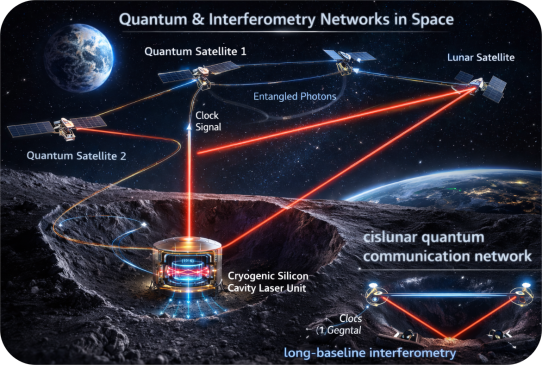
Scientists from Skoltech and their Chinese colleagues have discovered conditions that might allow for the existence of a unique ion called aquodiium. This ion is essentially a water molecule that has gained two extra protons. This means, the “regular” H₂O formula with two additional protons (H⁺), will make its chemical formula H₅O²⁺.
Read MoreInsulin Resistance: Ketones Found to Revive Neuron Function
Recent research conducted by the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester focused on understanding how ketones affect the brain’s hippocampal network. The hippocampus is a crucial brain region involved in memory formation and spatial navigation.
Read MoreBook Review: The Demon in the Machine by Paul Davies
The Demon in the Machine: How Hidden Webs of Information Are Finally Solving the Mystery of Life by Paul Davies was first published in 2019. This book comes with a wealth of knowledge, as the author has put together physics, chemistry, biology, and information theory.
Read MoreElectronic Spider Silk: A Versatile Solution for Bioelectronics
Super-thin and flexible electronics are here to stay. This tech will not only create but it will also revolutionize the use of gadgets. Since, it leads to unlimited possibilities for innovative and practical applications. Some of the them include but not limited to – wearable tech, portability, healthcare applications, space probes etc.
Read MoreBook Review: Pedro Páramo by Juan Rulfo
When I decided to read One Hundred Years of Solitude by the Colombian author Gabriel García Márquez, I found out that it was inspired by Juan Rulfo’s Pedro Páramo. So, I thought it would be fun to read Pedro Páramo first!
Read MoreBook Review: A Pale View of Hills by Kazuo Ishiguro
“A Pale View of Hills” is Kazuo Ishiguro’s debut novel, published in 1982. This is actually my third time diving into Ishiguro’s world. After being captivated by “Never Let Me Go” and “Klara & the Sun,” I couldn’t resist exploring more of his work.
Read MoreInterview: Dr. Laura E. Newman, a Cell Biologist at the University of Virginia School of Medicine, US
Meet Dr. Laura E. Newman, an Assistant Professor in the Department of Cell Biology at the University of Virginia School of Medicine, United States. Her research delves into the intriguing role of mitochondria—these tiny powerhouses that were once ancient bacteria now living inside our cells—as crucial regulators of cellular signaling.
Read MoreBook Review: The Symmetries of Things by John Horton Conway, Heidi Burgiel, and Chaim Goodman-Strauss
“The Symmetries of Things” explores mathematical symmetry and the symmetrical properties of geometric objects. The book was a collaborative effort spanning many years, authored by John Horton Conway, Heidi Burgiel, and Chaim Goodman-Strauss. It was first published in 2008 by A K Peters.
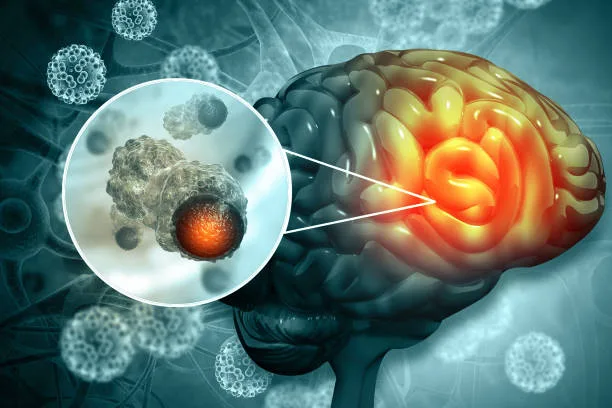
Read MoreNanoparticles Break Blood-Brain Barrier for Cancer Treatment: Targeting Metabolic Adaptability
Scientists at the Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, part of the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, have crafted a tiny particle capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier. The team envision to tackle both primary breast cancer tumors and brain metastases in a single treatment. Their investigations indicate that this approach can reduce the size of both breast and brain tumors in lab experiments.
Read MoreBook Review: Fahrenheit 451 by Ray Bradbury
“Fahrenheit 451” is a dystopian fiction, written by American author Ray Bradbury in 1953. It stands as one of his most acclaimed works, delving into a dystopian world where people are programmed for efficiency and superficial contentment through constant exposure to television. In this society, intellectuals and free thinkers are absent, and replaced by passive TV viewers. The Plot: Guy Montag’s Evolution The narrative unfolds through the eyes of Gus Montag, a member of the fire brigade. Also, the central character, Guy Montag, is tasked with identifying and incinerating forbidden…
Read MoreBook Review: The Three-Body Problem by Liu Cixin
“The Three-Body Problem,” an absolute gem of a story was crafted by Liu Cixin. Originally released as a serial in Science Fiction World back in 2006, the work hit bookshelves as a standalone novel in 2008. It snagged the prestigious Galaxy Award for Chinese science fiction in 2006 and quickly became a literary sensation in China.
Read MoreBook Review: Klara and the Sun by Kazuo Ishiguro
Klara and the Sun is my second read from the vault of Kazuo Ishiguro. The book was first published in 2021. It is a dystopian science fiction novel set in a future where android companions are designed for children. In this era, wealthy parents can choose to enhance their children’s intelligence through a process known as “lifting,” which likely involves genetic engineering, although the specifics are not fully explained in the book. While “lifting” boosts intelligence, it also carries risks such as chronic illness and even mortality.
Read MoreBook Review: The Blind Assassin by Margaret Atwood
“The Blind Assassin” is a book authored by Canadian writer Margaret Atwood, initially published in 2000. This marks my second time reading the same book, yet I still don’t feel adequately prepared to provide a review. This book is intricately and elegantly crafted. As we delve into its pages, we gain deep insights into the characters, yet there’s a veil of uncertainty about whose perspective we’re truly witnessing. I felt myself compelled to hunt for subtle clues sprinkled throughout the book, determined to unravel the mysteries concealed within its pages.
Read MoreInterview: Dr. Shoji Takeuchi, a Biohybrid Systems Scientist at The University of Tokyo, Japan
Welcome to our chat with Dr. Shoji Takeuchi, a Biohybrid Systems Scientist rocking it at The University of Tokyo. Dr. Takeuchi’s research covers a bunch of cool stuff like Biohybrid Systems, MEMS, Microfluidics, Tissue Engineering, and Artificial Cell Membrane. Basically, he’s all about blending biology and tech to create awesome bio-hybrid systems.
Read MoreBook Review: The Brothers Karamazov by Fyodor Dostoevsky
When I seek literature that is intricate and profound, I turn to the works of Dostoevsky. And this time, I picked up, “The Brothers Karamazov”. Dostoevsky dedicated almost two years to crafting “The Brothers Karamazov,” serialized in The Russian Messenger from January 1879 to November 1880. Sadly, he passed away less than four months after its publication. This masterpiece has since been hailed as one of the paramount accomplishments in world literature.
Read More