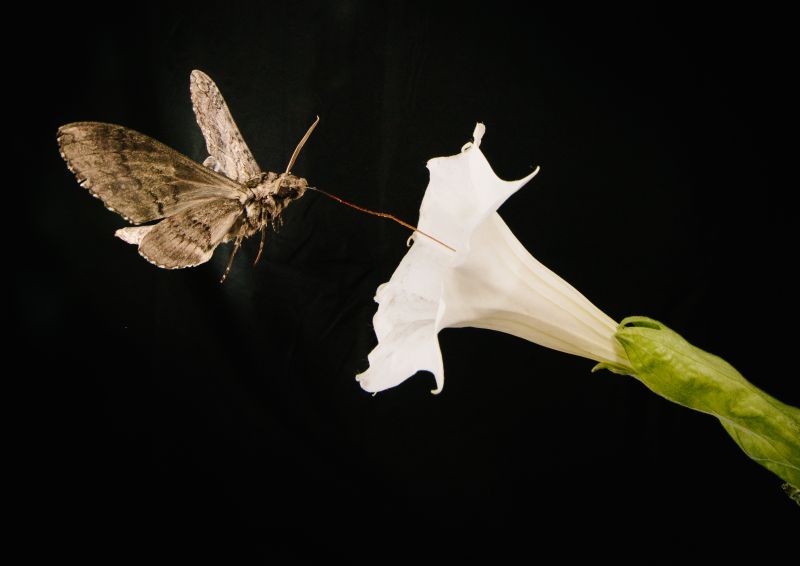
According to a latest research, pollution and other odors causes hindrance for insects in search of flowers to feed on. In a joint study, researchers from the University of Arizona and University of Washington studied tobacco hornworm moths (Manduca sexta) while they searched and interacted with flowers. The moth likes to feed on nectar from the plants like the Sacred Datura, which usually are seen growing hundreds of meters apart. Therefore, the moth uses its sense of smell to locate flowers. Researchers observed that the moth could locate the scent…
Read MoreTag: ecology
Recycling Plastic into Oil: A New Initiative by PK Clean
Plastics are highly popular because of its properties like durability, low cost, ease in manufacturing, versatileness and invulnerable to water and is widely used in all kinds of fields, ranging from household to spaceships. Plastic has replaced many conventional materials used so far such as wood, glass, metal, stone, bone, leather, horn and ceramic.
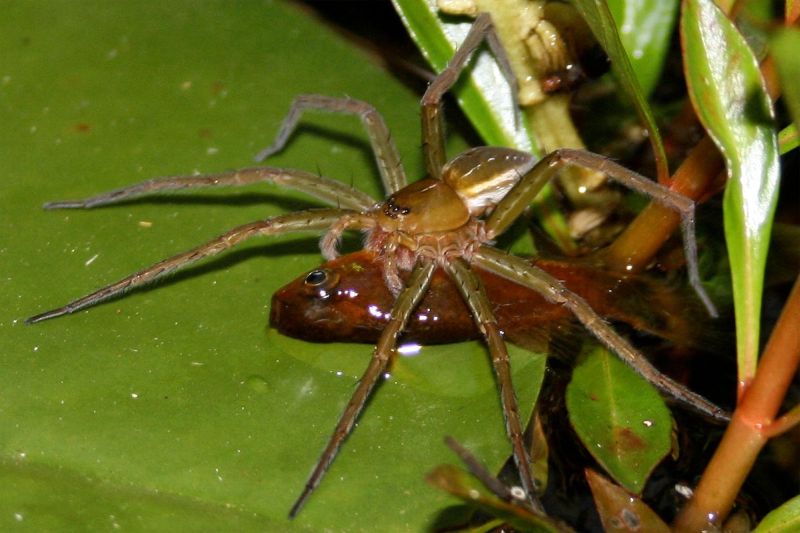
Read MoreFish Eating Spiders Discovered: Arachnid’s New Diet Supplement
It is a well known fact that spiders are insectivorous and part of their diet also includes plant material like pollen. But not everyone knows that spiders like to go for fishing too. According to a study conducted by Martin Nyffeler who is a spider expert and Zoologist at the University of Basel, Switzerland and Bradley Pusey, a fish expert coming from the University of Western Australia discovered that a few large sized spider varieties include small fish in their diet too. They have recorded incidents of spiders hunting fish from all the continents except Antartica. Majority…
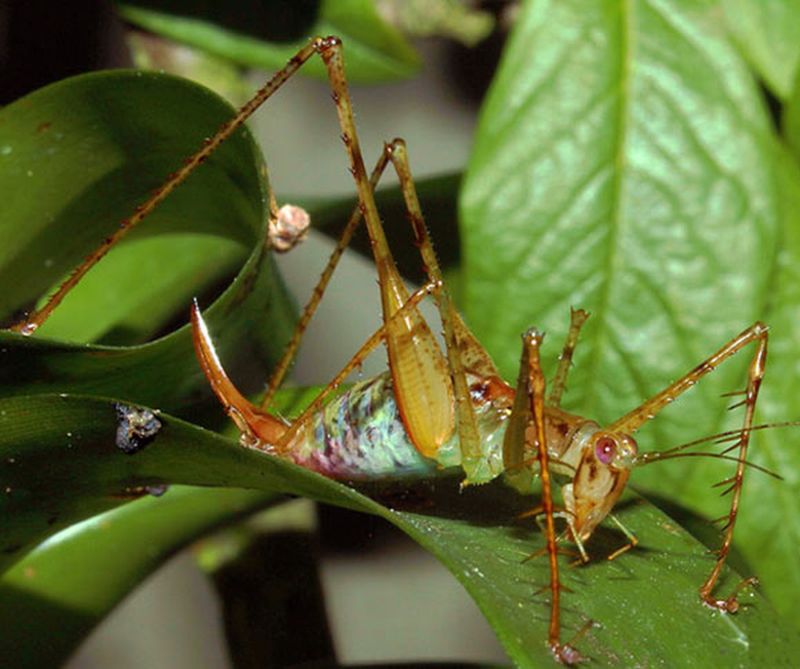
Read MoreHighest Frequency Ultrasonic Calls Recorded from an Arthropod: Jungle’s Crooning Band
Katydids (better known as bushcricket) are nocturnal insects and are predominantly known for their loud mating or love calls. These calls are produced when the males looking for females, rub their forewings together (stridulation).
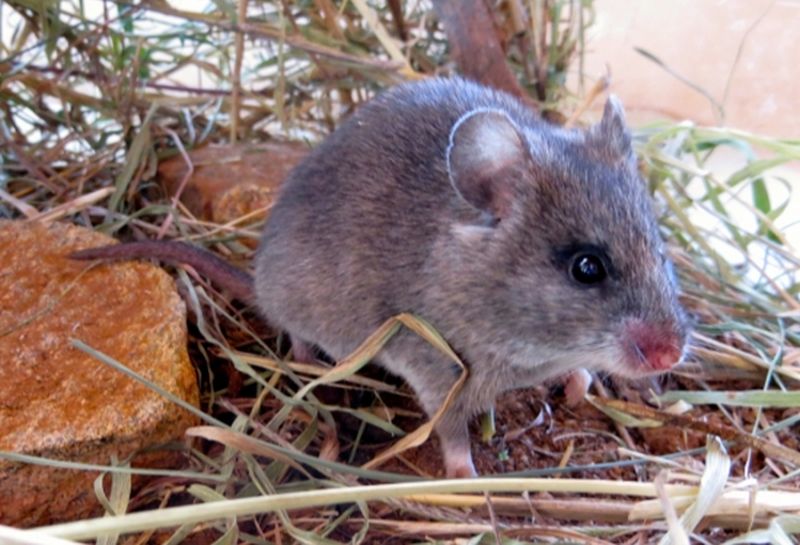
Read MoreAbsence of Large Mammals Lead to Escalation of Disease-Carrying Rodents: Ecological Imbalance
Every creature that lives on this planet has a role to play in maintaining a balance in the nature. Many animals have got extinct or on the verge of getting extinct, mainly because of human activities like deforestation, poaching, pollution and other activity. Following the extinction of large animals, the population of smaller animals like rodents will surge rapidly and this imbalance will have dire consequences on the health of humans.
Read More10 Extinct Species of Animals That Ruled in Yester Decades: Wild Life That Was
Time and tide wait for none! Well, who’s not aware of this fact? Even the Earth has never been the same. Dominated by man today, the planet was ruled by some other species in yester decades. And who knows – how long are we as humans gonna make it here! Species come and go but what are left behind are their trials. The reasons for sudden disappearance of these long gone species are many, namely – catastrophic meteor collisions, ice age and of course there’s inexorable threat of one specifically…
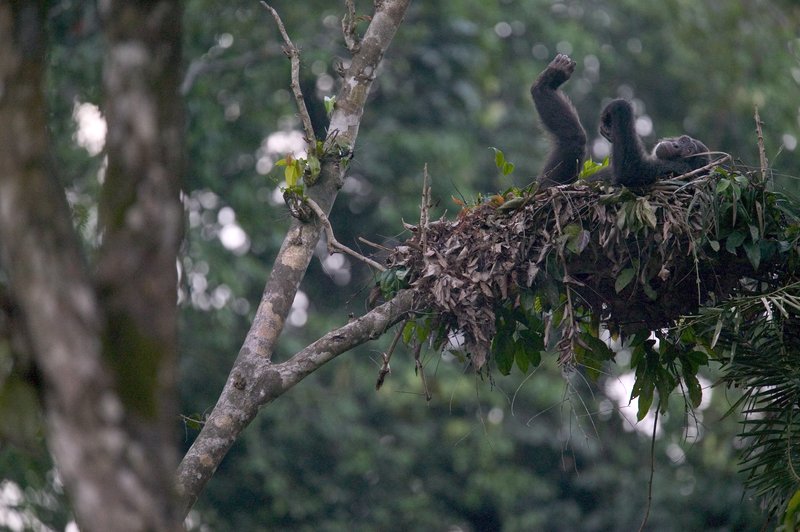
Read MoreChimpanzees Select Tree for Making Their One-Time Use Bed: The Sophisticated Primates
A new study suggests that like humans, chimpanzees are also very particular about their bed. Chimpanzees unlike humans are known to create their bed every day starting from scratch just before their bedtime. The exclusive chimpanzees beds are called nests and it require bending, breaking stems of tree, and piling leaves in an interwoven pattern, on this structure. But researchers noticed that chimpanzees do not make their nest on any random tree, rather choose branches of Ugandan ironwood trees for the purpose. These trees provided them with sturdy and stable…
Read More10 Weird Facts about Spiders: The Creepy Crawlers
Spiders are famous for their architectural skill that is displayed by weaving of web. Majority in the species prefer solitary life, alone in their cobwebs. They look eerie no doubts but they show such unique and weird characteristics that researchers across the globe are still trying to figure out the reasons behind these awestruck potentialities that these arachnids exhibit. Some of them are described below: 1) Bulky DNA The DNA of one spider egg is equal to the amount of genetic material of four humans combined. 2) Immortals There is…
Read MoreFrogs Resort Competition via Cannibalism: The Voracious Predators
Cannibalism in the animal kingdom is very well known fact among the inhabitants. Animals whether big or small in their race for survival, resort to kill their competition by eating them. Animals like jungle king, lions are known to kill the offspring of the revival king to pave way for better future of its own offspring. But researchers say, the behavior of cannibalism can be also seen tiny wood frog tadpoles. These innocent looking tadpoles when hungry can eat other tadpoles present in the pool. Such behavior has also been…
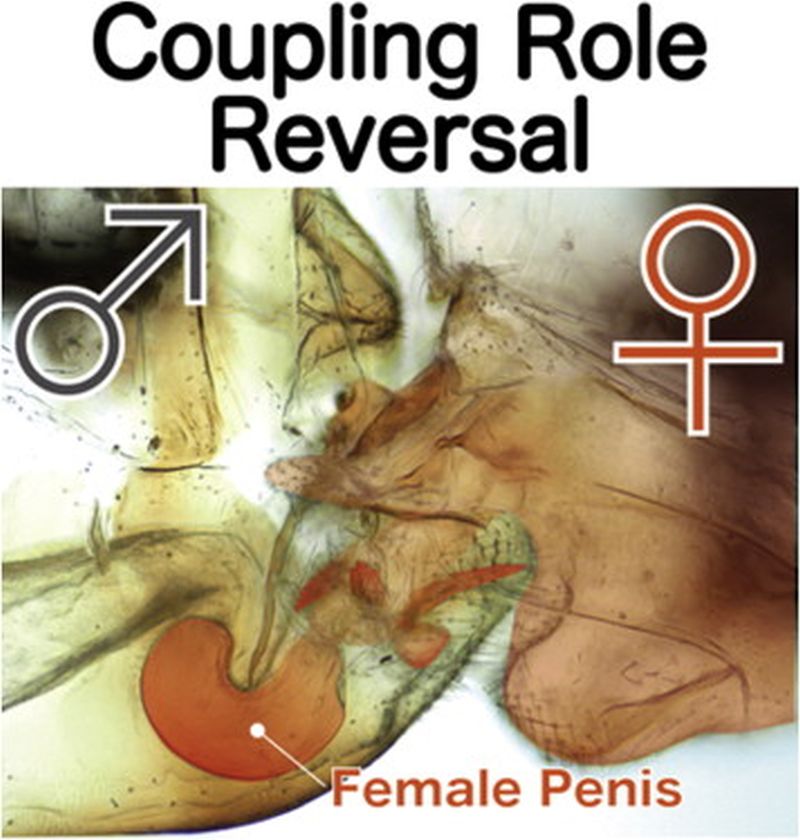
Read MorePenis Discovered in Female Insect: Novel Structure in Evolution
While studying the Brazilian cave insects, researchers to their surprise discovered a penis like genitals in females and organ similar to a vagina in males. For the first time they have noticed, such an extreme switch of sex organs and have dubbed the newly revealed penis of the female insects as “gynosome” and “phallosome” for the vagina like organ in male insects.
Read MoreAncient ‘Spider’ Images Surface Secrets: Arachnids Evolution
Studying the 305 million years old harvestmen fossil images, researchers and archaeologists have discovered that the forefathers of existing arachnids had 2 pair of eyes and not just one.
Read MoreSightless Mechanism of Navigation: Mouth Suction by Cavefish
When it comes to visualizing environment, eyes play an important role. But there are other ways of navigation such as echolocation used by bats and dolphins. Recently, researchers studying Mexican blind cavefish (Astyanax fasciatus), have found a unique and new method of navigation. These fishes spend their entire life in the deep sea or dark caves, which are devoid of any source of light and so as the name suggests, their eyes are rendered useless and over the time the fish losses their eyeballs.
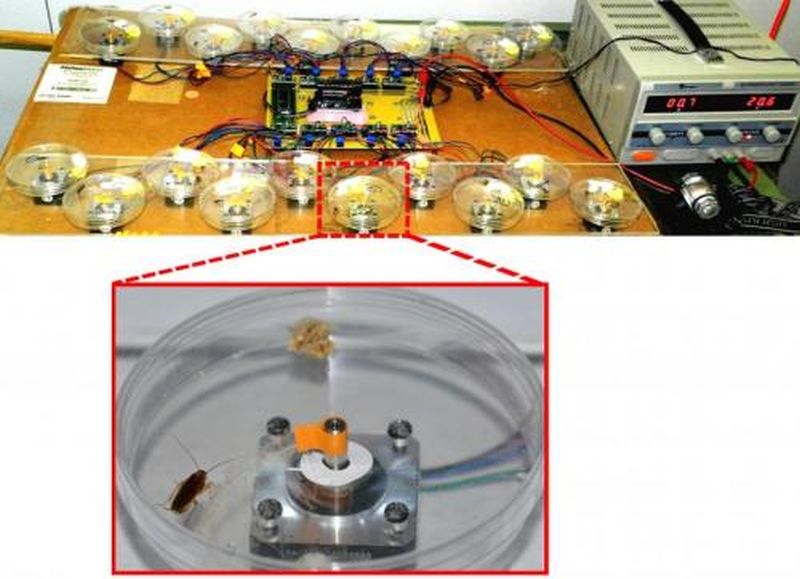
Read MoreTactile Stimulation and Reproduction go Hand in Hand Amongst Female Cockroaches
Generally, the antenna, key sensory organ of insects is known to aid insects in perceiving information about its surroundings such as availability of food, danger of predator, obstacles and potential mates and so on. They have many sensory receptors for audition, olfaction, balance, stability, gustation, graviception, thermo, hygro and mechanoreception, to name a few. They also play an important role during social interactions. In German cockroaches (Blattella germanica), during such social interaction, antennal contact alters juvenile hormone production which leads to an increase in female reproduction rate. In short the…
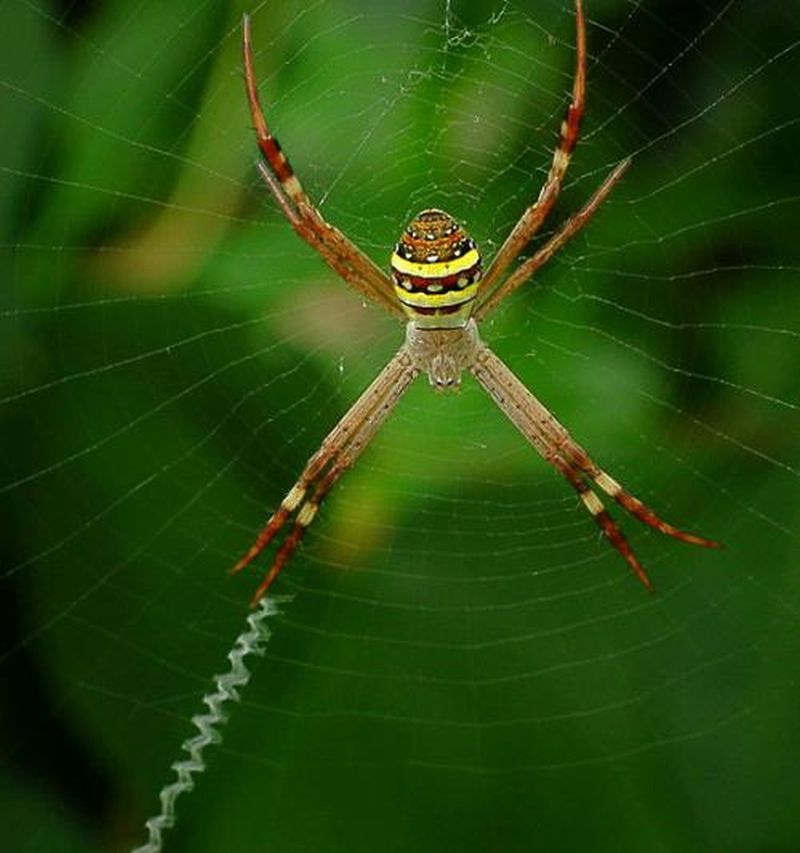
Read MoreSniffing Web Pheromones Helps Male St. Andrew’s Cross Spiders Determine Female Availability
Researchers from the University of Hamburg, Germany and Macquarie University in Australia, studying St. Andrew’s Cross spiders, have found that male spiders looking for suitable mates, smell the webs woven by females and determine the females are ready for mating. The researchers observed several specimens of the species and conducted numerous experiment in their laboratory and finally concluded that smelling the pheromones present on the female web, male spider make a decision whether to move closer to the female for mating or not.
Read MorePlants Uses Chemical Weapons and Employ Insect Armies to Defend Themselves
When we encounter a danger, the first thing that strikes in our mind is to run away and hide (though many of us might choose to give a fight). But the article is in the context of animals and plants. Animals when encounter any danger of being attacked, the first instinct is to escape from the danger is to run. Unfortunately, the plants cannot do that. Rather, plants in order to defend themselves from their predators have evolved various defense techniques such as chemical weapons and insect armies.
Read More