
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has revolutionized our understanding of the early universe, particularly with its discoveries in 2024. The objects that have been discovered have revealed properties and structures that challenges our current understanding of cosmic theories. These groundbreaking findings, many made possible by the phenomenon of gravitational lensing, have opened new avenues of research into how the earliest galaxies and stars formed.
What is gravitational lensing?
Gravitational lensing is a phenomenon which occurs when the intense gravity of a massive object distorts and magnifies light coming from a more distant object.
As per general relativity, gravity is the distortion or bending of space-time fabric, which happens due to the presence of matter and energy. This bending of the space-time fabric also effects the path of light. So, when a light is passing through this massive object, it bends and magnifies the image (of the distant object). In effect, causing the object to appear brighter and larger than it would otherwise. This entire process is called as gravitational lensing.
Astronomers leverage this magnification as it helps them in identifying the galaxies, which in other circumstances wouldn’t have been possible. Gravitational lensing can also reveal the structure of the cosmic web, a network of gas and dark matter that connects galaxies. It not only helps astronomers in tracking far flung galaxies but it also assists in understanding the distribution of matter across universe.
What early universe structures did JWST discover in 2024?
In 2024, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) made some super interesting discoveries about the early universe. The main highlights include – the formation of galaxies and star clusters. These discoveries really shed light on the early years of our universe, which we call the cosmic dawn.
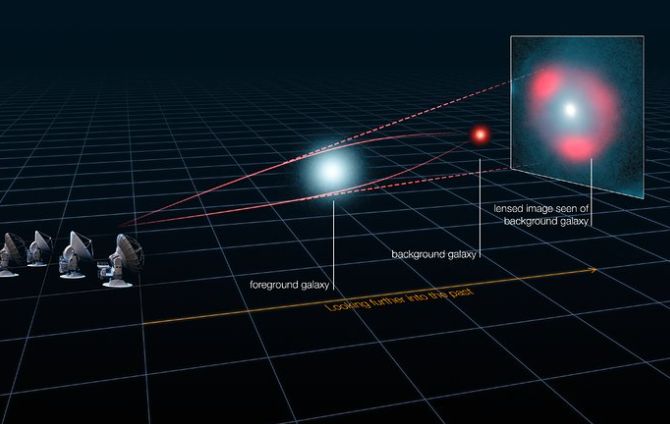
Here are some of the key early universe structures JWST discovered in 2024:
- Proto-Globular Star Clusters: JWST spotted five incredibly dense proto-globular clusters in the Cosmic Gems arch, a galaxy which was formed around 460 million years post the Big Bang effect. These clusters are held together by gravity and are packed with millions of stars. Their density is three times more than the young star clusters in the local universe, which means, they could possibly be a remnant of an older system. Since, these clusters were the first discovery of JWST, so they are like stepping stones for astronomers to understand how the first stars were formed in early galaxy. The Cosmic Gems arc is magnified by gravitational lensing to observe in detail the smaller structures it contains.
- The Cosmic Gems arc: This is the galaxy, where the five super dense proto-globular clusters were discovered. The galaxy is also termed as SPT0615-JD. This cosmic island is the most zoomed-in area we’ve been able to observe from the first 500 million years of our universe.
- Early Galaxies: Data gathered by JWST suggests that there are more massive galaxies in the early universe than we had previously expected. This also means that star systems were formed quickly and profusely during the early formation of the universe. Galaxies from far flung regions have generally, flattened oval disk and tube-like shapes, rather than the spiral or elliptical shapes we typically think of as ‘default’. It is maybe because of their evolving nature. Mature or stable galaxies have well-defined spiral and elliptical structures.
- Filament of the Cosmic Web: TheJWST also tracked an interesting body of gaseous tendril, which is made up of 10 galaxies packed tightly together, stretching across 3 million light years. As per the data, researchers concluded that the structures could be formed when the universe was just 830 million years old. This also happens to be one of the earliest strands of our observable universe.
- Reionization Era: JWST surfaced that many galaxies emitting extreme ultraviolet light than expected, they termed it the Reionization Era. This idea too challenged the established models and has led to a need for further exploration and adjustments to our understanding of this pivotal period in the universe’s development.
These relics from the past are providing us with hints about how the early galaxies were formed and how it changed from being neutral to ionized during the Epoch of Reionization. JWST is one of the most remarkable tools created by humanity as it is helping the astronomers to re-create and understand distant galaxies from structural point of view. Along with getting insights into the conditions that could have prevailed in the early universe.
Takeaway
These discoveries highlight that when it comes to understanding the universe, we, as humanity, are just beginning to scratch the surface. The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) will help us in levelling up our knowledge of space and time. This makes me think, how will uncovering the origins of galaxies and stars transform our understanding of life and humanity’s place in the cosmos?



[…] And with its ability to operate in ultraviolet wavelengths, AeSI would complement missions like the James Webb Space Telescope, filling in gaps in our understanding of the […]
[…] it might have a hydrogen-rich atmosphere and liquid water oceans. This study is based on data from JWST’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument), and it’s the first time we’ve gotten a mid-infrared […]
[…] of black holes have always been a mystery to astrophysicists. Now, observations from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) may offer a radical new answer to the existence of “dark […]