There’s a scene in Interstellar that I always think of, which goes like this… the crew is aboard the Endurance, orbiting Miller’s planet. They know that every hour on the surface equals seven years back on Earth, but they go anyway, because the mission demands it.
Read MoreTag: concepts
When Light Starts To Think: A Journey Into Optical Computing
If I ask you, what scene in The Matrix that’s always stuck with you, I’m sure most of us would say, the bullet-dodging or the red pill. But for me it’s when Morpheus tells Neo that what he thinks is real is actually just electrical signals interpreted by his brain.
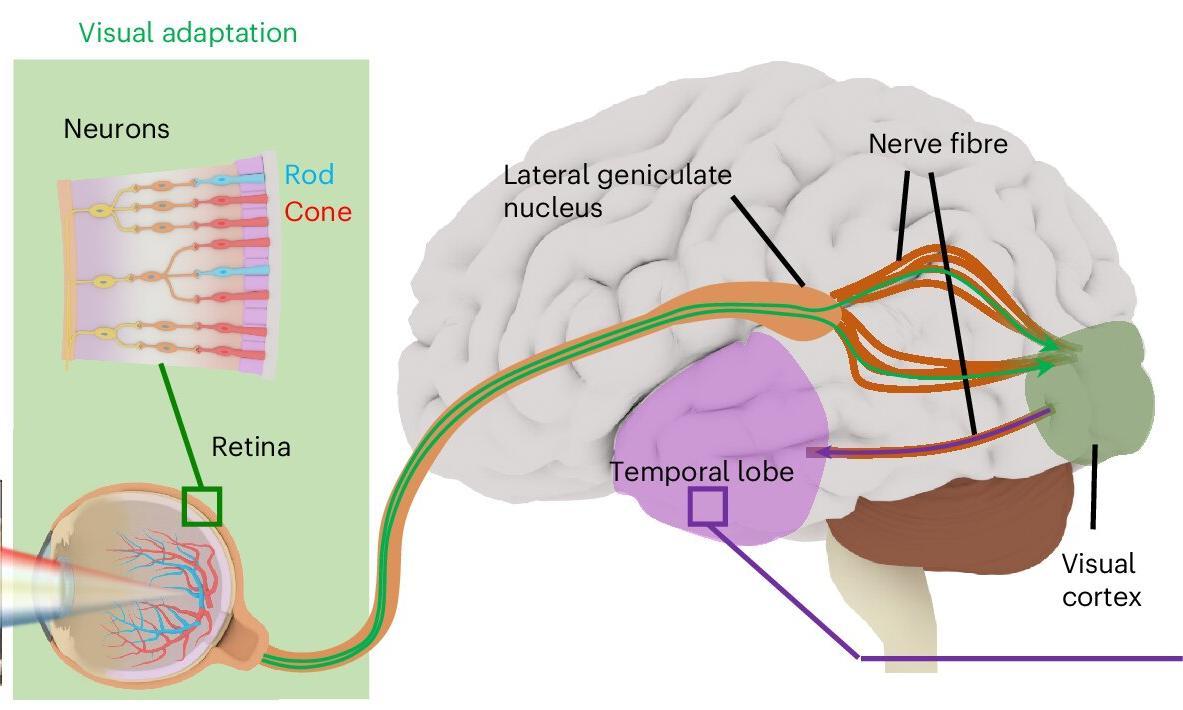
Read MoreArtificial Neurons That Learn Like the Brain: The DRAM–MoS₂ Breakthrough
I came across some research from Fudan University recently that really caught my attention – Artificial neuron merges DRAM with MoS₂. As the headline suggests, they’ve built an artificial neuron that doesn’t just copy the way brain cells connect to each other, but also how they adjust their own internal behavior.
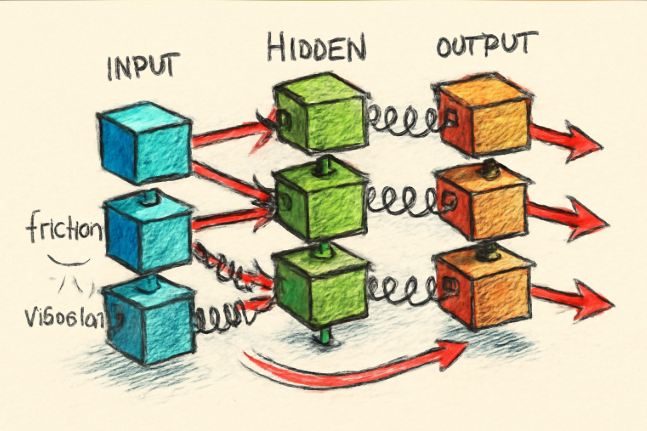
Read MoreSpring-Block Model: A Mechanical Analogy for How Deep Neural Networks Learn and Separate Data
I’ve been thinking a lot about how deep neural networks actually learn. I mean, those complex stacks of layers, how do they figure out the mechanics to recognize images or understand speech? These layers must be working together to make sense of raw data, but how?
Read MoreMeasuring Convexity in AI: Linking Machine Learning to Human Concept Understanding
Researchers at Technical University of Denmark have found an interesting connection between how humans learn and how computers learn. It talks about a special shape in math called convexity. This shape might help us understand how our brains and computer programs figure out ideas and understand things around us.
Read MoreGravity’s Secret: Order, Chaos, and Quantum Bits
Isaac Newton figured out how gravity behaves way back in the 1600s. He could describe what it did, how apples fall, how planets move, but he didn’t really know why it worked. Even he wasn’t totally satisfied with it. One of his ideas was that maybe invisible particles were pushing things together from all directions. That didn’t hold up, but the question remained, how does gravity actually happen?
Read MoreBreakthrough in Nonreciprocal Light Speed Manipulation via Cavity Magnonics
Imagine you’re standing on a road where cars drive in both directions. Generally, the speed limit is the same whether you’re heading north or south. That’s exactly how light usually works in most systems, the “speed limit” stays the same no matter which way it’s going. This is called reciprocal control, the system treats both directions equally.
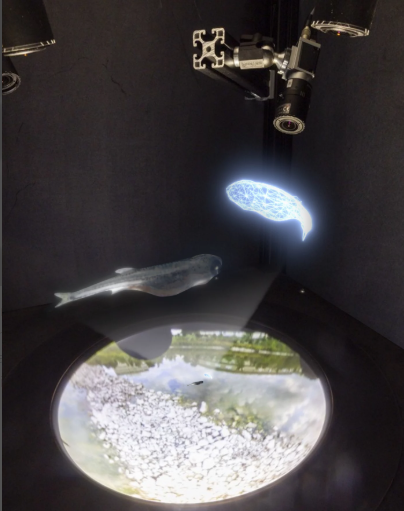
Read MoreScientists Use VR to Teach Robots Swarming Behavior by Studying Fish
A team of biologists and robotic engineers recently used virtual reality (VR) to crack the code of how fish school, with the goal of teaching robots to swarm in the same way. Imagine you’re at a party where everyone’s dancing to the same rhythm, but there’s no DJ or leader telling people what to do. Everyone just knows how to stay in sync, avoid bumping into each other, and respond to changes in the crowd. That’s basically what schools of fish do, and it’s something that robots have struggled to…
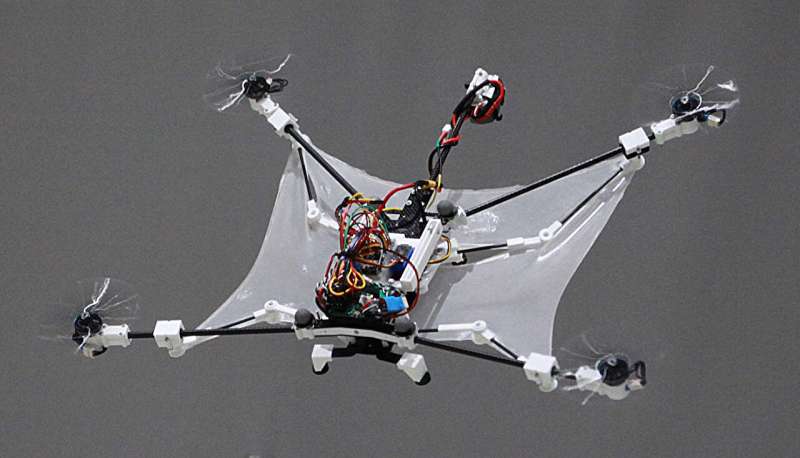
Read MoreBiomimicry: Squirrel Drone with Foldable Wings Shows Superior Maneuverability
Drones that we see today are very well equipped with focusing systems that allow for high-resolution imaging, precise navigation, and advanced object tracking capabilities. However, when it comes to executing sharp turns, a key limitation of today’s drones, the tech is still in its early stages of development.
Read MoreSmaller Than a Grain of Rice, This Pacemaker Runs on Light
Northwestern engineers have come up with something pretty wild, a pacemaker so small it can fit inside the tip of a syringe. Not only that, but it’s wireless, dissolves inside the body after doing its job, and can be injected without surgery.
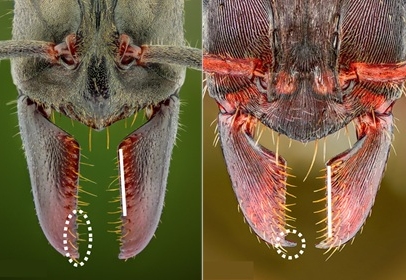
Read MoreAntGrip: Enhancing Gripper Performance with Ant-Inspired Hairs
Whenever I find myself really fascinated by biomimicry, I often discover new things inspired by it. This time, it’s a robotic hand that takes ideas from how ants work. Imagine you’re picking up a slippery soda can with a simple two-finger robot gripper. No suction cups, no fancy sensors, just friction. Sounds tricky, right? That’s exactly the kind of challenge researchers tackled by taking inspiration from “ants”.
Read MoreCracking the Mystery of Strange Metals with Quantum Entanglement
Quantum criticality in metals is an exciting area of study where physics explores mysterious concepts. A new study in Nature Communications looks at a unique way to understand entanglement at a specific point called the Kondo destruction quantum critical point (QCP). Instead of using standard methods, the researchers focus on concepts like mutual information and quantum Fisher information (QFI) to explore how quantum connections change as they get closer to this transition.
Read MoreULVAC and IBM Quantum Team Up to Revolutionize Quantum Computing Cooling
Quantum computing is one of the most promising technological frontiers, but it comes with a major challenge, which is, maintaining the extreme cold temperatures that is required for qubits to function. Today’s quantum computers rely on dilution refrigerators, complex and highly specialized cooling systems that keep qubits operating near absolute zero. However, these systems are expensive, tough to maintain and don’t scale easily.
Read MoreHigh-Performance 2D Semiconductor Transistor Fabrication: h-BN Dielectrics and Metal Gate Tech
Two-dimensional (2D) semiconductors hold enormous potential to transform the future of electronics. However, their full potential is hindered by a major challenge: interface defects that form between the semiconductors and insulating layers, which degrade overall performance.
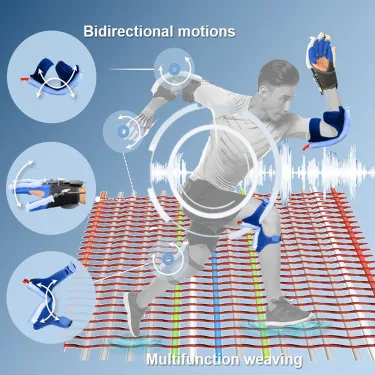
Read MoreYarn-Based Weaving for Soft Robotics: Revolutionizing Healthcare
Globally, electronics engineers are busy developing devices that are flexible, adaptable, and built for high performance. These devices are designed for real-world applications, including – robotics, healthcare and wearable technology. Similar efforts are underway in developing smart textiles as well. Interestingly, these fabrics can detect environmental changes or perform specific functions.
Read More