When a blood clot blocks an artery, it leads to an ischemic stroke. The blockage or ischemic stroke prevents blood and oxygen from reaching areas of the brain. This gives rise to one of the following symptoms: According to the statistics, the older one gets, the higher the risk of experiencing ischemic strokes. Although, neuroscience has helped us understand what happens in the body during a stroke. However, we have no idea how the immune system helps with recovery after a stroke.
Read MoreCategory: Health Tonics
Protein FAM110A’s Role in Cell Division Unveiled: Microtubule-Actin Interaction During Mitosis
An international research collaboration led by Prof. Dr. Robert Grosse, Dr. Libor Macurek, and Dr. Zdenek Lansky has uncovered a new mechanism of crosstalk between microtubules and the actin cytoskeleton during cell division. They revealed unique characteristics of the previously unexplored protein FAM110A, enhancing understanding of critical processes related to developmental disorders and cancer.
Read MoreBrain-like Artificial System: Dendristor to Mimic Brain’s Dendritic Computations
As artificial intelligence (AI) technology is expanding its tentacles rapidly across globe, engineers around the world are designing new types of computer architectures and hardware. One interesting aspect of most brain-inspired technologies developed so far is that researchers focus on mimicking how neurons fire (i.e., send electrical signals) rather than replicating the entire structure of the brain.
Read MoreUmboMic Revolutionizes Cochlear Implants with PVDF Technology
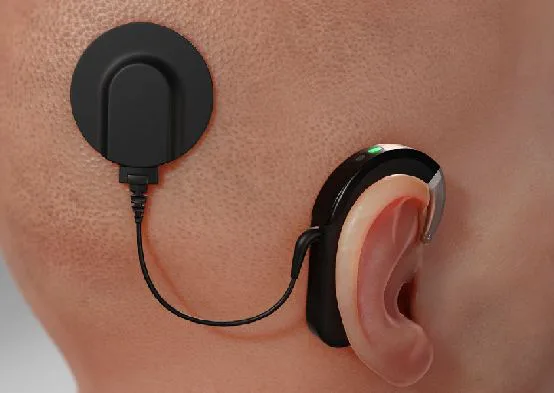
What if a microphone, which is fabricated from a flexible material can be placed inside our ear, to be more specific, directly on the eardrum? This biocompatible sensor will pick up sounds and sends them to a tiny amplifier, which makes the sounds loud enough to be processed by a cochlear implant. Doesn’t it sound like a boon for those who are deaf or hard of hearing?
Read MoreInsulin Resistance: Ketones Found to Revive Neuron Function
Recent research conducted by the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester focused on understanding how ketones affect the brain’s hippocampal network. The hippocampus is a crucial brain region involved in memory formation and spatial navigation.
Read MoreNanoparticles Break Blood-Brain Barrier for Cancer Treatment: Targeting Metabolic Adaptability
Scientists at the Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, part of the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, have crafted a tiny particle capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier. The team envision to tackle both primary breast cancer tumors and brain metastases in a single treatment. Their investigations indicate that this approach can reduce the size of both breast and brain tumors in lab experiments.
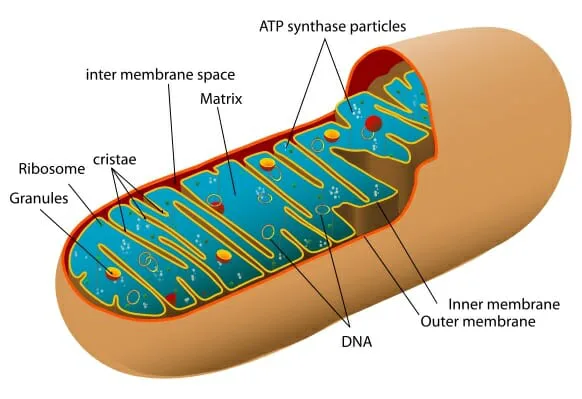
Read MoremtDNA: Key Component of Energy Production and Trigger of Inflammation
Entity responsible for powering our cellular functions and in keeping us going is mitochondria. These powerhouses are little sausage-shaped organelles in most types of cells that have a nucleus. These organelles convert chemical energy from the food that we ingest into usable form of energy. This energy is termed as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is the fuel that we require to carry out the regular activities at cellular level.
Read MoreArtificial Life: Researchers Forge New Building Blocks
Researchers at the University of Cologne (UoC) have achieved a groundbreaking milestone by creating artificial nucleotides. Nucleotides forms the building blocks of DNA. So, if we go by the research, the innovative development will make way for potential advancements in genetic engineering as well as molecular biology.
Read MoreProtein Overload: Amino Acid Blamed for Arterial Health Risks
Interesting research from University of Pittsburgh show that too much dietary protein might actually up the risk of atherosclerosis. So, while protein is good for our bodies but consuming in abundance might not be the best idea when it comes to keeping our arteries happy and healthy. The experiment not only combined the human trials but researchers roped in mice and cells in a Petri dish for the study. When the consumption increases to more than 22% of their daily calories from protein, it kicked off a chain reaction. Consequently,…
Read MoreHeart Healing: Microenvironment’s Role in Cardiac Recovery
A group of scientists led by James F. Martin, has been delving deep into the intricacies of cardiac function at The Texas Heart Institute. Their objective is to illuminate the innate regenerative potential of the heart. At a global level, the primary challenges associated with heart attacks, also known as myocardial infarctions, stem from unhealthy lifestyle choices and genetic predispositions. Also, surviving a heart attack doesn’t guarantee immunity from severe damage to the heart muscles. The cardiomyocytes are severely affected.
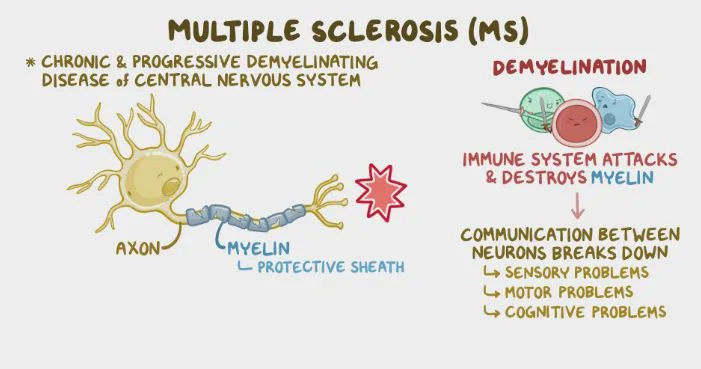
Read MoreMK03: Key Player in Multiple Sclerosis Pathway
To achieve a holistic understanding of multiple sclerosis, an international team of scientists led by the Department of Medicine and Life Sciences (MELIS) at Pompeu Fabra University, has devised a computational biology instrument. This innovation also holds potential for probing into other intricate illnesses, like various forms of dementia. Understanding multiple sclerosis is not that easy. It’s an autoimmune condition. In such a situation, the immune system mistakenly attacks the brain and spinal cord. Gaining insights as to why it happens is slightly tricky, as it involves everything, from genes…
Read MoreMitochondrial Energy Crisis: Unraveling the Alzheimer’s Puzzle
Brain cells crave immense energy to survive and communicate through connections known as synapses. These cells are like energy enthusiasts, which are busy in making way through synapses. But, in the Alzheimer’s scenario, it’s like they’re facing an energy crisis. This messes up their power production. And so, it leads to crumbling down of the synapses and consequently, our fresh memories slowly slip away.
Read MoreMCJ Breakthrough: New Hope for Pulmonary Hypertension
In a groundbreaking study featured in Science Advances, researchers unveil a potential breakthrough in treating pulmonary hypertension. Pulmonary hypertension is a medical condition characterized by elevated blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries. These arteries are the blood vessels that carry blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation.
Read MoreIs Algae the Next Green Protein Alternative?
Discover a green protein alternative – algae. Forget meat, researcher says algae is the new and eco-friendly protein that we’ve been ignoring so far. The University of Exeter just dropped a study in The Journal of Nutrition. The research demonstrates that two everyday algal species are protein powerhouses. And so, ingestion of those can help young as well as healthy adults remodel their muscles.
Read MoreGut Defense: Microbiome Blocks Pathogens’ Nutrient Access
Deep within our stomach, a lively neighborhood thrives. The community is known as the gut microbiome. It is housing hundreds of bacterial species. The fascinating world of the gut microbiome steps up to shield us from nasty invaders called pathogens. Details of its protective powers have been a bit fuzzy until now. Scientists have been tackling and exploring which bacterial players hold the secret to its protective magic.
Read More