Till now, we have known, humans and animals (including insects) have survival instincts. Its not just grit, its instinct. Sometime or the other, in our lives, we have experienced it too. But ever heard of plants displaying this survival strategy?
Read MoreTag: ecology
Queen Bee’s Tooting Initiates Swarming: Preserving Biodiversity
It has been widely known for some time that queen bees make use of acoustical signals for communication amongst themselves. Now researchers have discovered an assortment of behavioural cues and other social signals that goes on within the waxy walls.
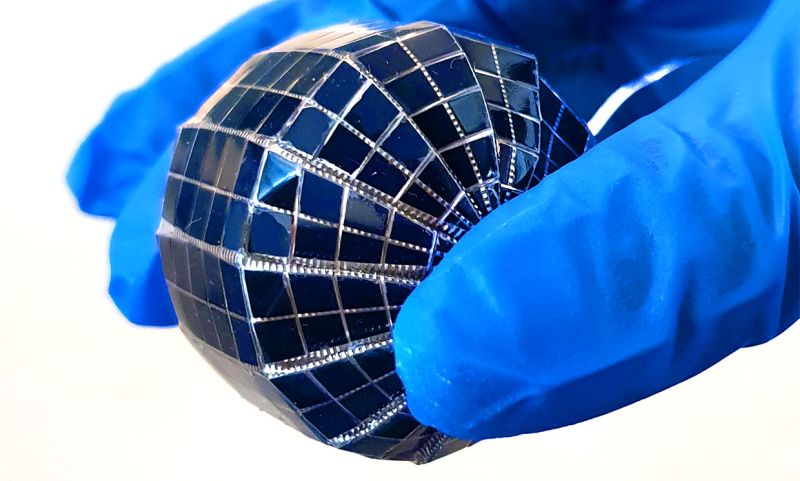
Read MoreSpherical Solar Cells Boost Up Solar Energy Harvesting
Flat solar panels dominate the world market when it comes to capture solar energy directly from the Sun. However, the flat design has a major limitation as it cannot keep track of sun’s apparent motion.
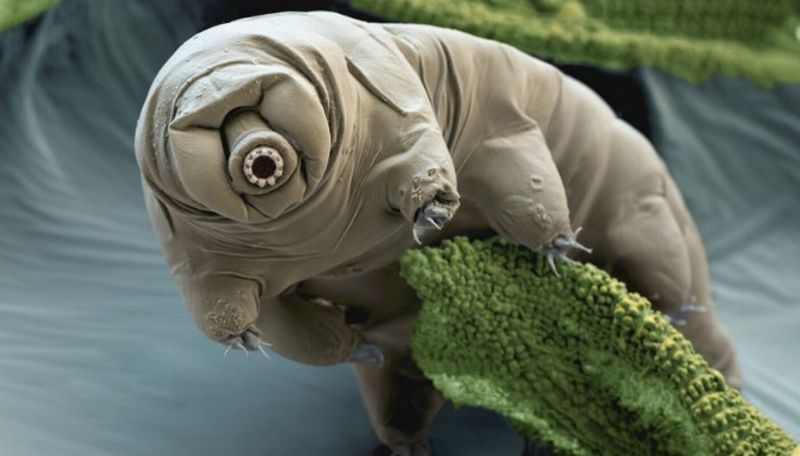
Read MoreProtective Protein Guarding DNA Makes Tardigrades Indestructible: An Offbeat Genetic Constitution
Tardigrades are water dwelling, eight legged microscopic organisms, also known as the water bears, are one of the most resilient organism (extremophile) known to survive in the most inhospitable conditions on earth and even in the space. They are found to thrive in extremely low temperature (as just above the absolute zero), in high temperatures (i.e above the boiling point of water), high pressure and can even withstand high radiation.
Read MoreMale Widow Spiders Inseminate Young Females And Avoid Being Cannibalized: Spidery Sex Life
Sexual cannibalism is very common in some species like the male coin spiders. Black widow and Redback female spiders are famous for slaying their partners soon after mating. The male widow spiders that are considerably smaller in size, are often seen voluntarily offering themselves to be eaten, with a hope that the female will give birth to his offspring. Sometimes, the males reaching out females are mistaken for prey and are killed even before copulation occurs.
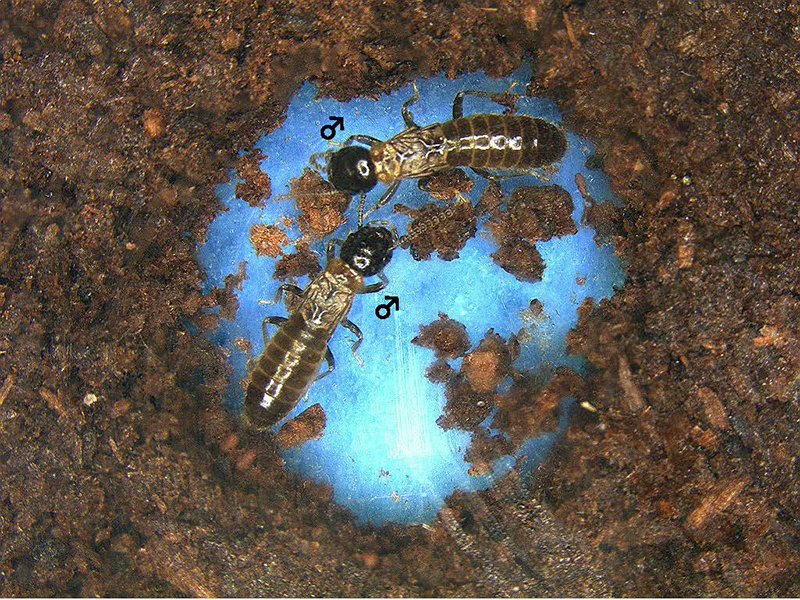
Read MoreEvolutionary Edge for Male-Male Pairing: Homosexual Termite
According to a latest research conducted at Kyoto University, lone male termites that do not happen to find a female mate often end up forming homosexual pair. Such pairing gives male Japanese termites better chances of survival. Just like a couple they are seen making nests and sharing resources.
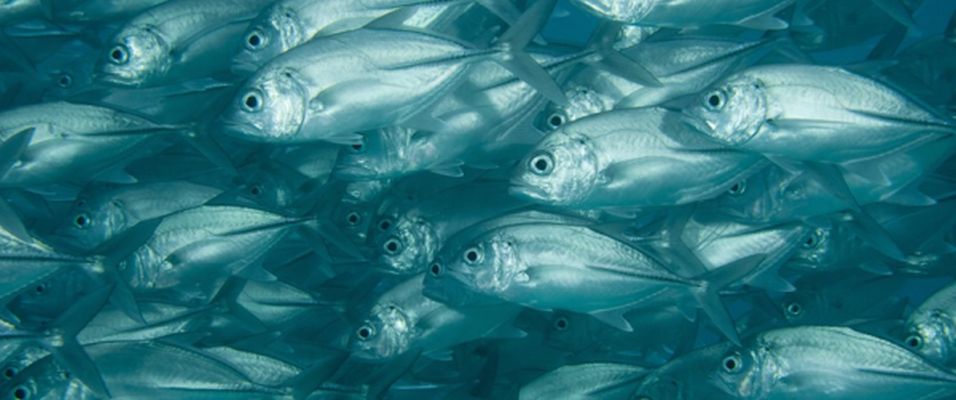
Read MorePolarized Vision does not Beat Camouflage: Marine Visual Detection Model
Animal camouflage is a very common technique. And when it comes to an open sea, things ought to look slightly difficult. However, for fishes like herring, mackerel, and sardines this is not the case. These fishes have a smart camouflage technique, the shimmering silver scales, that can even beat the super sight.
Read MoreWhisker System Reveals How Neurons Communicate Touch: Sensing Mechanism
Sense of touch helps us in distinguishing things in regions where sense of sight or our eyes can’t go, let’s say in purse or pocket. If we are to fetch keys from loose change in our pockets, without giving it a second thought, we take out the required thing, this happens due to sensorimotor integration.
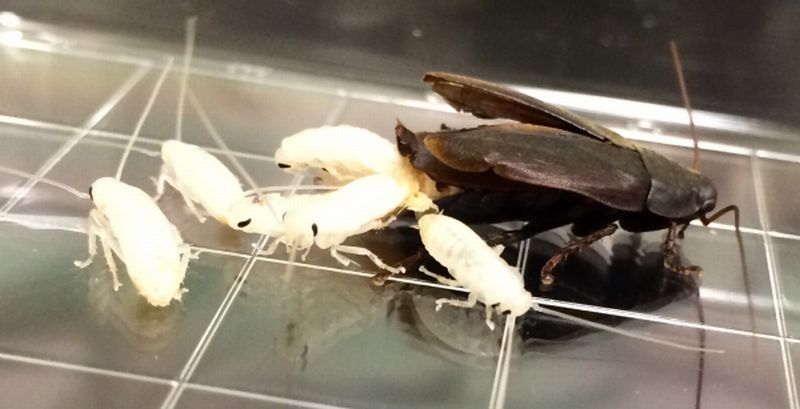
Read MoreCockroach Milk An Ideal Protein Supplement: The Superfood Of The Future
Humans do not welcome cockroaches. Their existence is often questionable and creepy especially to women folk. But what if you are told that the milk produced by the cockroaches are going to be the next super food of tomorrow. Bizarre!
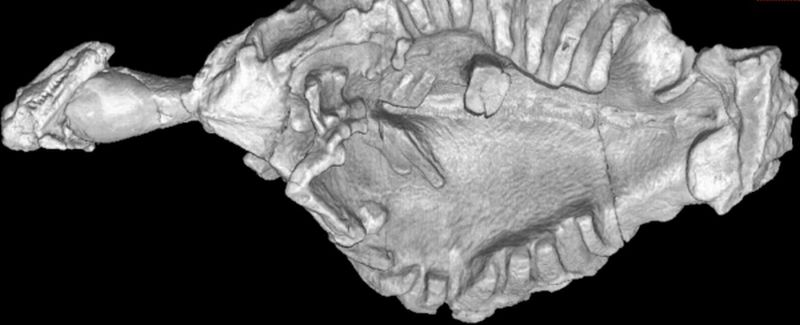
Read MoreDigging Adaptations Facilitated Shell in Turtles: Study on Eunotosaurusafricanus
Turtle shell, conventionally, is considered an outer covering for protection and lodging for the animal. Till date, turtle is the only living vertebrate with such a sturdy broad ribbed proto shell. However, recent study of fossil turtles, which happen to be around 260- million-year-old, has revealed that the hard and rigid protective structure of the animal is not adapted for protection rather for digging underground. Dr. Lyson, the scientist behind this discovery said that during the early (evolutionary) phase, birds’ feathers too were not employed for flying. Nevertheless, birds starting…
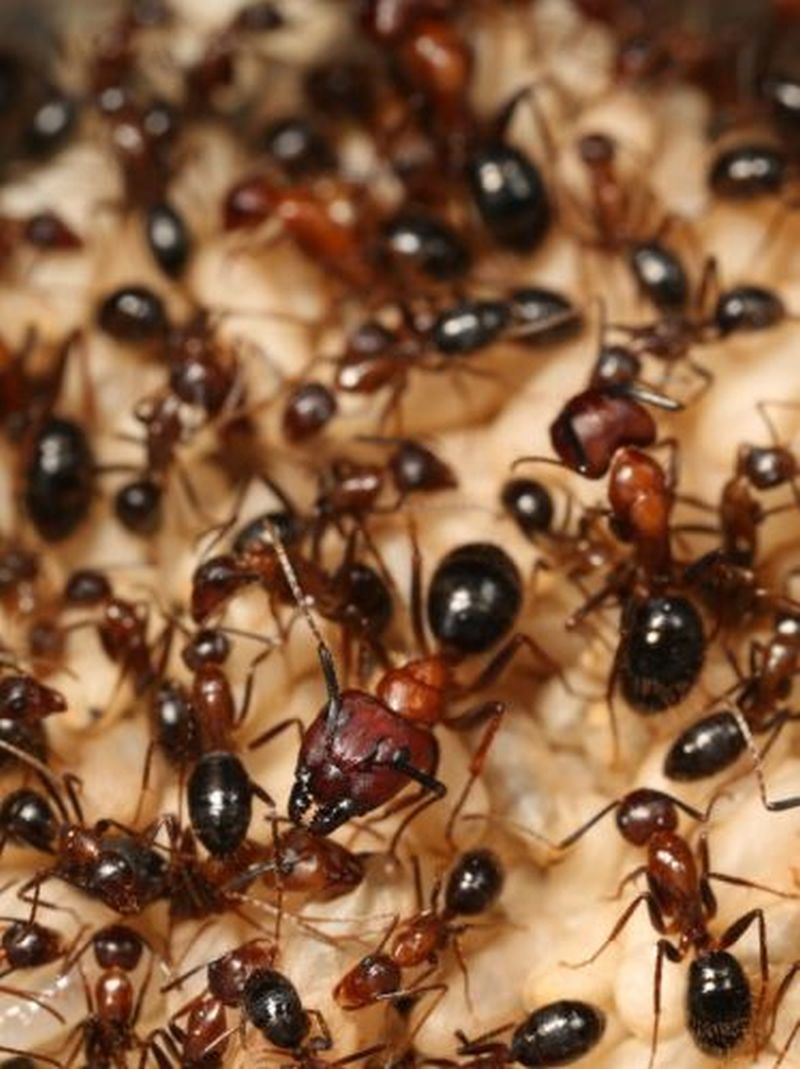
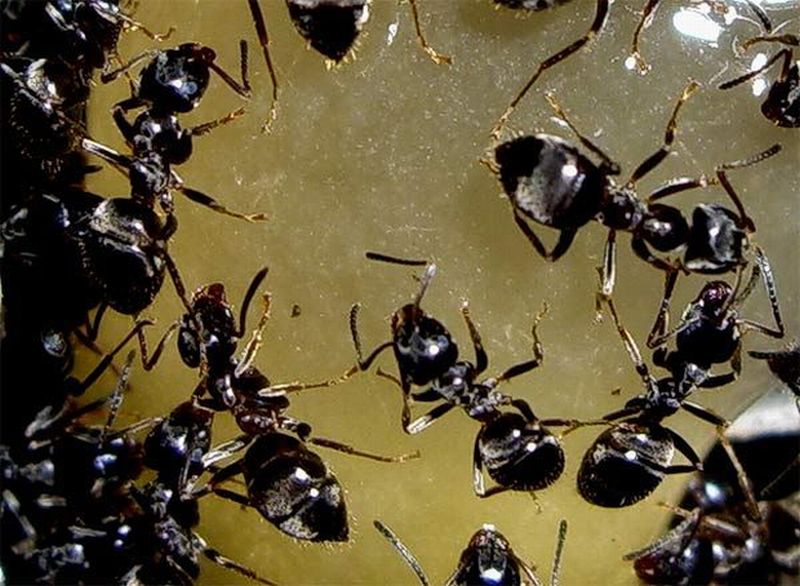
Read MoreAdvanced sense of odor helps ants identify individual ants: Nestmate versus Non-nestmate
Scientists studying ants have always wondered how ants living in huge colonies, identify other ants belong to same colony or is an intruder or enemy ant. Researchers from The University of California, Riverside have found an answer to this question. They have found that ants communicate via diverse hydrocarbon chemicals present on the their outer shells (or cuticles).
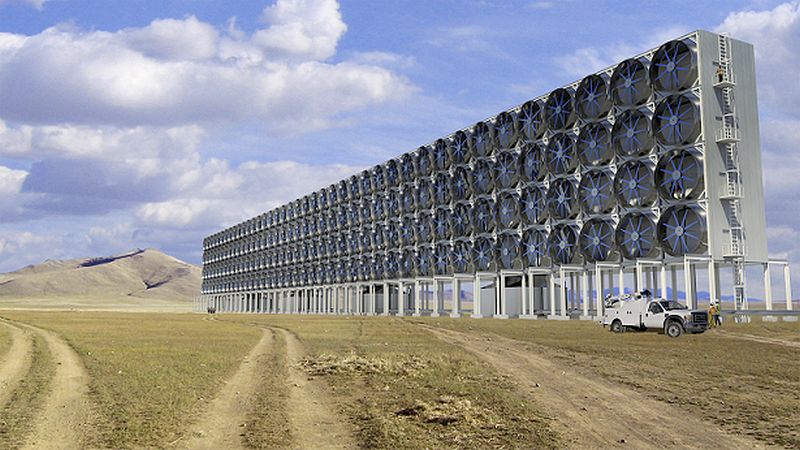
Read MoreAir Capture Technology to Trap CO2: Carbon Engineering’s Initiative for Green Earth
A Canadian company known as Carbon Engineering (CE) has designed an innovative technology to capture atmospheric carbon dioxide and utilizing the captured carbon dioxide for the generation of ultra low carbon intensity liquid fuels.
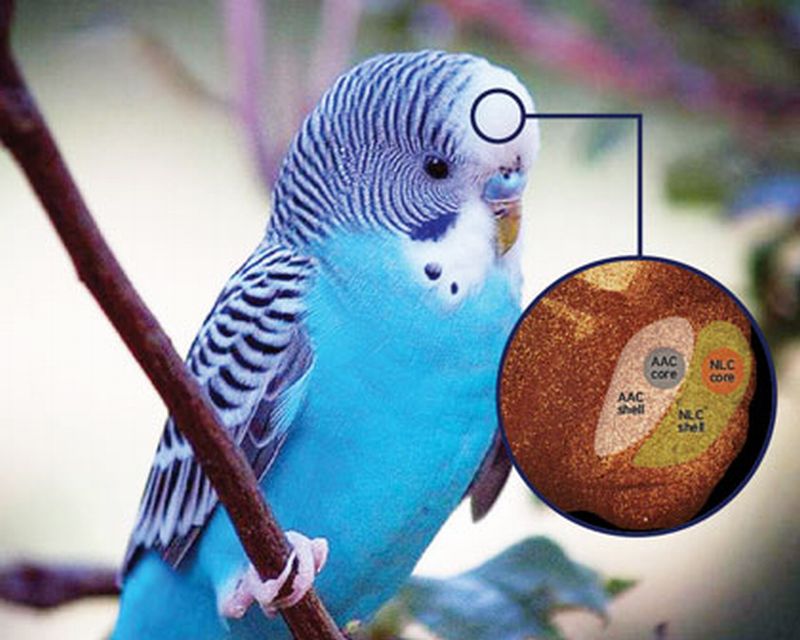
Read MoreKey Structural Differences in Brain leads to Vocal Imitation in Parrots: The Talking Birds
Researchers from Duke University, North Carolina have revealed the presence of key structural differences in the brain of parrots that leads them to ‘talk’ than the other birds. The discovery might also give some understanding into the neural mechanisms especially the neural circuits of human speech.
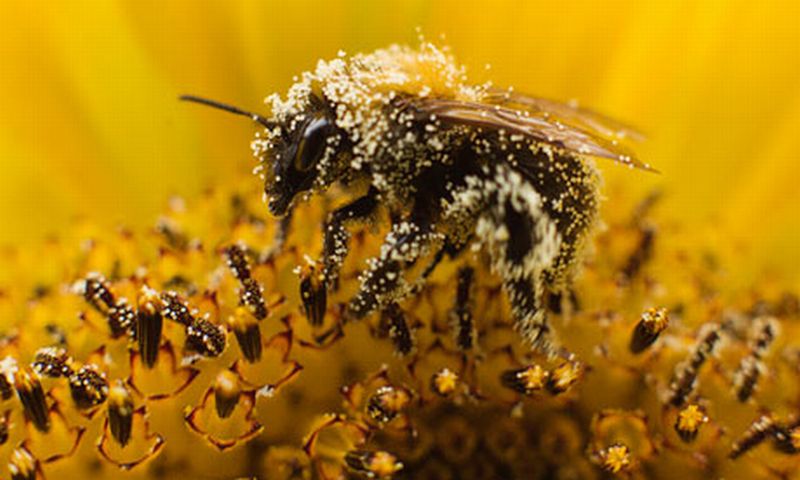
Read MoreBees prefer Pesticides ridden Nectar: Insect Pollinators
Pesticides are used across the world to kill pests that cause damage to the food that would be consumed by humans. This implies that the effect of pesticides should repel insects but in some cases, it is not so. Researchers at Newcastle University and Trinity College Dublin have discovered that certain species of bees are fascinated towards nectars that contain pesticides in them. Neonicotinoid-laced food chosen by bees Prior studies have proposed that bees would have to face negative consequences in terms of health in case the specie is exposed…
Read MoreCleaning Behavior affects Disease Spread: Hygienic Interaction Networks within Ant Colonies
Taking care of infected individual not only happens in human societies but in animal kingdom as well. The phenomenon is seen in insects and social animals, like ants and meerkats.
Read More