It is my honor to interview Dr. Artem R. Oganov, a world-renowned scientist whose expertise spans chemistry, crystallography, mineralogy, and materials science. He is the winner of many awards, including the prestigious European Mineralogical Union medal. And since 2017, he has been a proud member of the European Academy of Sciences.
Read MoreTag: futuretech
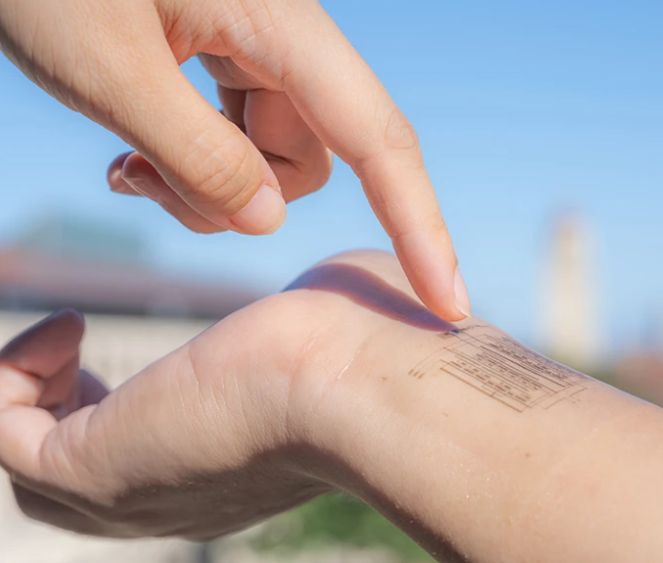
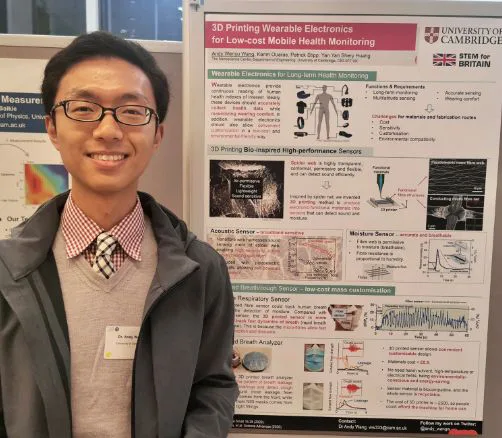
Interview: Dr. Andy Wang, a Bioelectronics Scientist at the University of Cambridge, England
Meet Dr. Andy Wang, PhD, a leading researcher in the Biointerface Group at the University of Cambridge, under the esteemed Prof. Shery Huang. Dr. Wang brings a wealth of expertise to the field, having earned a Bachelor’s degree in Mechanical Engineering from the prestigious Tsinghua University in 2016, followed by a PhD in the same field from the world-renowned Cambridge University Engineering Department in 2021.
Read MoreInterview: Dr. Matthew Bergin, an Experimental Physicist at The University of Newcastle, Australia
I’m thrilled to introduce Dr. Matthew Bergin, a rising star in the world of Organic Electronics research. Armed with a Master of Science degree in Natural Sciences and a Ph.D. in Physics from the prestigious University of Cambridge, Dr. Bergin is making waves with his groundbreaking work at the Centre for Organic Electronics (COE). Dr. Bergin went deep into studying how things work in scanning helium microscopy. He was in charge of creating a better electron ionization mass spectrometer during his Ph.D. research. It’s like he’s breaking new ground in…
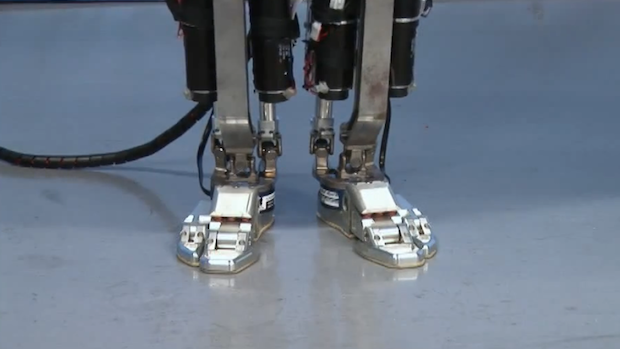
Read MoreBiohybrid Bipedal: Muscle-Powered Two-Legged Robot
Unlike robots, our bodies are super flexible and can make delicate moves effortlessly. Components like muscles, joints, and nerves work in tandem and allow us to make precise and delicate movements with ease. Robots, on the other hand, rely on rigid structures and predefined movements; in contrast, our bodies can adapt and respond dynamically to various situations.
Read MoreCosmic Recycling: NASA’s Discards Turned into Futuristic Nanomaterials
Sussex researchers just unveiled the game-changing power of Martian nanomaterials! Dr. Conor Boland, the materials physics maestro at Sussex, along with his team investigated the potential of nanomaterials. These materials are smaller than a human hair for Mars’s sustainable future. The same tech rocking the International Space Station and NASA’s playbook might be Mars’s ticket to eco-friendly living.
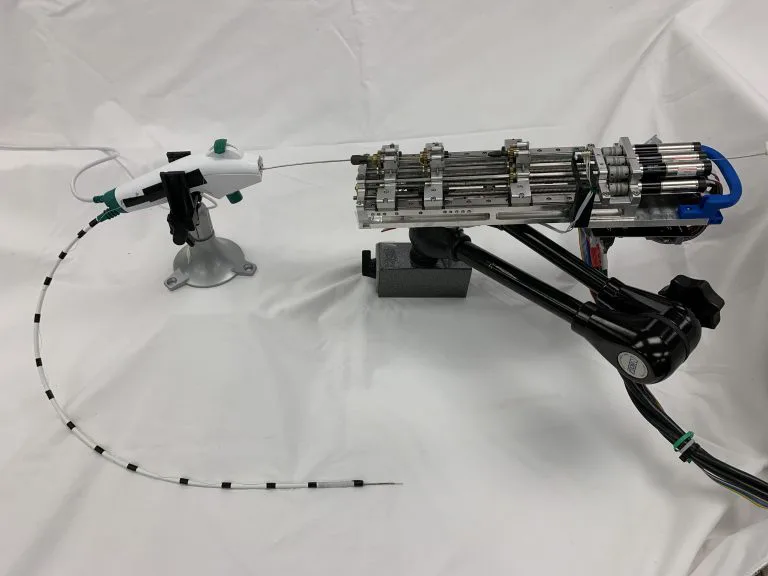
Read MoreRobotic Needle Achieves Precision Navigation in Living Model
When it comes to cancer-related fatalities, lung cancer tops the list. One of the main reasons could be the presence of tiny tumors in deep within the lung tissue. This poses a major challenge for surgical accessibility. To address this challenge, researchers at UNC Chapel Hill and Vanderbilt University have been trying to fabricate an exceptionally flexible yet durable robot. The device will have the capability of maneuvering through the intricate terrain of the lungs.
Read MoreBook Review: Regenesis by George M. Church and Edward Regis
Regenesis: How Synthetic Biology Will Reinvent Nature and Ourselves is an exhilarating journey that re-shapes our understanding of life itself. The book is written by George M. Church and Edward Regis. It was first published in 2012. The renowned geneticist and science writer collaborated to present an all-encompassing exploration of synthetic biology. And highlighting its thrilling potentialities along with obvious challenges. In this remarkable masterpiece, they have woven following three distinct levels of exploration.
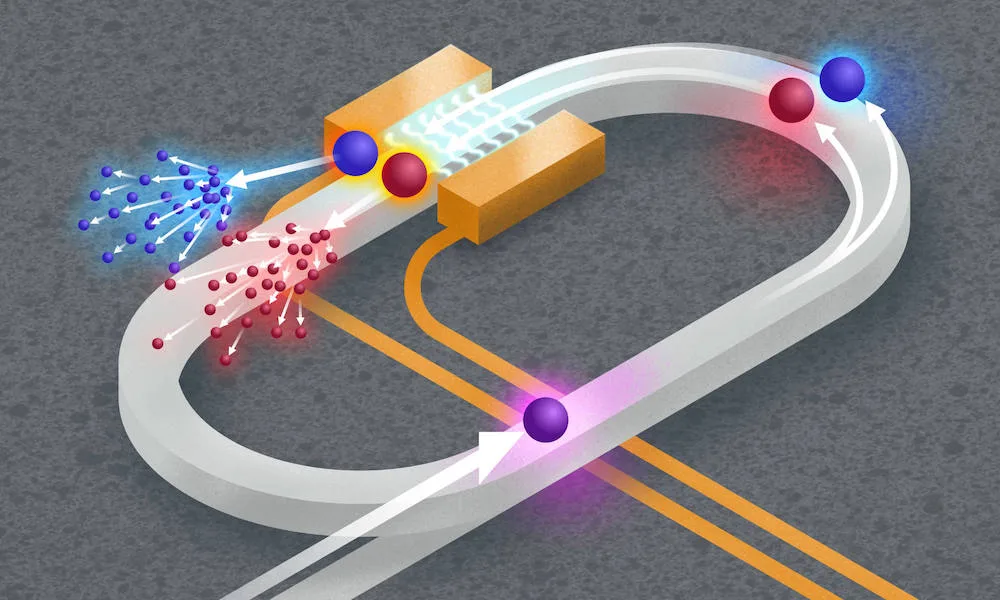
Read MoreChip-scale Optical Quantum Simulation System: Quantum Computing Milestone
A team of researchers have successfully simulated complex natural phenomena at the quantum level. Scientists at the University of Rochester’s Hajim School of Engineering & Applied Sciences have developed a chip-scale optical quantum simulation system. Conventionally, photonics-based computing involves controlling the paths of photons. This time, the team led by Qiang Lin has taken a different approach. According to which, they have simulated the phenomena in a synthetic space. And they have manipulated the frequency, or color, of quantum entangled photons as time progresses.
Read MoreLithography-Free Photonic Chip: Redefining AI Architecture
When it comes to data-heavy applications and sustainable computing, photonic chips have emerged as a promising technology. The use of photonic circuits, powered by laser light, offers an edge over traditional electronic circuits. Some of its remarkable advantages over electronic circuits are: Speed of light: Photonic chips make use of light to transmit and process information, which of course happens at the “speed of light”. Thus, leveraging the feature of light makes them move faster than electrons in electronic circuits.
Read MoreILT and SMO continue to push the Boundaries of Resolution: Semiconductor Manufacturing
Semiconductor manufacturing is experiencing rapid and dynamic growth. The exponential evolution is making it one of the most swiftly evolving industries globally. As technology is advancing, the electronic devices are progressively shrinking in size. Behind this constant innovation lies the incredible field of “computational lithography”. It is the heart of semiconductor industry. After all, it blends the power of computers, mathematics, and precision engineering. Only to create intricate microscale structures on silicon wafers.
Read MoreGame-Changing Diode Enhances Quantum Computers and AI Performance: Quantum Leap
Researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities have created a ground-breaking superconducting diode, which is a crucial element in electronic devices. This innovation has the potential to not only enhance the development of quantum computers for industrial applications but it will also boost the performance of artificial intelligence systems.
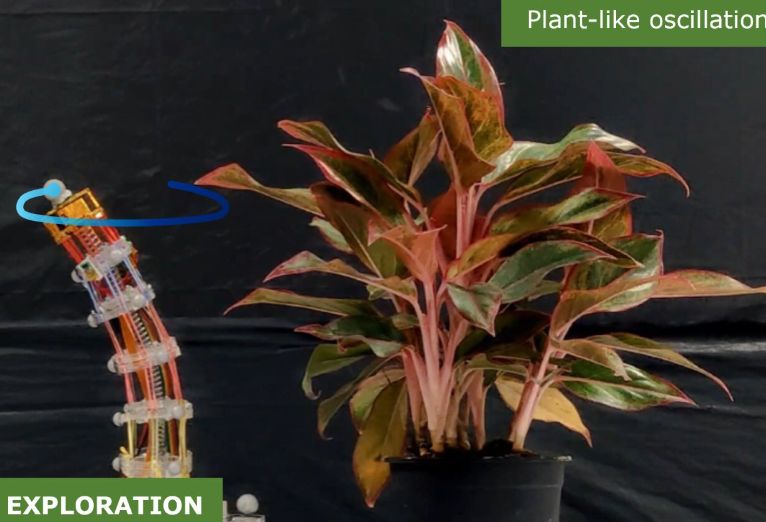
Read MorePlant-inspired Controller for Robotic Arms: Biomimicry
Biomimicry is the practice of imitating biological systems and processes. So far, it has been a valuable approach in robotics. By copying animals’ designs, engineers have tried to replicate billions of years of evolution. It has resulted in highly efficient and adaptable designs that nature has already passed on to. For instance, energy-efficient walking patterns inspired by animal gaits or bio inspired vision systems or lizard inspired four-legged robot.
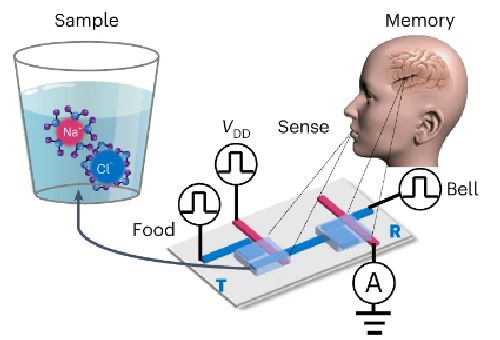
Read MoreAn Organic Electrochemical Transistor: AI Hardware
Lately, there has been growing interest in creating brain-inspired hardware for enhancing efficiency of AI models. Conventional hardware architectures are specialized in three specific tasks, which are: Researches across the globe, however, are exploring the possibility of combining these functionalities into a single device. They aim to mimic the parallel and distributed nature of the human brain.
Read MoreArtificial Skin to Mimic Sensory Feedback of Biological Skin: E-Skin talking to Brain
Researchers at Stanford University have created a special kind of electronic skin that can sense things like heat and pressure and send signals to the brain. Electronic skin has been around for a while, but in the past, the devices used to convert these sensations into signals were bulky and inflexible. However, the new electronic skin is as soft and thin as real skin.
Read MoreBio-Inspired Device that Mimics Human Eye: Artificial Vision Systems
Inspired by the natural design of our retinas, scientists at Penn State have created a sensor array using narrowband perovskite photodetectors to replicate the function of our cone cells. Cone cells in our eyes are responsible for color vision. And they are sensitive to red, green, and blue light wavelengths.
Read More