Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 is one of the farthest probes that we’ve sent so far. As of July 2024, it’s a whopping 24.4 billion kilometers away from Earth, making it the most distant human-made object ever. Yet, there are things in the space that we have absolutely zero clue. Yes, I’m referring to – Dark Matter. Dark matter helps slow the black holes down and lets them come together for supermassive black hole mergers, at least the recent research says so. Typically elusive, this invisible matter seems to play…
Read MoreCategory: Space Tonics
From Urine to Water: The Latest Breakthrough in Spacesuit Technology
Of all the things in movie, Dune, I particularly got fascinated with the idea how the people used those suits to recycle sweat and urine into drinkable water. It got me thinking: why can’t we make this tech a reality? Well, it turns out researchers at Cornell University are on it! They’ve developed a prototype for a new urine collection and filtration system for spacesuits. Isn’t that awesome?
Read MoreGravitational Wave Memory: A Tool for Measuring Spacetime Symmetries
When we talk about the fabric of reality, in terms of physics, we deal with interesting abstractions and tonnes of complexities. One such intriguing concept of Einstein’s theory of general relativity is the existence of gravitational waves. As the name suggests, these ripples are generated in the spacetime by some of the universe’s most violent and energetic processes, such as mergers of cosmic stars or dent in the landscape due to black holes. Interestingly, whenever these waves pass through, they leave a measurable imprint on the relative positions of objects—a…
Read MorePlanetary Puzzle: Aquodiium Ions may Influence Uranus and Neptune’s Magnetic Fields
Scientists from Skoltech and their Chinese colleagues have discovered conditions that might allow for the existence of a unique ion called aquodiium. This ion is essentially a water molecule that has gained two extra protons. This means, the “regular” H₂O formula with two additional protons (H⁺), will make its chemical formula H₅O²⁺.
Read MoreAnalyzing Pulsars: To Detect Subnanohertz Gravitational Waves
Detecting gravitational waves have always been a challenging task. It is caused due to high energetic events, like colliding black holes or neutron stars. And so, the phenomenon is like ripples on the fabric of space-time. By the time, this effect reaches us (from deep space), the signals become extremely weak. And hence, too faint to detect.
Read MoreCosmic Conundrum in the Milky Way: Lightest Black Hole or Heaviest Neutron Star
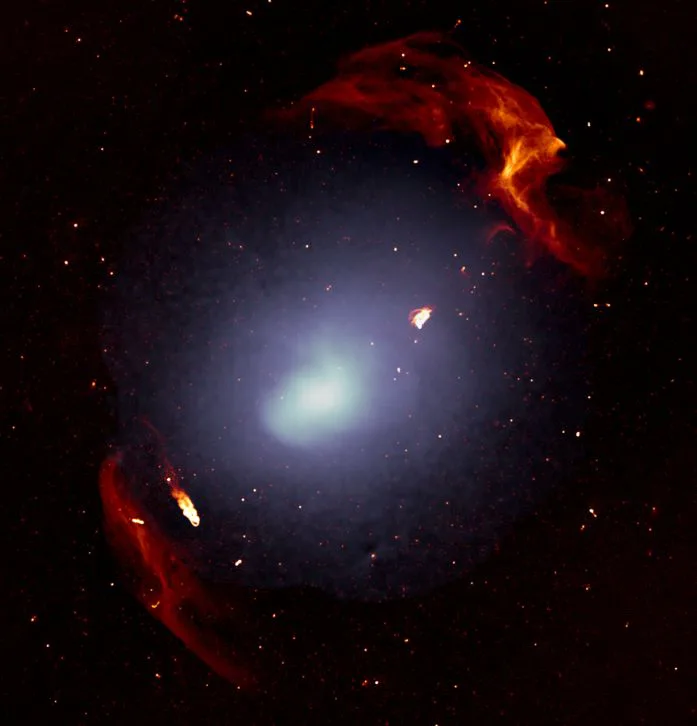
Exciting news from the cosmos! Astronomers from around the world, including the brains at The University of Manchester and the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy in Germany, have stumbled upon an unknown object in the Milky Way. The newly discovered object is heavier than the heaviest neutron stars we know. And lighter than the lightest black holes we’ve seen. The team used the MeerKAT Radio Telescope, to spot this mysterious object. This celestial entity is in orbit around a high-speed millisecond pulsar, situated around 40,000 light years away in…
Read MoreAstronomers Pinpoint Oldest Known Black Hole: Time-Traveling with Telescopes
Recently, astronomers have detected a super-old black hole, which is devouring its galaxy. It is dated back to the earliest black hole ever. It’s like the ultimate space buffet for the oldest black hole. Researchers at the University of Cambridge, unleashed the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) to spot this ancient black hole. The gravity well is chilling out 400 million years post-Big Bang, that is, over 13 billion years back.
Read MoreCosmic Recycling: NASA’s Discards Turned into Futuristic Nanomaterials
Sussex researchers just unveiled the game-changing power of Martian nanomaterials! Dr. Conor Boland, the materials physics maestro at Sussex, along with his team investigated the potential of nanomaterials. These materials are smaller than a human hair for Mars’s sustainable future. The same tech rocking the International Space Station and NASA’s playbook might be Mars’s ticket to eco-friendly living.
Read MoreGalactic Breakthrough: Abell 2108 Reveals Its Second Radio Relic
Indian and Taiwanese astronomers recently upgraded Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (uGMRT) to snoop around the galaxy cluster Abell 2108. And guess what? They stumbled upon a second, way bigger radio relic that’s like, totally different from the first one they knew about in the same cluster.
Read MoreM87 Black Hole Unveils Magnetic Brilliance in Spiraling Light
In 2019, the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) unveiled the first-ever images of M87. It was a mind-blowing moment for astronomy. M87 is a supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy Messier 87. The EHT dropped the first snapshots of M87. It was like getting an up-close look at a supermassive black hole for the first time ever!
Read MoreMeteorites Unveiled as Earth’s Nitrogen Messengers
Tiny meteorites from the icy outer reaches of the Solar System might be the reason nitrogen ended up near Earth. Yes, we are talking about the early days of our solar system. A team of scientists from the University of Hawai’i at Manoa along with Kyoto University and others from around the globe recently published their discovery in Nature Astronomy.
Read MoreBe Stars’ Dancing in Triple Systems
Jonathan Dodd and Professor René Oudmaijer’s recent research at the University of Leeds challenges the assumption that massive Be stars are mainly found in double star systems. The study, however, suggests evidence supporting the idea that these stars might be part of triple star systems. Thus, introducing a new perspective in stellar science.
Read MoreEarth’s Electrons: Unexpected Contributors to Lunar Water Formation
Our planet, Earth, is not merely a rock in space but an interesting entity with various forces acting within and outside of it. For instance, magnetosphere. Earth’s core consists of molten iron. This liquid iron creates electric currents. Which, consequently, generate a magnetic field that surrounds Earth. This magnetic field extends far out into space, creating the magnetosphere. It acts as a formidable defence against the solar wind.
Read MoreBlack holes in the Hyades Star Cluster
In an international collaboration between astronomers from University of Padua (Italy), the Institute of Cosmos Sciences of the University of Barcelona (ICCUB) and the Institute of Space Studies of Catalonia (IEEC), there are indications that multiple black holes might exist within the Hyades cluster.
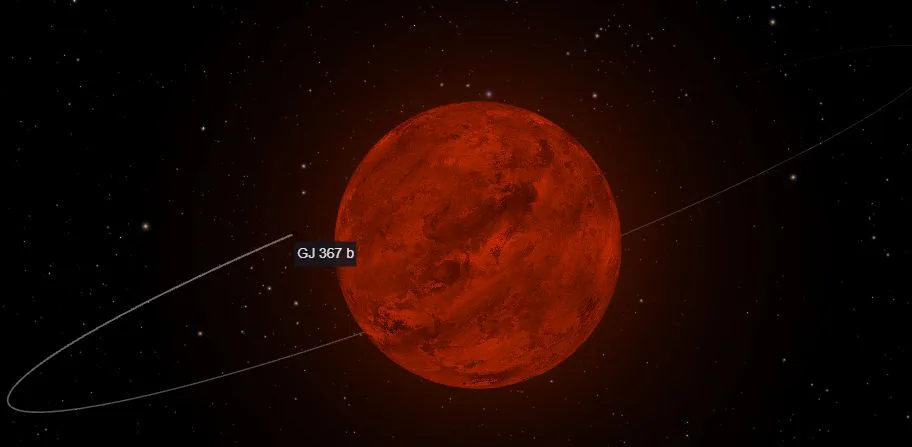
Read MoreNew Exoplanets Discovered in GJ 367: A Cosmic Surprise
In an effort to explore the mysterious GJ 367 planetary system, an international team of astronomers embarked on a dynamic quest. Armed with the High Accuracy Radial velocity Planet Searcher (HARPS), they set out to unravel the secrets hidden in the vastness of space.
Read More