Globally, electronics engineers are busy developing devices that are flexible, adaptable, and built for high performance. These devices are designed for real-world applications, including – robotics, healthcare and wearable technology. Similar efforts are underway in developing smart textiles as well. Interestingly, these fabrics can detect environmental changes or perform specific functions.
So?
These textiles can be integrated into various technologies to enhance efficacy and performance. Some of these systems include:
- Robotic systems
- Medical devices
- Wearable technologies
Thus, it will offer new possibilities for stretchable, adaptable, and even interactive materials.
Scalable and Customizable Soft Actuators
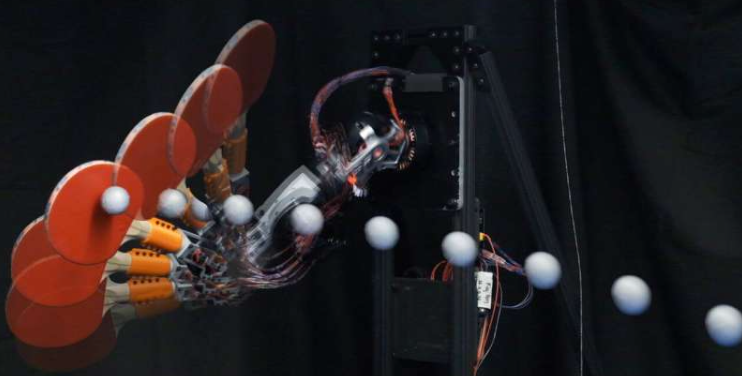
Researchers at Jiangnan University have made significant progress in this field. They have developed soft actuators. These devices can move or change shape when triggered by external stimuli (e.g., heat, light, or electrical signals). The uniqueness of their approach lies in the fact that it is scalable (i.e., suitable for mass production) and easily designable (allowing for a wide range of designs and applications).
Limitations of Traditional Techniques
Traditional techniques, like 3D printing and elastomer casting, do come with certain limitations. While these methods allow for the creation of flexible and functional devices, they often fall short in areas critical for real-world applications—particularly adaptability, comfort, and scalability, explained Dr. Fengxin Sun, corresponding author of the paper.
Additionally, soft robotics need both flexibility and comfort, since, they are subjected for prolonged use in medical applications. Achieving this with rigid or semi-rigid structures has always been challenging.
Therefore, the researchers approached this problem by how traditional clothing is made, that is, starting from yarn and transforming it into fabric. In this “yarn-to-clothes” manufacturing process, individual threads (yarns) are woven together to create garments.
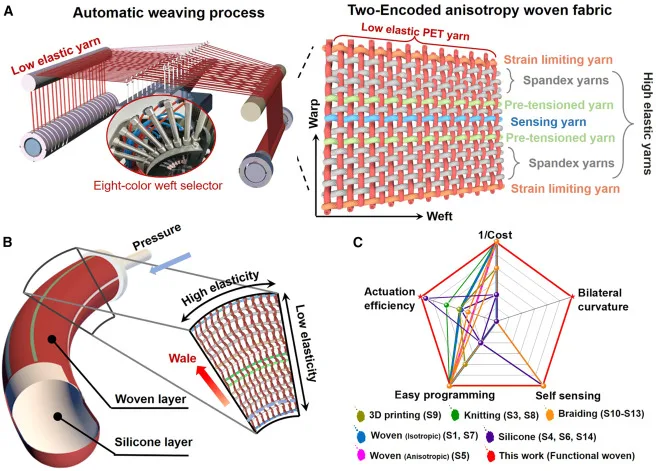
Yarn-to-Clothes Approach
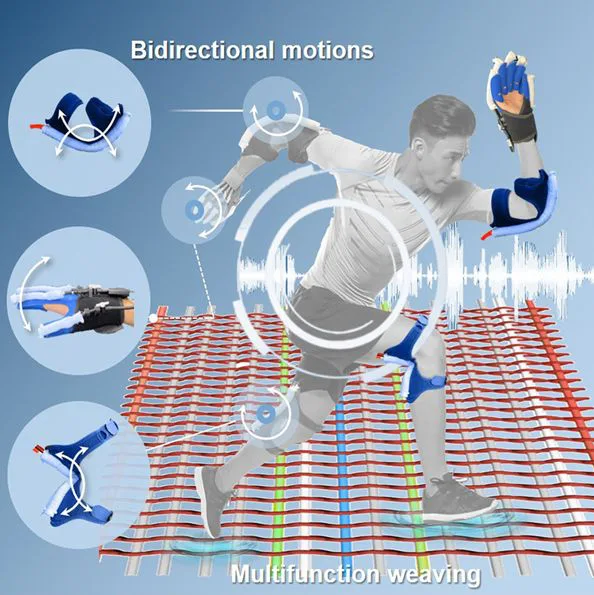
Sun and his team fabricated the two main types of yarns used in fabrics—those that run lengthwise and those that run crosswise—into a flat pattern while weaving. This setup allows them to create special woven materials that can be customized by adjusting how the yarns are arranged and what types of yarns are used.
As per the researchers, this approach allows for personalized morphing and real-time sensing feedback in the woven actuators. Thus, the mechanism makes it highly suitable for applications like rehabilitation wearables.
How?
Firstly, with the help of personalized morphing, woven actuators can change shape or conform to an individual’s body based on specific needs. For instance, the garment that can adjust its tightness or apply controlled pressure to assist in exercises or recovery processes.
Secondly, the real-time sensing feedback can monitor the user’s movements, body temperature, or other health metrics. For example, in a rehabilitation setting, the wearable can adapt its support based on the user’s performance and progress, offering customized assistance to enhance the effectiveness of exercises.
Takeaway
Pneumatic soft robotics, which are based on air pressure, are flexible but when it comes to efficiency and responsiveness, they fall short. The current Yarn-to-Clothes Approach looks promising to create better soft robots.
By developing robot parts that can change shape and do multiple things at once could be a game changer as it will take the functionality and versatility of soft robotics to the next level.
Additionally, the method will be cost-effective and easy to scale up, which means they can be produced in large quantities without driving up costs. This surely is an exciting implication for fields like healthcare, robotics, space exploration and wearable technology.
Via: Cell Press