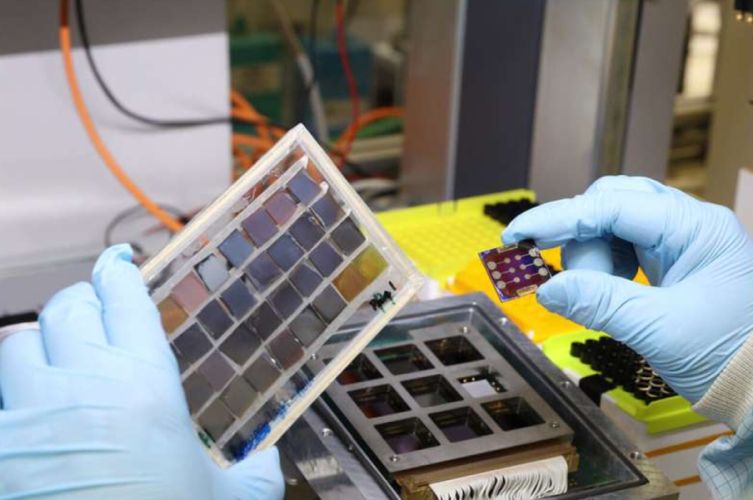
Zinc batteries have been explored as an alternative to lithium-ion batteries for large-scale energy storage since long. Zinc-based batteries is preferred over li-ion batteries because it is abundant, low-cost, and environmentally friendly compared to other metals. However, their efficiency has been limited due to issues with the zinc metal anode. However, with the recent development of a new electrolyte that improves the efficiency of the zinc metal anode to nearly 100%, researchers envision that it could make zinc batteries a viable alternative.
Read MoreCategory: Futuretech Tonics
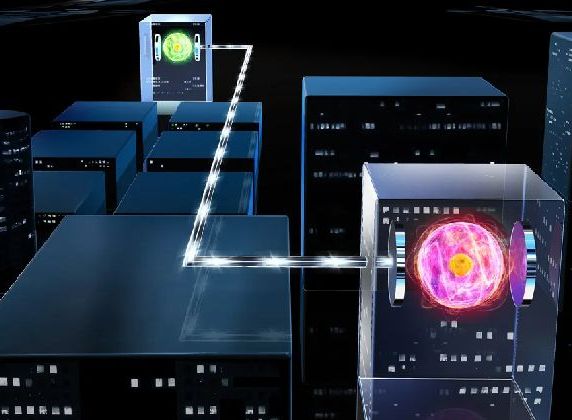
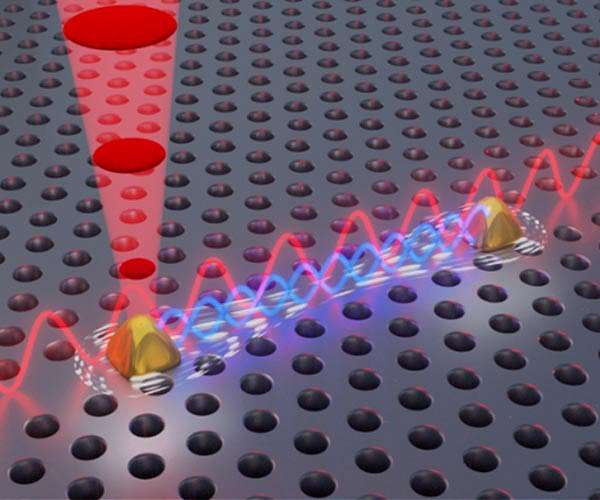
Dynamics between Quantum Entanglement: Coupling at a Distance
Entanglement is a unique and powerful feature of quantum mechanics. It allows two or more particles, such as photons of light, to become correlated in such a way that the state of one particle is immediately determined by the state of the other particle, regardless of the distance between them. This phenomenon has been studied extensively in the field of quantum physics. It has important implications for the development of quantum technologies such as quantum cryptography and quantum computing.
Read MorePlatform for Building Quantum Networks: Entanglement of Trapped-ion
The researchers at the University of Innsbruck and the Université Paris-Saclay have developed a method for linking multiple quantum systems by trapping atoms in optical cavities. And then transferring the quantum information to light particles which can then be sent through optical fibers. They have successfully entangled two trapped ions located more than a few meters apart for the first time.
Read MoreTwo/Quasi 2D Perovskite Heterostructures: Optoelectronic Innovation
Two-dimensional perovskite materials have unique properties that make them attractive candidates for use in next-generation optoelectronic devices, such as photovoltaic solar cells, LEDs, and photodetectors.
Read MoreWearable Electrotactile Feedback System: Skin VR
Haptic systems are mainly designed to control virtual objects. Their efficacy is good, but when it comes to controllers, joysticks, and steering wheels, things look slightly bulky. And tangled wires is another task to deal with. Researchers at City University of Hong Kong have come up with a portable solution to enhance the tactile VR experience.
Read MoreMicrobial Miners to Colonize the Moon and Mars: Biomimetic Mining
Evolutionary biological processes take time but what if we introduce microbial catalysis to the system? The phenomenon of how cyanobacteria obtain nutrients for its survival from rocks in Atacama Desert inspired an international team of collaborators from University of California and Johns Hopkins University to consider the microbes as tools that may help humans to develop colonies on the moon and Mars.
Read MoreCeramic based Micro Glucose Fuel Cells: Implantable Power Sources
In the coming two decades, nanotechnology will surely touch the lives of nearly all people across globe. As technology progresses, we will experience next generation sensors embedded in all things that we use, including our clothes, kitchen and within ourselves. Yes, IoT is coming here to stay. So, the next question is what will be the efficient power source for these devices, especially the implantable sensors and drug-delivery systems? Researchers at MIT have paved a way for glucose powered medical implants. With their newly designed glucose fuel cell, they are…
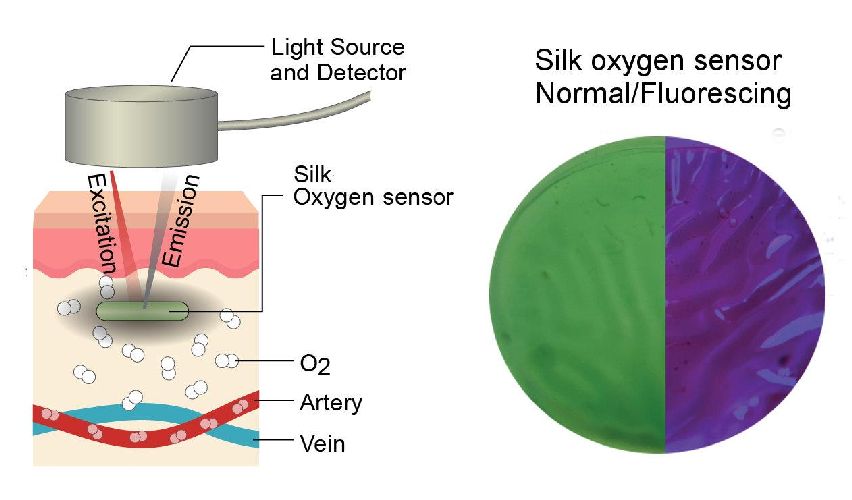
Read MoreTattoo like Sensors to Reveal Blood Oxygen Levels: Silk based Biomaterials
Soft skin sensors are beginning to transform the health care industry. We can surely predict that within a decade, people will be wearing skin sensors to detect the blood glucose level, oxygen level and to track other different blood components which currently require an incision. Researchers at Tufts University have developed a tattoo-like sensor that glows when exposed to light. The degree of brightness depends on the level of oxygen in blood. Silk fibroin hydrogel The sensor is made up of silk fibroin hydrogel. Fibroin is an insoluble protein that…
Read MoreChina’s Particle Collider to Gear up: A Future Higgs Factory
To explore more exotic particles, Beijing Electron Positron Collider (BEPC), the particle-physics lab, is undertaking a major re-equipping. The work is expected to complete by 2024. Dubbed as BEPCII-U, the new version will not only triple the current collision rate but it’ll also extend the maximum collision energy to 5.6 GeV from the existing 2–5 GeV. With the plans underway for next-generation collider, China might head the world in high-energy physics research.
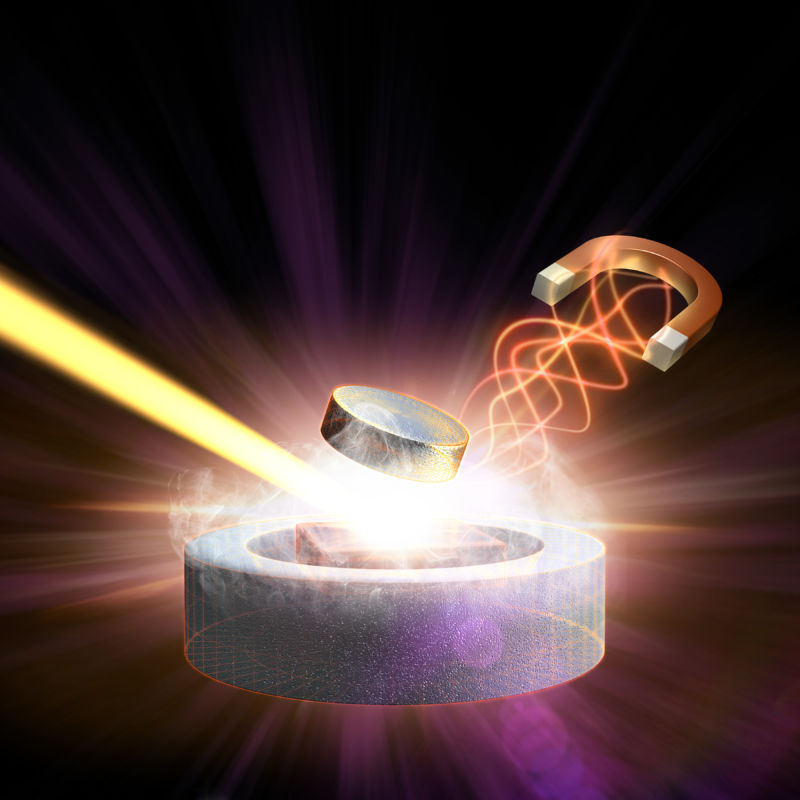
Read MoreInsulation-free Magnet to Facilitate Development of Fusion Power Plant: Superconductors
Replicating fusion on earth is one of the things that scientists globally look forward to. Once they are able to reach a state through which fusion could be created, we might get virtually inexhaustible supply of power to generate electricity.
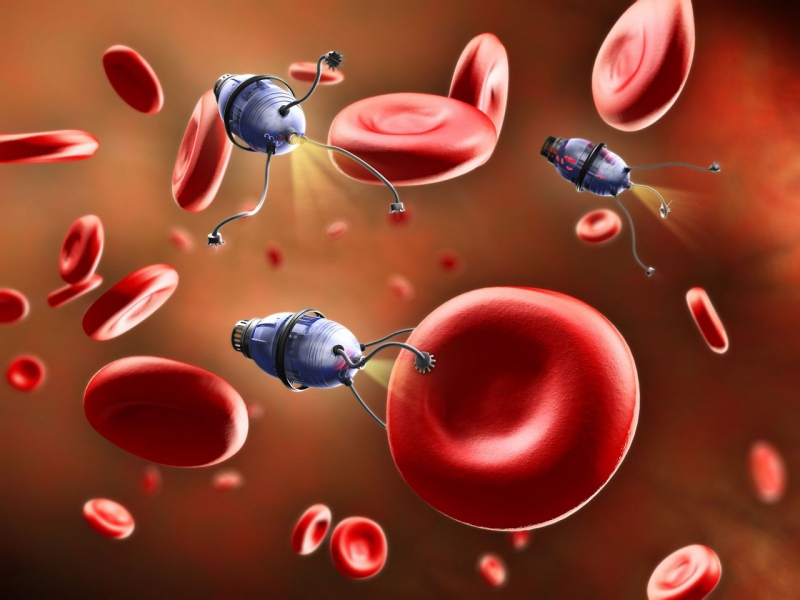
Read MoreLight controlled Organic Microswimmers: Semi Autonomous Microrobots
The idea that nanobots flowing through our blood streams to deliver localised medication or to detect any tumour formation is no more a far-fetched dream. A group of researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems (MPI-IS) in collaboration with the Max Planck Institute for Solid State Research (MPI-FKF), have developed microswimmers that can navigate through biological fluids, areas that are otherwise difficult to access. Steering is done through external form of light energy.
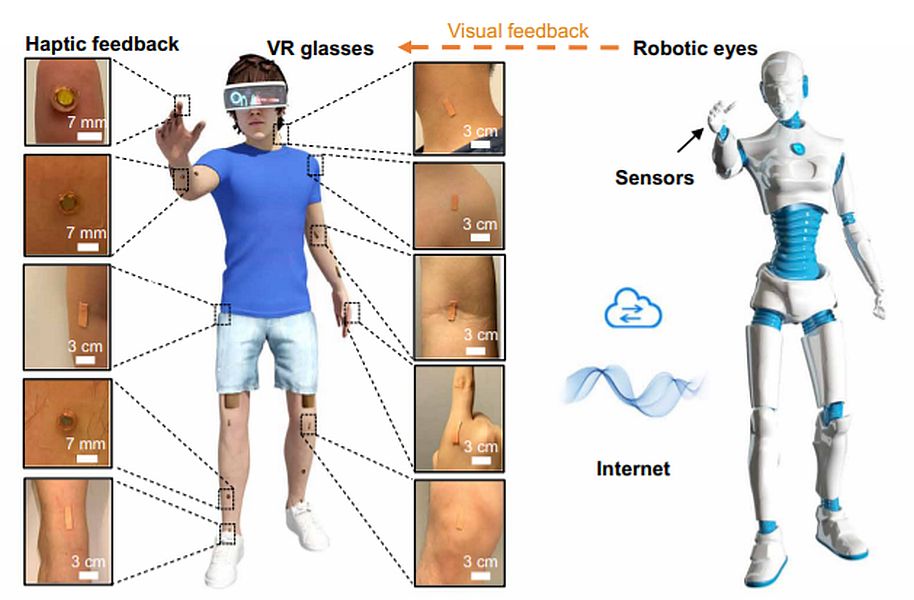
Read MoreSkin-Integrated Electronics to Capture Haptic Feedback: Human-Machine Interfaces
To control a remote robot via electromechanical devices, require the operator to wear huge and at times bulky gear. To make things easier, researchers from Hong Kong and China have fabricated a flexible skin patch, which has an ability to provide haptic feedback. Now not only the user can receive feedback from another (human) user but also from a robot to be more specific, haptic feedback from remotely controlled robot.
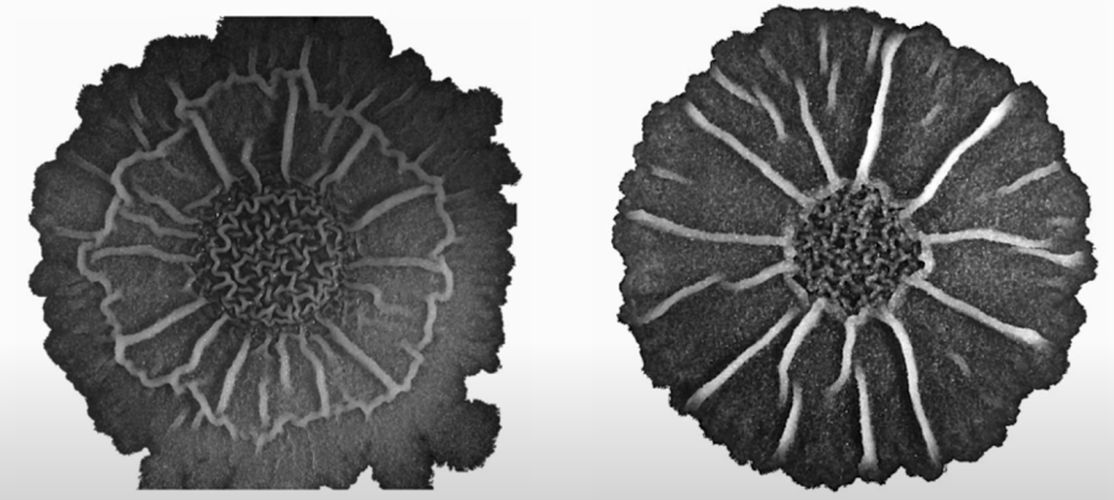
Read MoreBacterial Biofilm is a Complex Community: Selective Sporulation
Structural organisation has always been the hallmark of complex organisms, this however is not the case anymore. Researchers at University of California, San Diego have discovered that bacterial biofilms are not at all simple but is a complex community, which has a direct relationship with its external settings.
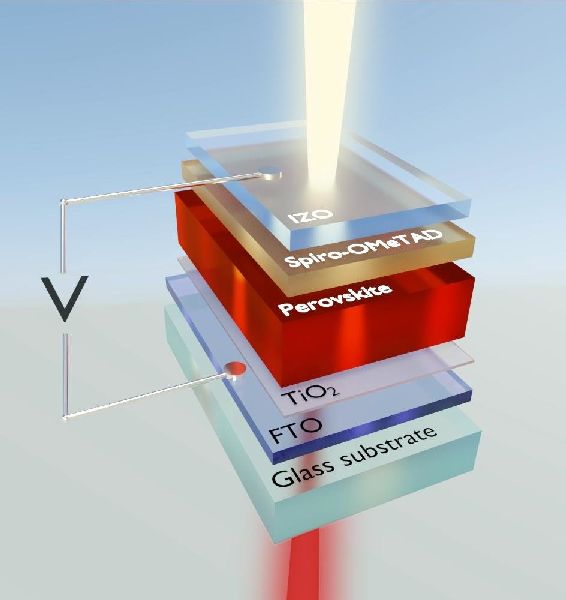
Read MorePerovskite Solar Cell Shows Long Stability: Photovoltaic Tech
Perovskite is an emerging name in the new generation of solar modules. Due to its super power conversion efficiency, it is extensively studied by researchers in photovoltaic technologies.
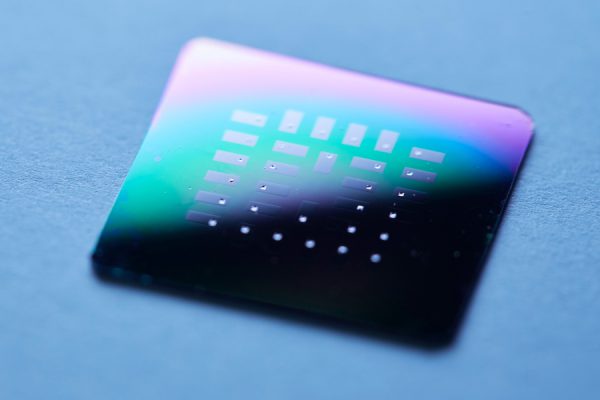
Read MoreSurface Optics & Neural Based Processing: MetaOptics
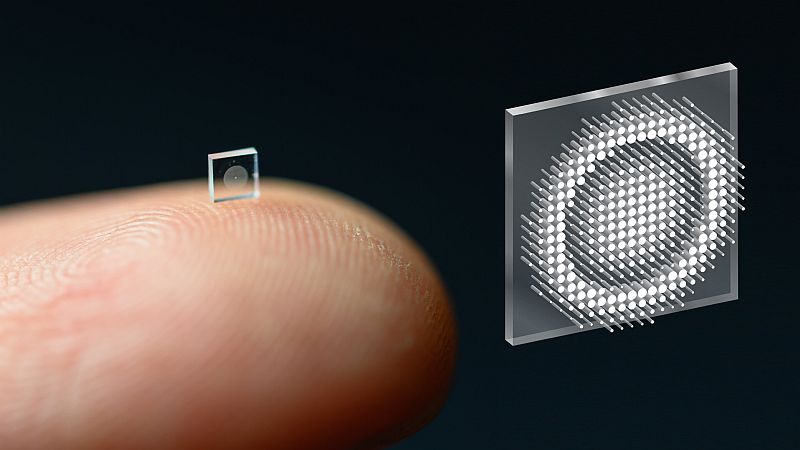
An international team of researchers at Princeton University and the University of Washington has developed a micro-sized camera to the size of a salt grain.
Read More