Unlike robots, our bodies are super flexible and can make delicate moves effortlessly. Components like muscles, joints, and nerves work in tandem and allow us to make precise and delicate movements with ease. Robots, on the other hand, rely on rigid structures and predefined movements; in contrast, our bodies can adapt and respond dynamically to various situations.
Inspired by how humans walk, Japanese researchers created a fantastic two-legged biohybrid robot using a concept known as biomimicry. They blended muscle tissues with artificial materials to bring this innovation to life!
A Rising Fascination in Combining Biology and Mechanics
According to Shoji Takeuchi from the University of Tokyo, Japan, there’s a rising fascination with biohybrid robots, combining biology and mechanics. This innovative field is gaining momentum. And accordingly, it is establishing itself as a new frontier in robotics with biological functionalities.
Using muscles as actuators allow us to design a compact robot that can move efficiently, quietly, and with a gentle touch, added Dr. Takeuchi.

Bipedal Robot Powered by Muscles
The research team’s new two-legged robot is a groundbreaking bot that’s truly a marvel in bipedal design! It’s powered by muscles for a cutting-edge performance.
While typical muscle-driven biohybrid robots move straight and turn, they struggle with sharp turns. But not this one! It can smoothly pivot and make sharp turns. A crucial feature for robots to adeptly navigate and avoid obstacles.
Robot that Walks, Swims, and Stays Upright Underwater
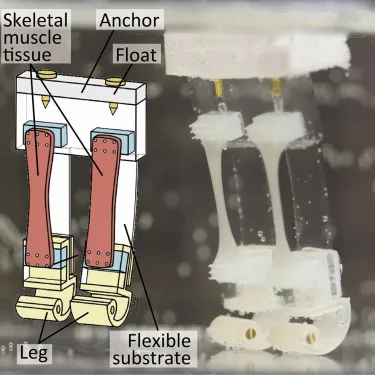
The bipedal bot mirrors human walking and functions in water. It boasts a buoyant foam top and weighted legs so that it can maintain an upright position in underwater. Its flexible skeleton, primarily composed of bendable silicone rubber, mimics the adaptability of human muscles.
The final step in perfecting the design included affixing strips of laboratory-cultivated skeletal muscle tissues to both the silicone rubber structure and every leg.
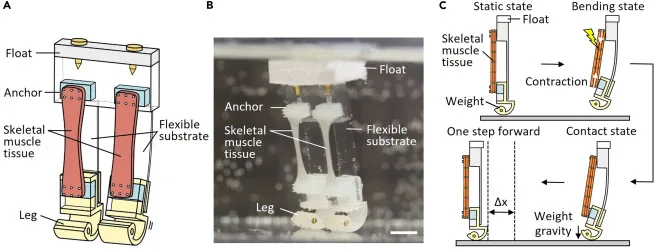
Muscle-Driven Bipedal Robot
When the researchers introduced electricity to the muscle tissue, it responded by contracting and lifting the leg. Once the electrical stimulation ceased, the leg’s heel landed forward, showcasing the controlled and responsive nature of the muscle-driven mechanism.
By alternating electric pulses between the left and right leg every 5 seconds, the biohybrid robot successfully “walked” at a speed of 5.4 mm/min (0.002 mph).
To make turns, the researchers applied repeated stimulation to the right leg every 5 seconds, while the left leg served as an anchor. This method allowed the robot to smoothly execute a precise 90-degree left turn in just 62 seconds. These findings clearly illustrate that the muscle-driven bipedal robot is not only capable of walking and stopping but can also perform intricate and finely tuned turning motions.
Future Upgrades: Nutrient System
As of now, the bot is maneuvered manually, however, researchers aim to boost the robot’s speed even more efficiently by integrating the electrodes directly into its design.
The team is also envisioning an upgrade with joints and thicker muscle tissues. All geared towards achieving more sophisticated and powerful movements.
Before going all out with additional biological components, Takeuchi highlights the need to tackle a crucial step: figuring out how to integrate a nutrient supply system. This is essential to sustain the living tissues and device structures as the bipedal robot advances, especially when it starts operating in the air.
Takeaway
Future impact of such bipedal robots will be quite significant. As technology advances, we might witness faster and more efficient robotic movements. And more complex and adaptable robotic systems.
Additionally, the evolution of these biohybrid robots holds the promise of expanding their applications across diverse industries such as:
- healthcare
- search and rescue
- manufacturing
- entertainment
- space exploration
- aerial exploration or surveillance
In essence, the future impact could see these biohybrid robots playing a crucial role in various industries, offering solutions to challenges that traditional robotics may not easily address.



[…] What motivated the focus on developing biohybrid robots with two legs and cultured skeletal muscle tissue for driving? Ref: Biohybrid bipedal robot powered by skeletal muscle tissue […]
[…] What motivated the focus on developing biohybrid robots with two legs and cultured skeletal muscle tissue for driving? Ref: Biohybrid bipedal robot powered by skeletal muscle tissue […]