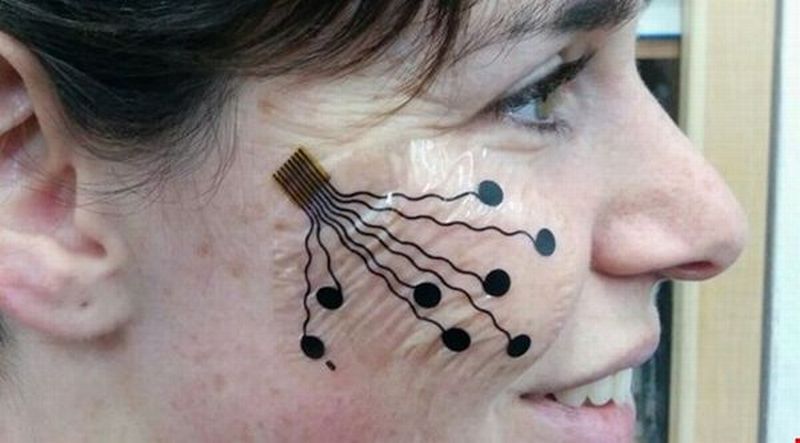
Scientists at Tel Aviv University (TAU) have fabricated an electronic tattoo that has the potential of recording muscle movements by mapping facial expressions.
Read MoreTag: biotechnology
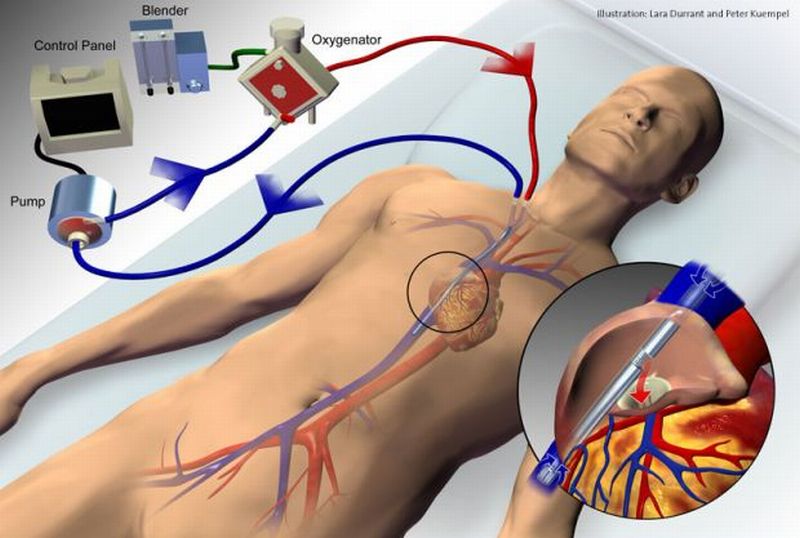
Microfluidic device that mimics the actual Biological System: Alternative to Lung Ventilators
Technology that would help in fabricating vital characteristics of lung structures would lead to safer and promising alternative to specific types of respiratory and cardiac machines used for treating patients whose lungs have failed to respond due to disease or injury.
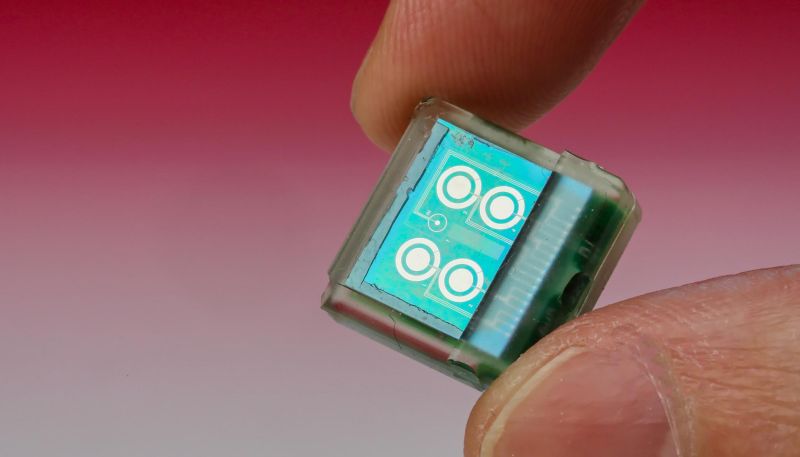
Read MoreBiosensing Chip for Remote Monitoring of Human Metabolism: Implantable Biomedical Device
Researchers at Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne (EPFL) Lausanne, Switzerland have developed a centimeter long biosensor chip that lays hidden under a patch of human skin and is communicated via smartphone. The chip tracks the concentration of molecules quantity like glucose, cholesterol and other drugs.
Read MoreIndividual Cell investigated at Bigger Scale: Single-Cell Genomics
There is still no evidence that suggests the exact number of cells present in human body. Although we can interpret them to be somewhere around hundreds of thousands but the figure is much more than that.
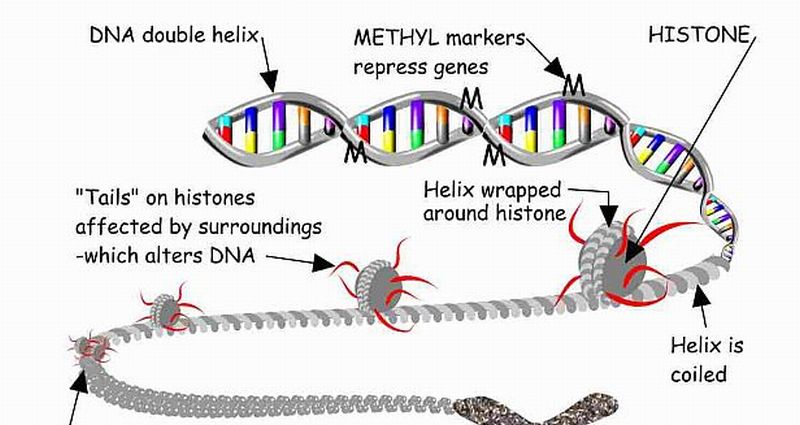
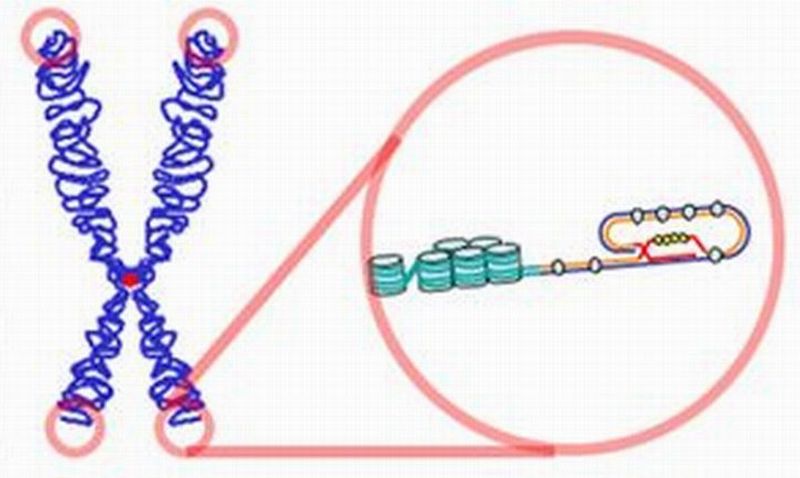
Read MoreInheritance of Characteristics are not decided only by DNA: Gene Regulation
It has always been believed that DNA is the storehouse of characteristics that pass-on from one generation to the next. However, there are other materials in a cell as well that can be attributed to passing on the hereditary traits, claimed a set of researchers at University of Edinburgh.
Read MoreHomo chippiens: Mimicking Human Body using networks of Simulated Organs
In an attempt to create a ‘body on a chip’, scientists are working towards fabricating minute working organs of human body on a set of inter-related plastic chips. They have already developed fingertip-sized lungs, guts and livers on the chips. For instance, researchers at Harvard University’s Wyss Institute are revamping ‘bone marrow on a chip’ for studying the effect of radiation.
Read MoreRevering Aging Clock at Cellular Level: Extending the Telomeres
In an interesting research in the field of microbiology, experts at the University of Stanford have tried to explore the process that might lead to eternal youth by maneuvering the key that is responsible for making human cells old.
Read MoreNanoparticle Compound delivered directly into the Gut Tissue: Self-propelling Nanobots
Experts believe that micromachines or nanobots use in the field of medicine can change the way some of the medical conditions are diagnosed and treated. Using these nanobots, medical payload would be sent directly to the specific injury site. Until now the researchers have achieved to test such micromachines in cell samples under laboratory conditions.
Read MoreSilicon Chip that mimics Nature’s Gene: A Step towards Artificial Cells
Researchers at the Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel have come up with a silicon chip that can mimic a human cell in producing proteins from DNA. The most basic function of cell is to produce proteins after receiving instructions in the form of DNA sequences. Other genes determine production of the quantity of churning out protein by a complex process involving feedback loops.
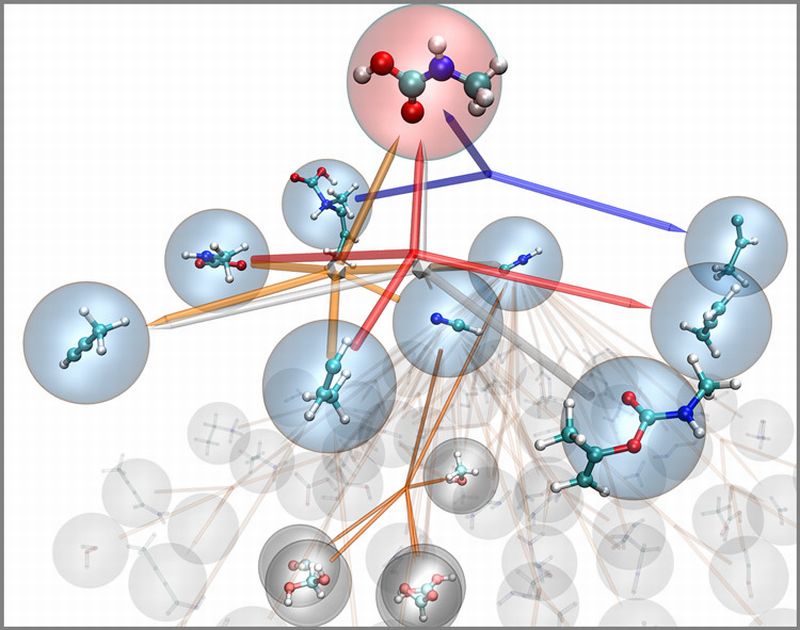
Read MoreNanoreactor developed for Discovering New Chemical Reactions: Virtual Chemistry Set
In order to replicate ecosystem and chemical origin of life, Stanley Miller, under the supervision of Harold Urey, performed the breakthrough Urey-Miller experiment in 1952. The experiment initiated more than 20 major molecules that form the integral part of life. A team of researchers at Stanford believes that they can do one-step better.
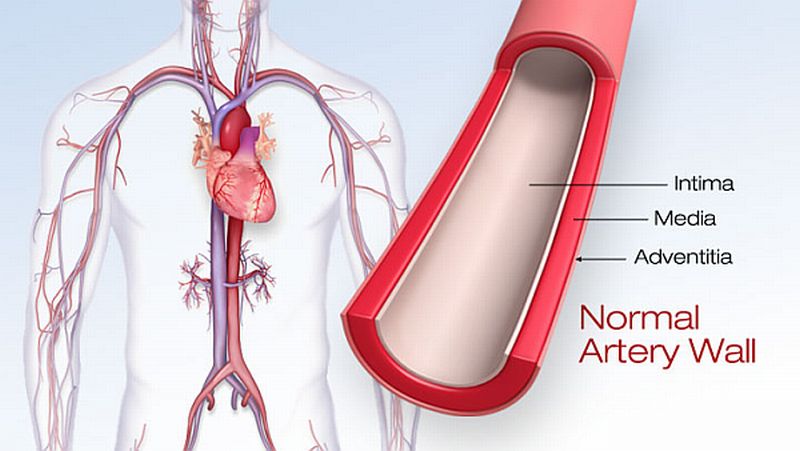
Read MoreHeart Disease starts from Stomach: Red Meat hardens the Arteries
Though red meat is one of the richest source of a powerful antioxidant called, lipoic acid, apart from harboring other essentials like iron, creatine, minerals and vitamins, findings from various studies suggest that red meat consumption is linked to significant health risks such as an increased chance of developing cardiovascular disease and even bowel cancer.
Read MoreMagnetic Nanoparticle Pill will detect Cancer: Searching Bloodstream with Google
Giant web search engine, Google is expanding its business in different technological areas, investing in research program to develop driver-less cars, goggle glasses, contact lenses, delivery drones, robots, providing internet facilities via balloons to name a few. Now Google is expanding into the field of advance medicine. With an aim of developing nanoparticles that would be delivered in the form of a pill in aiding cancer detection and other ailments, the big G unveiled its latest project called the “Nanoparticle Platform.
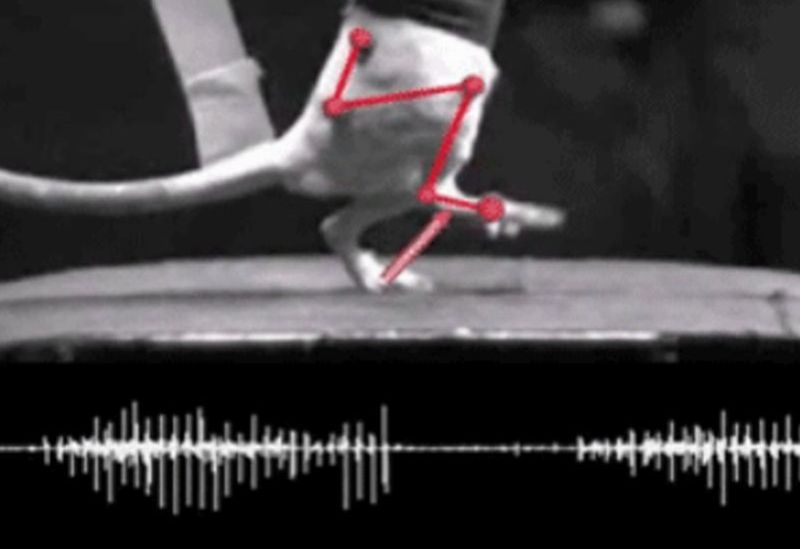
Read MoreElectrical Pulses used to reinstate Movements in Paralyzed Rats: Epidural Stimulation
In Frankenstein effort, Gregoire Courtine, a researcher at the École Polytechnique Fédérale in Lausanne, Switzerland, has developed a process that has helped a paralyzed rat in walking with a precise cadence. The neuroscientist has employed electronics to reinstate realistic movements to the disabled animal. With an aim of resurrecting life in the paralyzed limbs of people, the researcher has zapped spinal cords with electrical pulses. These undulations will substitute the commands being sent by brain in normal condition however, the signals are disrupted with an injury in the spinal cord.
Read MoreOn/off Switch for Aging Cells Discovered: Telomere Homeostasis
Newly divided cells of the human body have an ability of replenishing certain organs including lungs, skin and liver consistently. However, majority of these cells have an expiry date, which means, they cannot perform the function throughout, since each division also corresponds to shortening of chromosomes. Upon reaching a certain stage telomere, the area of repetitive nucleotide sequences situated at the peripheral of each chromatid, stops the dividing process. This leads to degeneration of organs and tissues and eventually aging. However, in the presence of telomerase, an enzyme that rebuilds…
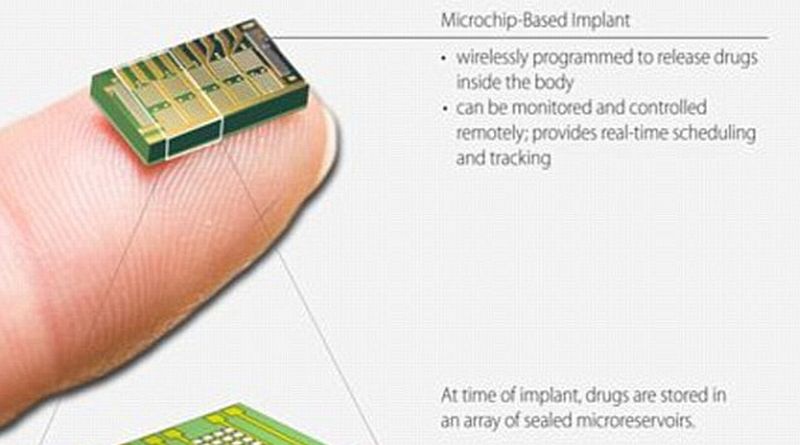
Read MoreContraceptive Implant with Remote Control: Women Conceiving with a Push of Button
Last month we witnessed MagnetoSperm microrobots for the nanoworld and now research scholars at MIT lab have devised a technology oriented birth control drug delivery system, which can be controlled from the outside. The 20 x 20 x 7 millimeters devise is supposed to be implanted inside the skin somewhere around buttocks, abdomen or upper arm. The mechanism Single implant will last for about 16 years with 30mg of levonorgestrel doling out per day. Levonorgestrel is the same hormone that is used in most of the over the counter contraceptives.…
Read More