Have you ever realized that at the very beginning, you started out as just one tiny cell. From that single cell, all the different parts of your body, like your brain cells, heart muscles, blood cells, even skin developed. The question is, how does that one original cell somehow “know” what to turn into? How does it decide to become a brain cell or a heart cell, instead of just staying the same?
Read MoreTag: futuretech
Adaptive Architecture Powered by Mini Robots That Can Bloom
I’m not really into top-down approaches. I believe that in most effective systems, decisions happen at the individual level. For instance, take the case of ants or bees, while there’s structure, there isn’t constant centralized control. Individuals act based on local information, and coordination emerges naturally without waiting for hierarchical alignment.
Read MoreFrom Chatbots to Clones: The Strange Evolution of AI Autonomy
I remember the exact moment in The Matrix Reloaded when Agent Smith, the then no longer bound by the rules of the system, looks at Neo and says, “Me, me… me too!”
Read MoreMeet the Chip That Could Change How Your Devices Use Power
Wireless communication seems easy because it happens without us noticing, but inside, devices have to carefully balance sending data quickly, keeping the signal clear, and using as little power as possible. When devices send signals through the air, the signals aren’t always perfect, and using more power to make the signals stronger costs more battery life. That’s why a new transmitter chip from MIT and a few partner universities is turning heads.
Read MoreListening to Spins One Atom at a Time: Cavity-Enhanced Spectroscopy
Scientists have been studying tiny magnetic bits inside solids called spins. These spins are important because they could be the building blocks for future technologies that use quantum physics, like super-secure communication or super-fast computers.
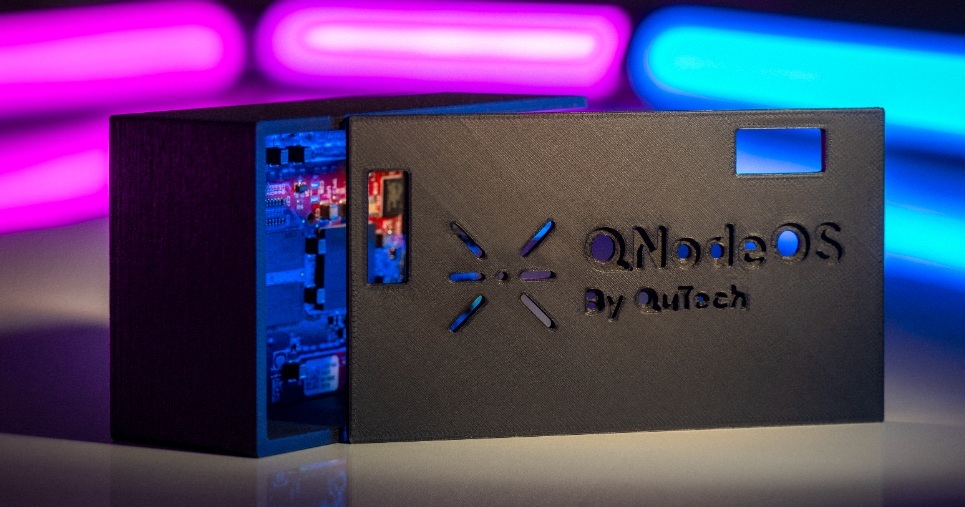
Read MoreQNodeOS: Making Quantum Network Development Accessible to All
For decades, quantum networks have always been looked as a research curiosity than a practical technology. I personally imagined it to be a field of entangled particles, stretching across galaxy and the quantum connections in the field space enables telepathic communication, this is how I concluded, quantum entanglement happens.
Read MoreCloud Messaging Platforms: Market Growth, Tech Trends and Leading Players
The trajectory of cloud-based messaging platforms is on an upward trend. As industries globally adopt advanced technologies, the demand for sophisticated applications is also increasing. As per Market Research Future, the Cloud Communication Platform market industry is projected to grow from USD 19.38 Billion in 2024 to USD 82.21 Billion by 2032, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.80% during the forecast period (2024 – 2032). While Mordor Intelligence estimates it to reach USD 40.13 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 18.44% during the forecast period…
Read MoreInterview: Dr. Yaqing Shen, Material Scientist at KAUST, Saudi Arabia
I’m excited to introduce Dr. Yaqing Shen, a highly accomplished scientist in the field of Material Science and Engineering. Her groundbreaking research on advancing the use of two-dimensional (2D) semiconductors in commercial field-effect transistors (FETs) caught my attention. Despite her hectic academic responsibilities, Dr. Shen graciously agreed to an email interview, where she shared insights into her work and career.
Read MoreInterview: Dr. Eunhye Baek, Research Scientist at Tsinghua University, China
I’m excited to introduce our latest interviewee, Dr. Eunhye Baek, whose impressive academic journey and cutting-edge research make her a standout in the field of electrical engineering and nanotechnology. Dr. Baek studied Electrical Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) from 2007 to 2010. In January 2011, she joined Professor Yoon-Ha Jeong’s group at POSTECH, where she focused on the biological functionalization of silicon nanowire BioFETs to detect biomolecules with high sensitivity.
Read MoreBiomimicry: Mantis-Inspired Biomimetic Vision System
A self-driving car approaches a street with a parked car and a cyclist waiting to cross. The car detects the cyclist moving but has difficulty judging the distance and speed of both the stationary parked car and the slow-moving cyclist, leading it to miscalculate the necessary response and causing a collision. This is similar to how some insects see the world: their eyes are good at noticing movement and seeing a lot at once, but they struggle to tell how far away things are. However, this is not the case…
Read MoreInterview: Dr. Boris Goncharov, a Senior Scientist at the Albert Einstein Institute, Germany
I’m thrilled to introduce Dr. Boris Goncharov, a distinguished figure in the field of gravitational wave research. Currently, he is a Senior Scientist with the Pulsar Timing Array (PTA) group at the Albert Einstein Institute (AEI) in Hanover, Germany, where he is exploring the fascinating world of nanohertz-frequency gravitational waves.
Read MoreFrom Urine to Water: The Latest Breakthrough in Spacesuit Technology
Of all the things in movie, Dune, I particularly got fascinated with the idea how the people used those suits to recycle sweat and urine into drinkable water. It got me thinking: why can’t we make this tech a reality? Well, it turns out researchers at Cornell University are on it! They’ve developed a prototype for a new urine collection and filtration system for spacesuits. Isn’t that awesome?
Read MoreGravitational Wave Memory: A Tool for Measuring Spacetime Symmetries
When we talk about the fabric of reality, in terms of physics, we deal with interesting abstractions and tonnes of complexities. One such intriguing concept of Einstein’s theory of general relativity is the existence of gravitational waves. As the name suggests, these ripples are generated in the spacetime by some of the universe’s most violent and energetic processes, such as mergers of cosmic stars or dent in the landscape due to black holes. Interestingly, whenever these waves pass through, they leave a measurable imprint on the relative positions of objects—a…
Read MoreBrain-like Artificial System: Dendristor to Mimic Brain’s Dendritic Computations
As artificial intelligence (AI) technology is expanding its tentacles rapidly across globe, engineers around the world are designing new types of computer architectures and hardware. One interesting aspect of most brain-inspired technologies developed so far is that researchers focus on mimicking how neurons fire (i.e., send electrical signals) rather than replicating the entire structure of the brain.
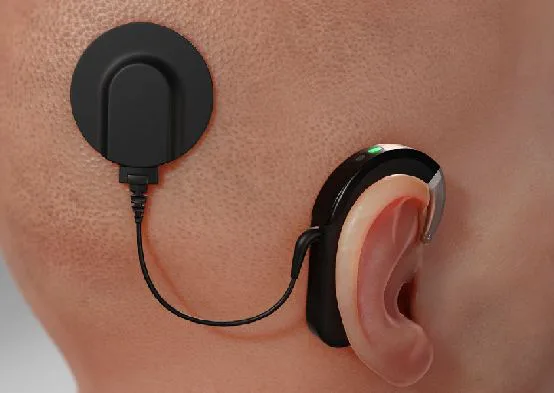
Read MoreUmboMic Revolutionizes Cochlear Implants with PVDF Technology
What if a microphone, which is fabricated from a flexible material can be placed inside our ear, to be more specific, directly on the eardrum? This biocompatible sensor will pick up sounds and sends them to a tiny amplifier, which makes the sounds loud enough to be processed by a cochlear implant. Doesn’t it sound like a boon for those who are deaf or hard of hearing?
Read More