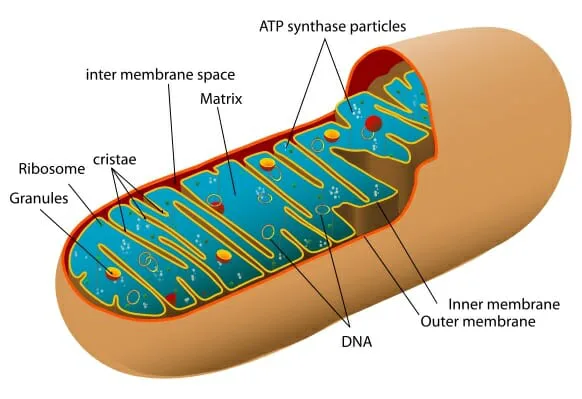
Researchers at the University of Cologne (UoC) have achieved a groundbreaking milestone by creating artificial nucleotides. Nucleotides forms the building blocks of DNA. So, if we go by the research, the innovative development will make way for potential advancements in genetic engineering as well as molecular biology.
Read MoreTag: biotechnology
Evolution of Life’s Molecular Systems: Insights into the Rise of Nanomachines
Researchers at Université de Montréal (UdeM) have made a significant discovery regarding the evolution of molecular systems crucial to the development of life. Through the linking of molecules, they have uncovered insights into the emergence of intricate self-regulating mechanisms. Alexis Vallée-Bélisle, a professor at UdeM and the lead researcher of the investigation, explained that life’s sustenance on our planet stems from myriad nanostructures. These nanomachines have undergone evolution over countless years.
Read MoreBiofilm Microstructure Could Enhance Pathogenic Infection Control: Microbial Ecology
Generally, bacteria are envisioned as tiny, single-cell organisms scattered thinly on surfaces or floating in liquids. However, in various settings, bacteria prefer to grow in clusters known as biofilms. The formation of biofilms provides certain advantages to bacteria. In these clusters, bacteria can collaborate and create a protective environment that enhances their survival and growth. Biofilms, while aiding in kombucha tea production, present a challenge by complicating the control of bacterial growth. When bacteria form a biofilm, it acts like a protective shield, making the cells resistant to antibiotics.
Read MoreMitochondrial Energy Crisis: Unraveling the Alzheimer’s Puzzle
Brain cells crave immense energy to survive and communicate through connections known as synapses. These cells are like energy enthusiasts, which are busy in making way through synapses. But, in the Alzheimer’s scenario, it’s like they’re facing an energy crisis. This messes up their power production. And so, it leads to crumbling down of the synapses and consequently, our fresh memories slowly slip away.
Read MoreGut Defense: Microbiome Blocks Pathogens’ Nutrient Access
Deep within our stomach, a lively neighborhood thrives. The community is known as the gut microbiome. It is housing hundreds of bacterial species. The fascinating world of the gut microbiome steps up to shield us from nasty invaders called pathogens. Details of its protective powers have been a bit fuzzy until now. Scientists have been tackling and exploring which bacterial players hold the secret to its protective magic.
Read MorePPAP53: A Game-Changer in Tuberculosis Treatment
Recently, Prof. Bernd Plietker and his team at the Organic Chemistry I lab, TUD, came up with this group of natural substances called polyprenylated polycyclic acylphloroglucinols, or simply PPAP. The interesting part is its derivative called PPAP53. Since, it has got some serious potential in the world of medicinal chemistry.
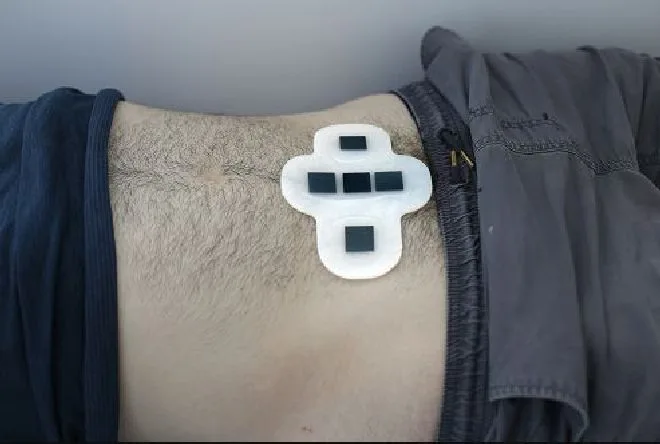
Read MoreWearable Ultrasound Patch for Real-Time Monitoring
Researchers at MIT have developed a wearable ultrasound patch that images organs without requiring an operator or gel. The team has successfully demonstrated that the patch can, not only accurately images, but it can also gauge the fullness of the bladder. This innovation has the potential to assist patients with bladder or kidney disorders. As it can monitor their organ function with greater convenience.
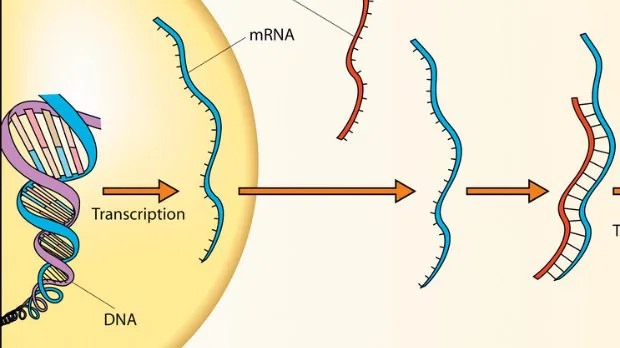
Read MoreLNP Formulation: To Transform Production of mRNA Therapeutics
The mRNA vaccines were made within no time during the second year of the COVID-19 pandemic. Thus, highlighting the importance of tiny fat particles or the lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) in medicine. LNPs are like special cars for delicate RNA treatments and vaccines. They not only shield the RNA (from degradation), but they also make sure it gets to its targeted location.
Read MoreDecoding the Immune System’s GPS: How Cells Find Their Way Through Molecular Mazes
Immune system’s ability to distinguish between infections and inflammation is pretty much fascinating. The combination of mechanisms and signals is quite intrigue. And scientists feel there is much to explore. This clearly shows how sophisticated our body’s defense mechanisms are. Our immune system has been protecting us from a wide range of threats. And yet at the same time evolving over a span of millions of years.
Read MoreCoordinated Gene Expression in Tumor Microenvironment: Cancer Research
Researchers at the Ludwig Cancer Research have surfaced a remarkable discovery in the realm of cancer research. They have identified a specific duo of genes which are involved in shaping the behavior of a particular type of immune cell within tumors. Like a hidden code, the duo genes guide these cells in during the progression of cancer.
Read MoreInterview: Dr. Jay T. Lennon, Microbiologist at Indiana University, Bloomington
Meet Dr. Jay T. Lennon. Within the intricate tapestry of microbiology, a realm of microorganisms thrives, weaving the intricate threads of ecosystems, interactions, and even human health. Dr. Lennon, a distinguished luminary in the field of microbial ecology, has passionately dedicated his career to unraveling the enigmatic world of these microscopic life forms. He emerges as an insightful figure who delves deep into the intricate relationships governing microbial communities.
Read MoreBook Review: The Epigenetics Revolution by Nessa Carey
Let’s step into the captivating world of epigenetics. It is a rapidly evolving science rarely explored beyond scientific literature. Very deftly, Dr. Nessa Carey has connected academia and scientific journalism into her groundbreaking book “The Epigenetics Revolution: How Modern Biology Is Rewriting Our Understanding of Genetics, Disease, and Inheritance”. The book was first published in 2012.
Read MoreInterview: Dr. Monica Dus, Nutrigenomics Scientist at University of Michigan, United States
Meet Dr. Monica Dus, an extraordinary trailblazer in the field of biology whose passion for unravelling the mysteries of our genetic makeup and its interaction with nutrition has earned her widespread recognition. As an Associate Professor with Tenure at the prestigious University of Michigan, she stands at the forefront of cutting-edge research in Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology. Beyond academia, Dr. Dus is a 2023 Guggenheim Fellow in Biology, a distinction that further underscores her outstanding contributions to the scientific community.
Read MoreLactate Enriches Neurogenesis: Neuronal Differentiation
Scientists at Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan made an exciting discovery regarding cellular mechanisms that assist in developing our brains. They discovered that lactate plays an important role in helping neural stem cells become specialized neurons. Lactate happens to be the by-product of exercise and metabolism. Researchers even gave this process a fancy name: neuronal differentiation.
Read MoreMolecular Biology of Insulin: Decoding its Secrets via Fruit Fly Discoveries
As the scientific revelation unfolded, the discovery of insulin became the life-saving elixir to people who were suffering from diabetes, globally. Although, terms like high sugar, glucose, insulin, diabetes, glycaemic index etc are very well known to most of the masses. Yet, the first step of insulin synthesis, has been a tantalizing secret, which is yet to be unravelled even by the researchers. In a similar quest, scientists at the University of Michigan observed the tiny world of fruit flies. They studied how insulin is made in fruit flies by…
Read More