Plants have a complex and in interesting biochemical communication networks. The workings of these networks resemble our web of social networks. Like we chat through words and sounds and emojis, the flora makes use of scents and signals.
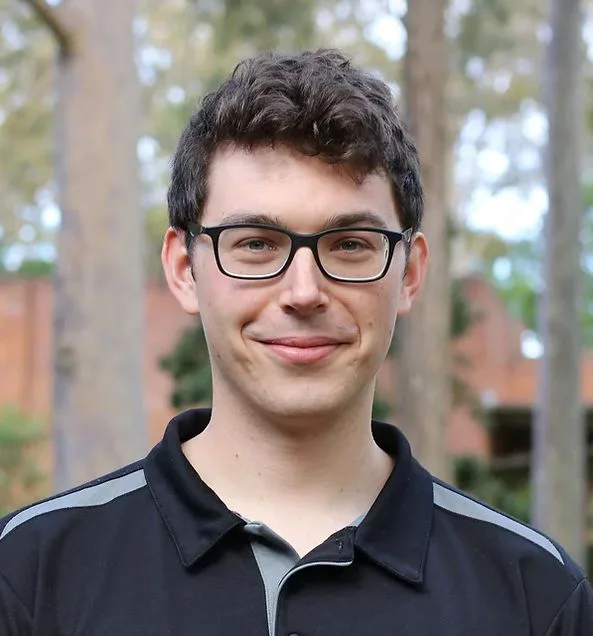
Read MoreInterview: Dr. Yuanbo Chen, Quantum Information Scientist at The University of Tokyo, Japan
Meet Dr. Yuanbo Chen, a dynamic and dedicated PhD student at The University of Tokyo. He is an invaluable member of the Hasegawa Group, where his intellectual curiosity and commitment to pushing the boundaries of quantum research shine brightly. In a recent scientific breakthrough, Dr. Chen, in collaboration with his accomplished team has captured headlines with their pioneering research in battery technology.
Read MoremtDNA: Key Component of Energy Production and Trigger of Inflammation
Entity responsible for powering our cellular functions and in keeping us going is mitochondria. These powerhouses are little sausage-shaped organelles in most types of cells that have a nucleus. These organelles convert chemical energy from the food that we ingest into usable form of energy. This energy is termed as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is the fuel that we require to carry out the regular activities at cellular level.
Read MoreBook Review: The War of the Worlds by H. G. Wells
Having read “The War of the Worlds” when I was younger, this time around, it was a quick read for me. Additionally, having seen the movie, the pace felt familiar and flowed well. The book written by H. G. Wells was first published in 1898. I am still completely in awe of the creativity that Wells showcased during that era. I’m certain this book was ahead of its time. Anyone considering writing a sci-fi story should first study Wells’ work.
Read MoreAnalyzing Pulsars: To Detect Subnanohertz Gravitational Waves
Detecting gravitational waves have always been a challenging task. It is caused due to high energetic events, like colliding black holes or neutron stars. And so, the phenomenon is like ripples on the fabric of space-time. By the time, this effect reaches us (from deep space), the signals become extremely weak. And hence, too faint to detect.
Read MoreArtificial Life: Researchers Forge New Building Blocks
Researchers at the University of Cologne (UoC) have achieved a groundbreaking milestone by creating artificial nucleotides. Nucleotides forms the building blocks of DNA. So, if we go by the research, the innovative development will make way for potential advancements in genetic engineering as well as molecular biology.
Read MoreBook Review: The Rebel by Albert Camus
The Rebel by Albert Camus is an exploration of the implications of the act of rebellion in response to facing the absurdism that the world has to offer. It was first published in 1951. This happens to be my second read after The Stranger by the same author. Being a collection of essays, the book lacks a conventional plot development. Moreover, it’s not an easy read. The following paragraphs resemble notes I took while reading the book. At the moment, I don’t feel equipped to review this work by Camus.
Read MoreBook Review: True Hallucinations by Terence Mckenna
“True Hallucinations: Being an Account of the Author’s Extraordinary Adventures in the Devil’s Paradise” is a book written by Terence McKenna. It was first published in 1989. In this book, McKenna recounts his experiences with psychedelic substances, particularly during his time spent in the Amazon rainforest with his brother Dennis McKenna and a small group of others.
Read MoreBook Review: Cat’s Cradle by Kurt Vonnegut
Kurt Vonnegut’s mind was a treasure trove of compelling and thought-provoking ideas, woven into narratives that challenged conventions, provoked introspection, and sparked conversation. His ability to engage readers on multiple levels – whether through his biting satire, profound insights, or dark humor – is both rewarding and intellectually stimulating. His books possess a timeless quality that resonates with readers across generations. And often reveal new layers of meaning upon each re-reading. Every time I dive into one of Kurt Vonnegut’s books, I can’t help but feel that whichever one I’m…
Read MoreProtein Overload: Amino Acid Blamed for Arterial Health Risks
Interesting research from University of Pittsburgh show that too much dietary protein might actually up the risk of atherosclerosis. So, while protein is good for our bodies but consuming in abundance might not be the best idea when it comes to keeping our arteries happy and healthy. The experiment not only combined the human trials but researchers roped in mice and cells in a Petri dish for the study. When the consumption increases to more than 22% of their daily calories from protein, it kicked off a chain reaction. Consequently,…
Read MoreInnovative SiPh Chip: Nanoscale Light Computing Breakthrough
Imagine a world where AI computations are not bound by the limitations of traditional power sources, that is, electricity but by the power of light waves. This is precisely the vision that researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have brought to life with their innovative chip design. This innovation will not only enable the chip to fast-track the processing speed of computers but it will also lessen their energy consumption.
Read MoreBook Review: Stephen Hawking by Michael White & John Gribbin
Michael White and Dr John Gribbin, adept science writers, have masterfully depicted an indomitable genius and an expansive scientific intellect in the book – Stephen Hawking: A Life in Science. It was first published in 1992. As I read the pages of this book, I’m struck by how the writers effortlessly blend clear explanations of Hawking’s scientific achievements with a heartfelt account of his personal life. Their approach allows readers like me to gain a deeper understanding and appreciation for both facets of his remarkable journey. The book recounts how…
Read MoreInterview: Dr. Matthew Bergin, an Experimental Physicist at The University of Newcastle, Australia
I’m thrilled to introduce Dr. Matthew Bergin, a rising star in the world of Organic Electronics research. Armed with a Master of Science degree in Natural Sciences and a Ph.D. in Physics from the prestigious University of Cambridge, Dr. Bergin is making waves with his groundbreaking work at the Centre for Organic Electronics (COE). Dr. Bergin went deep into studying how things work in scanning helium microscopy. He was in charge of creating a better electron ionization mass spectrometer during his Ph.D. research. It’s like he’s breaking new ground in…
Read MoreInterview: Dr. Alex Greilich, an Experimental Physicist at TU Dortmund University, Germany
Meet Dr. Alex Greilich, an experimental physicist who started his journey from Russia to his current endeavors in Germany. Venturing beyond mere theory, he dives headfirst into the intricate world of semiconductor nanostructures and spin dynamics, unearthing remarkable phenomena like time crystals along the way. Collaborating with esteemed institutions such as the Ioffe Institute, (research center within the Russian Academy of Sciences) Dr. Greilich’s work pushes the boundaries of what we know about the universe.
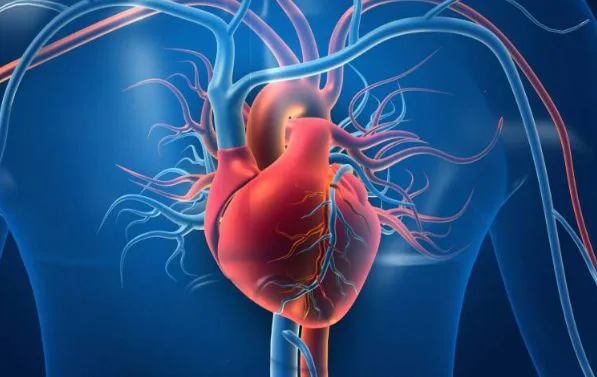
Read MoreHeart Healing: Microenvironment’s Role in Cardiac Recovery
A group of scientists led by James F. Martin, has been delving deep into the intricacies of cardiac function at The Texas Heart Institute. Their objective is to illuminate the innate regenerative potential of the heart. At a global level, the primary challenges associated with heart attacks, also known as myocardial infarctions, stem from unhealthy lifestyle choices and genetic predispositions. Also, surviving a heart attack doesn’t guarantee immunity from severe damage to the heart muscles. The cardiomyocytes are severely affected.
Read More