Vitamin D plays an important role in regulating normal function of human body. It helps the body to absorb and retain calcium and phosphorus, which are critical for building bone. In addition, it also helps in boosting energy levels.
Epidemiological studies too, have shown that Vit-D deficiency is closely associated with common chronic diseases such as bone metabolic disorders, tumors, cardiovascular diseases, and diabetes. In addition, similar corelation between vitamin D and skin cancers have also been investigated.
The research is primarily based on serum concentration of calcidol (the major circulating metabolite of vitamin D) and its association with skin cancers.
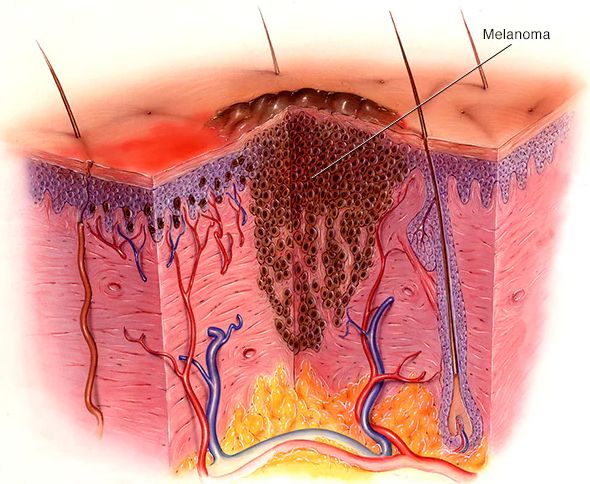
Vitamin D supplements leads to less aggressive melanoma
The study under North Savo Skin Cancer Programme spilled out interesting results. Research sample consists of 498 adult patients. All of them were on higher side of skin cancer, such as basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma or melanoma.
Patients’ background information and medical history were carefully examined by experienced dermatologists at the University of Eastern Finland. Based on the data, the individuals were then placed under three categories of skin cancer risk:
- low risk,
- moderate risk and
- high risk.
Depending on their consumption of oral vitamin D supplements, they were again separated into three groups:
- non-users,
- occasional users and
- regular users.
To evaluate the Vitamin D, serum calcidiol concentrations were analysed, which corresponded to their self-reported use of vitamin D. The results were as follows:
- People who consumed vitamin-D at regular intervals showed less signs of melanoma, and
- On the scale of skin cancer risk classification, they showed considerably better results than non-users’
The findings also suggested that occasional users of vitamin D might also fall in the lower range of melanoma graph than those who hardly consume or the non-users of vit-D.
What does vitamin D do for you?
Vitamin D is much beyond bone health. It not only helps in lessening cancer cell growth; it also assists in controlling infections and in reduction of inflammation.
Some studies have proved that vit-D also provides improved resistance to certain diseases. It also plays key role in:
- Reducing the risk of multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Decreasing the chance of heart disease
- Reducing the likelihood of severe illnesses
- Supporting immune health
- Fight back flu
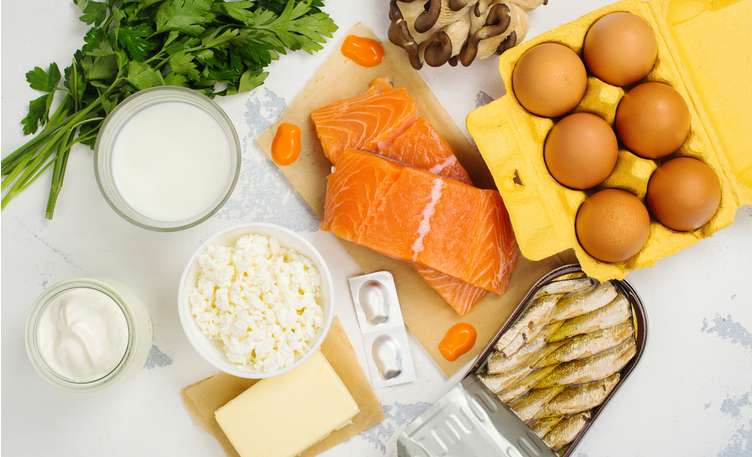

What foods and fruits are highest in vitamin D?
Sun is our daily dose of vitamin D. Our body naturally makes vit-D when we are exposed to the sun. Other than sun, we can also get the fat-soluble vitamin from:
Veggie sources – orange juice, mushrooms, tofu, dairy products such as yogurt & milk. And fortified cereals.
Others – cod liver oil, beef liver, egg yolks, swordfish, salmon, tuna, and sardines.
What are the signs you need vitamin D?
Progressively it has been observed that there is vitamin D deficiency across all age groups. Its scarcity in children often leads to delays in growth and rickets, a condition that leads to bone deformities, stunted growth, and easily breakable bones.
In case of adults, the deficiency may look like:
- Muscle pain
- Muscle weakness
- Dental problems
- Fatigue
- Bone pain or achiness
- Depression or feeling of sadness
- Cognitive impairment
- Loss of appetite
- Hair loss
- Not sleeping well
- Getting sick more easily
Takeaway
Vitamin D deficiency is common across globe. To maintain proper bone health and other aspects of well-being, adding vitamin D to diet is an essential step.
On daily basis, intake of vitamin D should be 1,000–4,000 IU, or 25–100 micrograms. This is enough to ensure optimal blood levels in most people.