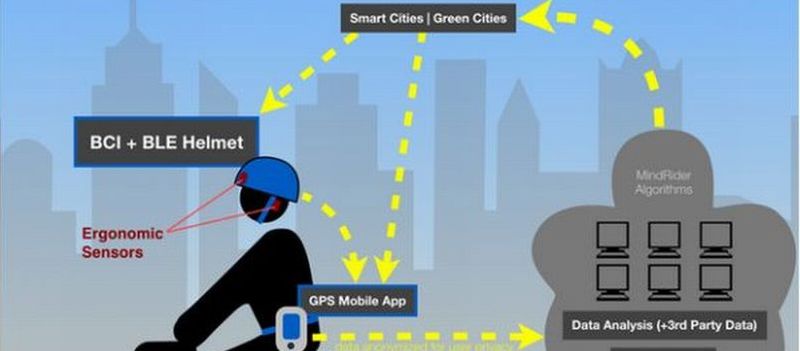
Researchers at the MIT Media Lab are working towards creating a novel helmet system that would reflect bike rider’s mind in the real time. It will be able to mind map rider’s engagement level from relaxed state to focused level while navigating through the routes. Mapping Mental Experience Sensors are embedded within the foam of the helmet that would act as a bridge between the brain waves and translating those ripples into the display of level of engagement. The technique is based on EEG (electroencephalography) where the embedded sensors act…
Read MoreThermometer for Ultrasensitive Measurements: Temperature Control
Physics researchers at the University of Adelaide have successfully created a rare thermometer, efficiency of which is thrice the existing best thermometers so far. Reporting further, the experts expatiated that they were able to gauge temperature with the ‘nano-Kelvin thermometer’, through an accuracy of thirty billionths of a degree. Researchers asserted that they have reached the highest level of precision in terms of measuring temperature at room temperature. Talking about the innovation, Professor Luiten one of the lead researcher said that temperature at subatomic level is not static rather fluctuating.…
Read MoreNano- Bots to Enter into the Arteries for Delivering Drugs: High-Performing Nanomotors
Very soon, we would be witnessing a 3D world on microchips. During the beginning of this year, researchers at Penn State University demonstrated the movement of nanomotors in controlled manner inside living cells. And now, experts at the University of Texas Austin have developed one of the fastest spinning and relatively longer shelf life nanomotor. The newly fabricated nanomotor has an ability of spinning continuously for nearly 15 hours with a speed of 18k rpm. This is an innovative product in the league where the existing nanomotors display an efficiency…
Read MoreEnergy Storage into Structural Materials: No More Power Cords for Devices
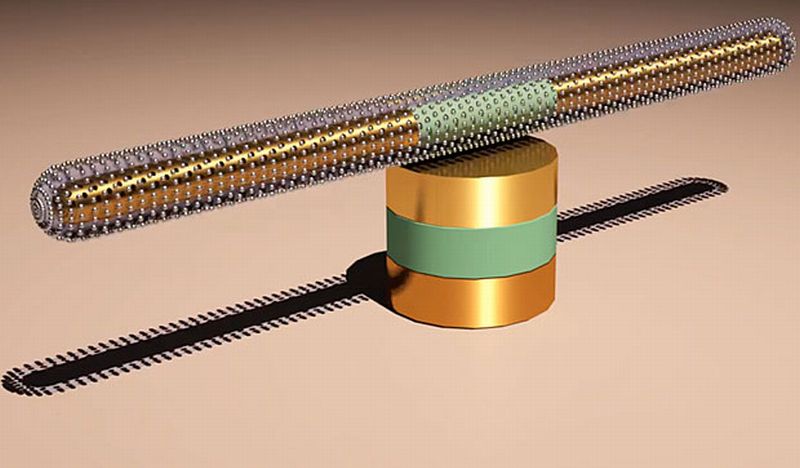
Researchers at Vanderbilt University have come up with an intriguing prospect that has complete essence of futuretech in itself. Their current interest hovers around the likelihood of a more technologically enhanced capacity for storing electrical energy directly across applications including but not limited to EVs, laptops and home appliances. They have demonstrated this idea by fabricating small wafers that have the potential of storing and discharging considerable amount of electricity while they are put through static loads or moving forces like vibrations or impacts.
Read MoreStanford-MIT System Aims at Harvesting Low-Grade Heat: New Battery Technology
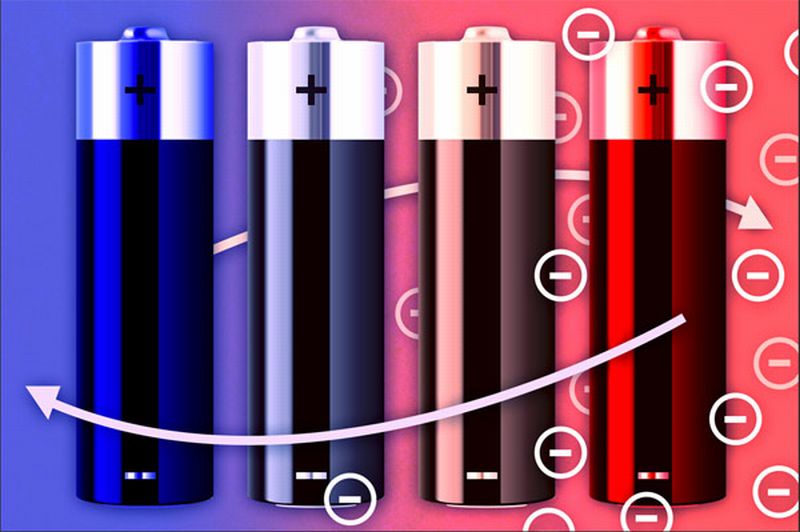
It’s been more than a decade researchers across the globe are working towards harnessing waste energy into something useful. Most of the times, their energy focused around thermoelectric devices but efficiency of this approach was limited to the accessibility of materials Lately, researchers at Stanford University in collaboration with experts from Massachusetts Institute of Technology have come up with an innovative technology, which captures and morphs waste heat into electricity. The approach holds the low temperature waste heat, that is, less than 100 degrees Celsius.
Read MoreInnovative Supercapacitor Architecture: A Hybrid between a Supercapacitor and a Pseudocapacitor
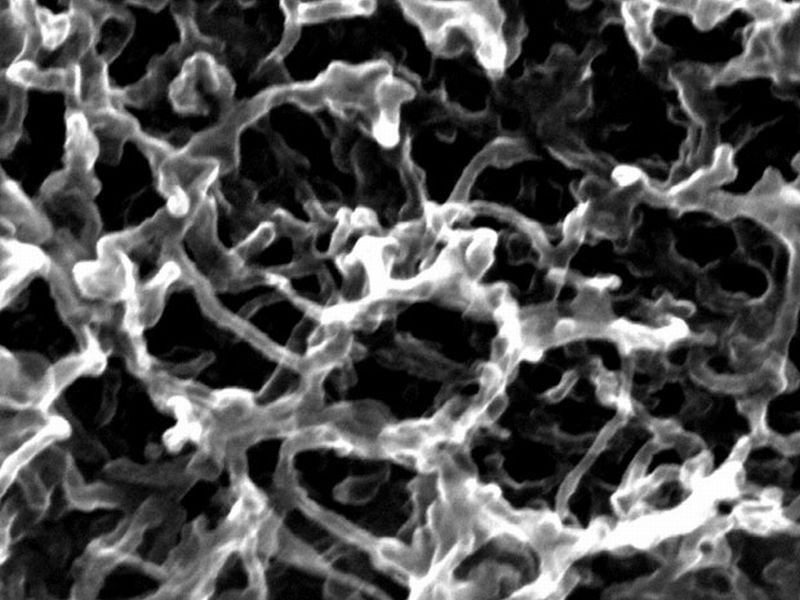
Using the nanoparticles of hydrous ruthenium oxide (RuO2) by first modifying them via carbon nanotubes (CNT) and graphene foam as the electrode material for the supercapacitor, the researchers at the University of California Riverside have developed an innovative energy storage device. They have simply called it a supercapacitor, which technically is a hybrid between a supercapacitor and a pseudocapacitor. Once the electrodes were formed via the modification (mentioned above), they were then added in an aqueous electrolyte. The resultant combination provided higher energy with more power density supercapacitors than the…
Read MoreGraphene Ushering the League of Viable Engine for Nanodevices: Lattice Mimics two-stroke Engine
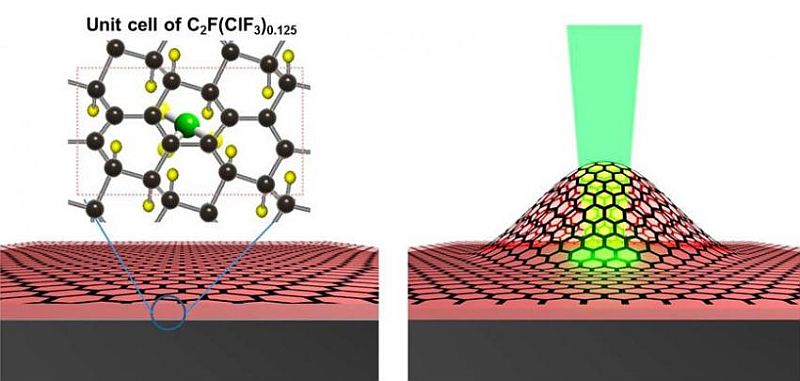
Graphene is one of those rare gifts of nanotechnology that is still not unwrapped fully. Not long ago, we discovered that how sliding water over graphene generated electricity. Every time, researchers conduct an experiment, the lattice of carbon atoms pops up with different surprise. Lately, such revelation has brought to the fore by researchers at National University, Singapore. They have morphed a single layer of graphene along with certain amount of chlorine and fluorine atoms to create a two-stroke combustion engine. Similar mechanism although at a macro-scale is used for…
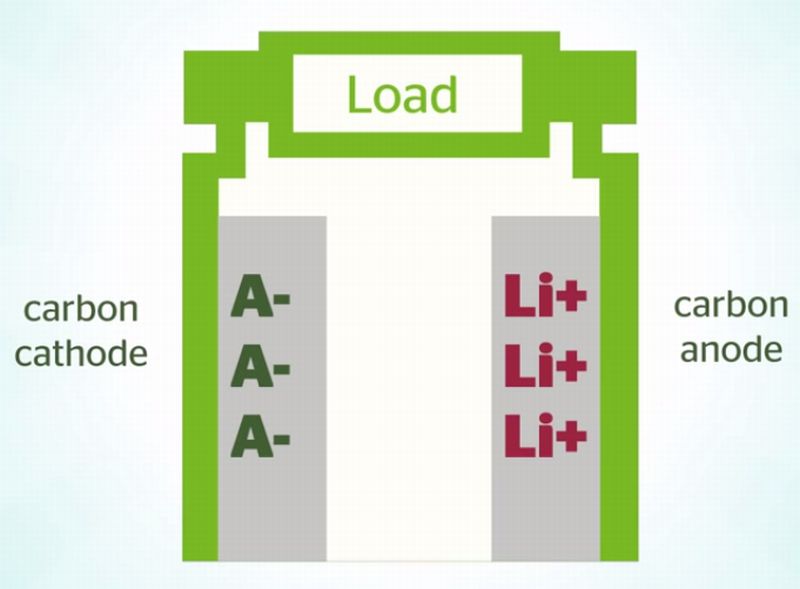
Read MoreRyden Dual Carbon Battery: The Energy Storage Breakthrough for EVs
Power Japan Plus, a Japanese power company has stated that they have come up with a revolutionary battery technology that can easily beat the energy density of stereotypical batteries used in automobiles. They have termed it the Ryden dual carbon battery. With respect to the existing lithium ion batteries, the product has an ability of charging 20 times faster without reaching to the highest level of temperature where it requires cooling or burst like lithium-ion battery. This makes it safer, reliable and sustainable relatively, claimed the company. Power Japan envisions…
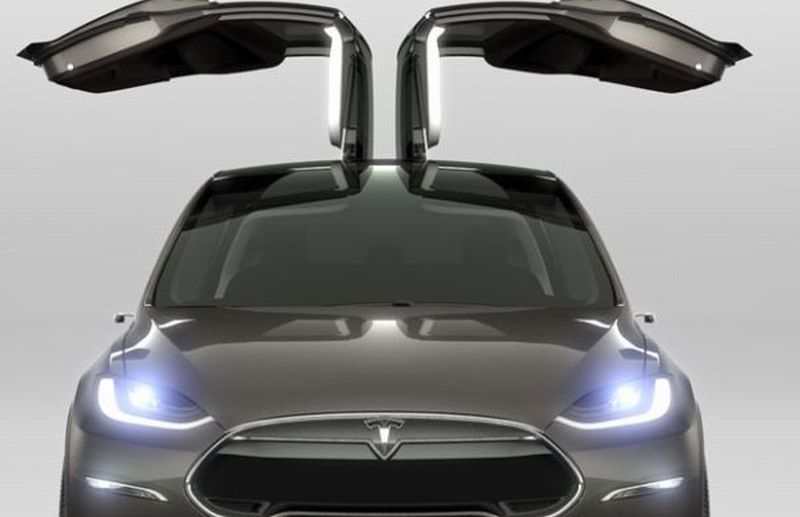
Read MoreTesla’s Model X: Style and Functionality Combo Driving up the Research Budget
Stylish is the word that resonates well with Tesla Motors. This time, the coolness is reverberated by the Falcon Wings of the highly anticipated Model X electric car. A beautiful blend of an SUV and minivan, the electric powertrain boasts of providing an unfettered performance and brilliant functionality. Unlike any other SUV, the center of gravity is positioned at the lowest level providing nimble reflexes at every curve of the road. The automobile conveys moment torque during path progressions or while entering into a different lane deftly even when there…
Read More10 Unanswered Puzzles about Science: Will They Ever Reach Consensus?
Even though we have made tremendous progress in science, yet there remains a mystery when it comes to give reasons to some everyday activities. These mundane stuffs generate the same kind of awestruck curiosity to scientists as it does to a toddler. Some of these bewildering questions are: 1) Slipperiness of Ice The unusual & unique properties of water have given numerous explanations about ice being slippery. Experts have dispensed most of the theories propagated so far and there could be more variations in the future discoveries envision majority of…
Read More