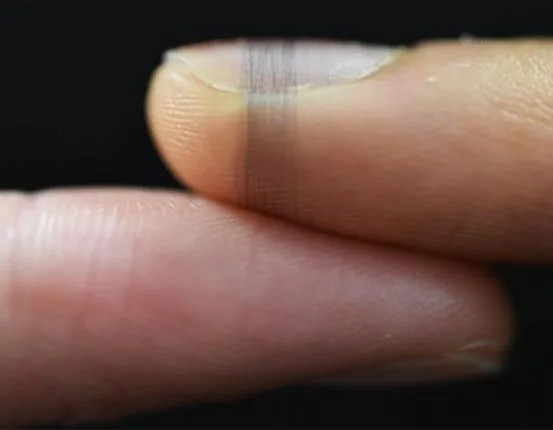
We are constantly surrounded by electronics. From LEDs to batteries, these electronics have become part of our lives. And so, more advanced and intricate components are needed to make them more efficient and reliable. However, as these components become increasingly sophisticated, getting reliable temperature measurements of specific elements inside an object can be a challenge.
Read MoreCategory: Futuretech Tonics
Electronic Spider Silk: A Versatile Solution for Bioelectronics
Super-thin and flexible electronics are here to stay. This tech will not only create but it will also revolutionize the use of gadgets. Since, it leads to unlimited possibilities for innovative and practical applications. Some of the them include but not limited to – wearable tech, portability, healthcare applications, space probes etc.
Read MoreInnovative SiPh Chip: Nanoscale Light Computing Breakthrough
Imagine a world where AI computations are not bound by the limitations of traditional power sources, that is, electricity but by the power of light waves. This is precisely the vision that researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have brought to life with their innovative chip design. This innovation will not only enable the chip to fast-track the processing speed of computers but it will also lessen their energy consumption.
Read MoreElectron Dance: Creating Robust Continuous Time Crystals
Researchers at TU Dortmund University have achieved a breakthrough by creating a remarkably resilient time crystal. It exceeds the temporal stability observed in previous trials by millions of times. This accomplishment not only validates a captivating phenomenon proposed by Nobel Prize laureate Frank Wilczek approximately a decade ago but also echoes themes that have fascinated science fiction enthusiasts. The intriguing findings have been officially documented in the prestigious journal Nature Physics.
Read MoreDecoding Quasicrystal Magnetism: Unveiling a Fresh Magnetic Blueprint
Quasicrystals are interesting materials since they defy regular atomic pattern. It’s non-repeating structure captivates researchers. Since, it leads to extraordinary properties. Thus, the exotic traits not only challenge the traditional material science views but the same also inspire countless innovations. However, there is a rebel in the family of quasicrystals, the Tsai-type icosahedral quasicrystal (iQC). It is a specific variant of quasicrystal with a unique atomic arrangement characterized by icosahedral symmetry. The symmetry involves a structure that resembles a 20-sided polyhedron.
Read MoreGreen Power Drive: Future Cars Might Run on Cobalt Free Batteries
In the world of electric vehicles, lithium-ion batteries are always preferred and they often contain cobalt. While cobalt plays a crucial role in these batteries, its extraction and processing bring about a set of challenges. Thinking on these lines, MIT researchers have crafted a battery material with the potential to revolutionize the sustainability of electric cars. This groundbreaking lithium-ion battery boasts an organic material-based cathode. Thus, stepping away from the conventional use of cobalt or nickel, which is often present in such batteries.
Read MoreQuantum Leap: Scientists Compute with Light Innovation
Our future tech game just got a major upgrade! Scientists at Heriot-Watt Uni in Edinburgh just dropped a mind-blowing method. Optical circuits are getting a turbocharged programming boost. The discovery promises unhackable communication networks and lightning-fast quantum computers.
Read MoreHelium Diffraction Patterns Under the Microscope: Atoms are Artists
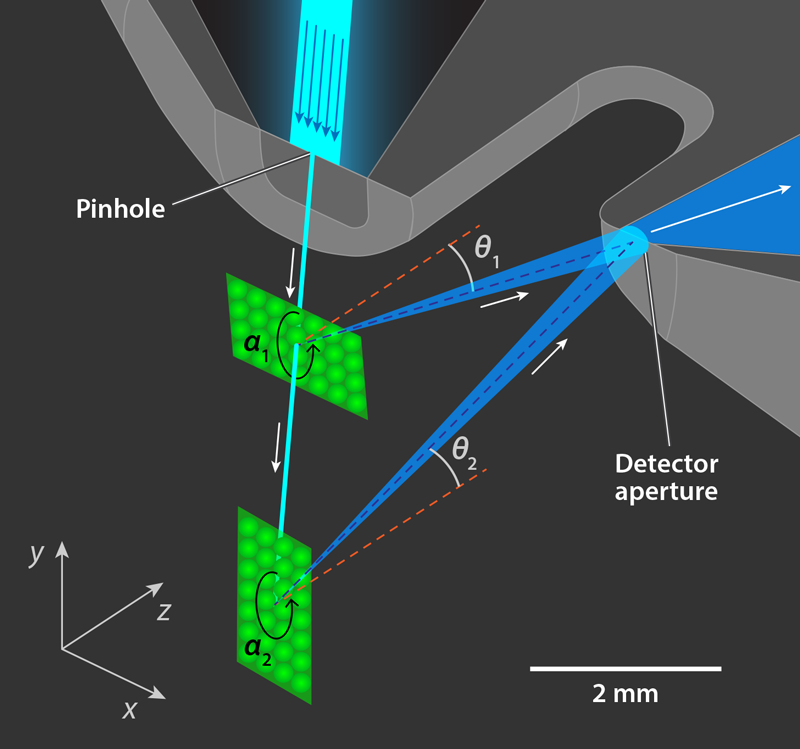
Witness helium atom diffraction like never before. All thanks to microscopic spatial resolution. Researchers from the University of Cambridge and University of Newcastle just dropped a game-changing technique. This breakthrough has allowed scientists to dive even deeper into the weird world of atoms.
Read MoreCondensing Neutron Pairs: Helium-8’s Exciting Revelation
Scientists at Peking University have successfully uncovered the elusive 02+ state of 8He. The 02+ state of 8He refers to a specific energy state of the helium-8 (8He) nucleus. The “2+” signifies that the state has a positive parity, and the “0” indicates a specific spin value. The observation and understanding of such nuclear states provide valuable insights into the structure and behavior of atomic nuclei.
Read MoreTransistors Get a Makeover with Sliding Ferroelectricity Power
Lately, tech wizards are aiming to create hardware that combines computation and data storage all in one gadget. These emerging electronics, called as computing-in-memory devices, will be a game-changer for faster speeds and improved data analysis.
Read MoreBattery Technology: Charging into the Future with Indefinite Causal Order
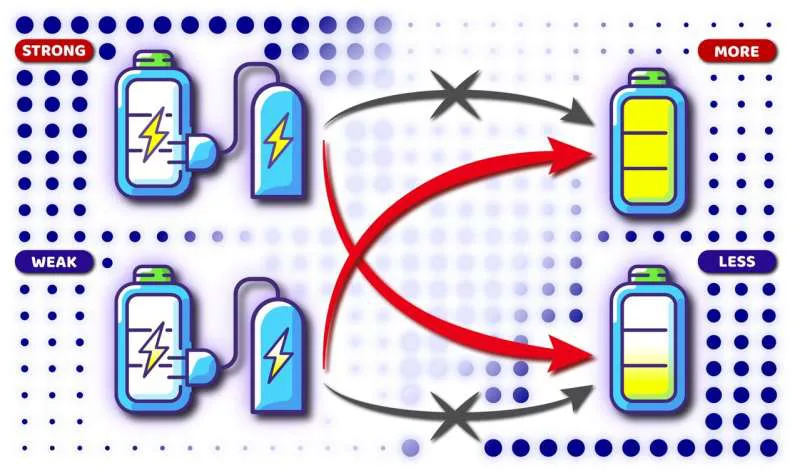
Whenever we talk about “quantum”, we immediately think about quantum computers. But guess what? There’s more cool stuff in the quantum world, like these things called quantum batteries. Although, it sounds a bit puzzling but once its out of lab, it could totally shake things up especially for sustainable energy. And might even power future electric rides.
Read MoreCompact Accelerator Tech Surpasses Energy Milestone
Particle accelerators are nothing less than super heroes! They rock the world of semiconductors, medical magic, and all kinds of cool research including materials, energy, medicine etc. The only down side of this tech is, they require huge space, like kilometers of it. This makes them super pricey and time consuming of course.
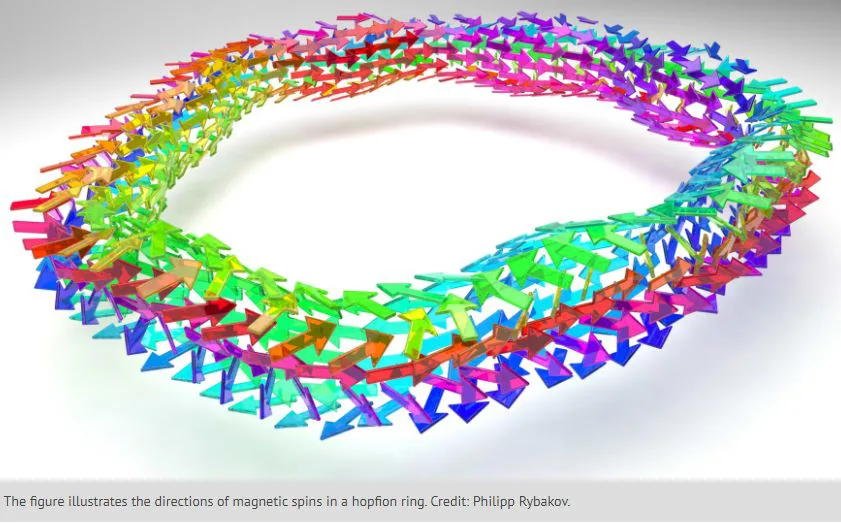
Read MoreHopfions Discovered: Pioneering Breakthrough in Crystal Structures
Hopfions, the magnetic spin structures, have gained significant attention in recent years. Although their predictions have been observed several decades ago. A collaborative research effort from Sweden, Germany, and China presents it’s the first experimental evidence.
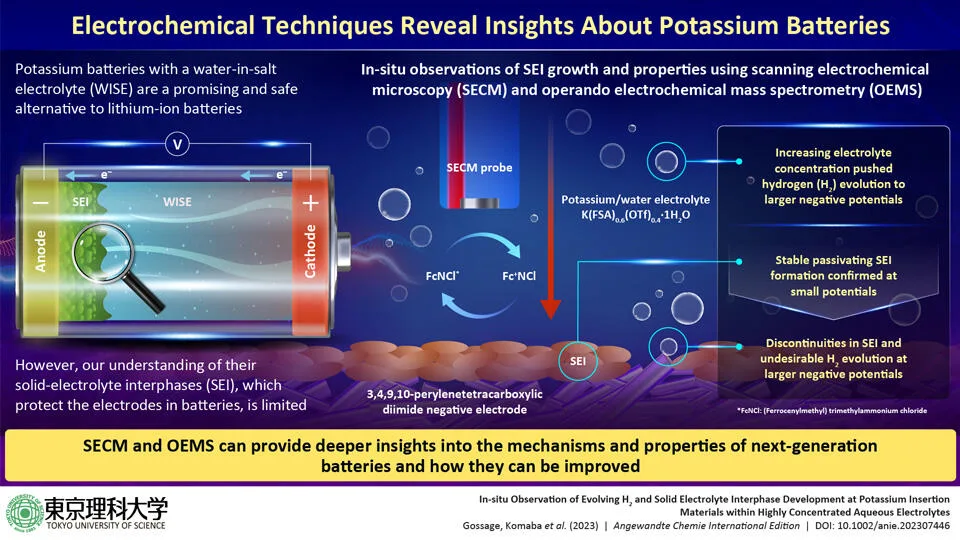
Read MoreSEI Insights in Advanced Aqueous Potassium-Ion Batteries
In the recent times, there has been significant focus around the development of high-performance energy storage solutions. Consequently, the idea has become the driving force behind the advancing battery technology. With the emergence of renewable energy sources such as wind, solar power including electric vehicles (EVs), the need for advanced energy storage systems has grown exponentially.
Read MoreComputational Lithography: Illuminating the Future of Semiconductor Manufacturing
Tech behind computational lithography has revolutionised the way semiconductors are fabricated. By harnessing the power of computer algorithms and simulations, chip designs have become more efficient and powerful than ever before. Its ability to optimize lithographic processes have given a huge boost to the overall performance and energy efficiency of electronic devices. As we move forward, computational lithography is expected to merge with other technologies and re-shape the future where technology knows no bounds.
Read More