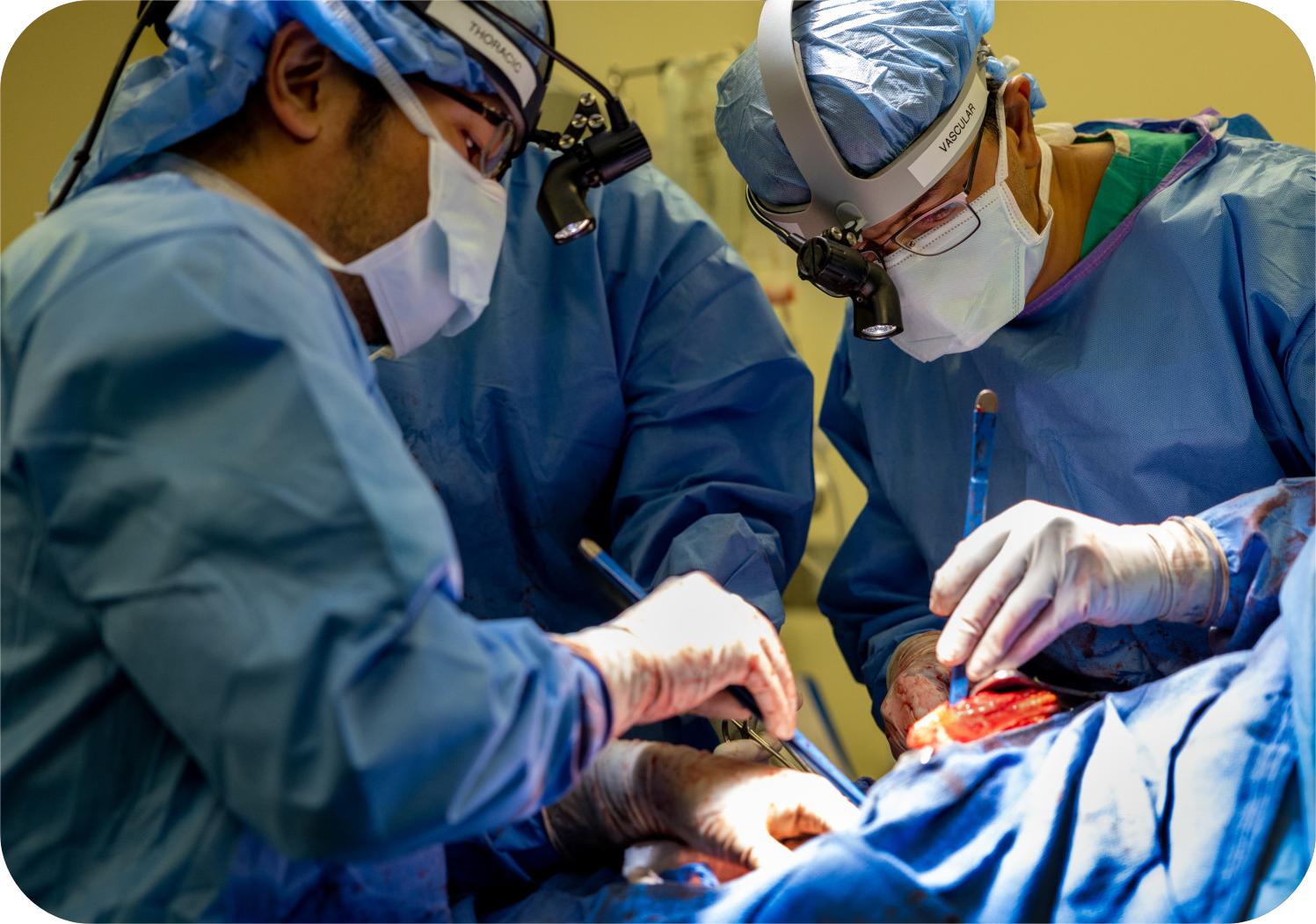
The man from Missouri should have been dead by spring 2023. By the time a medical helicopter delivered him to Northwestern Memorial Hospital on a rolling bed of tubes and machines, his body was already struggling to survive. What started as a seasonal flu had curdled into a resistant infection that was essentially melting his lungs from the inside.
Read MoreTag: innovation
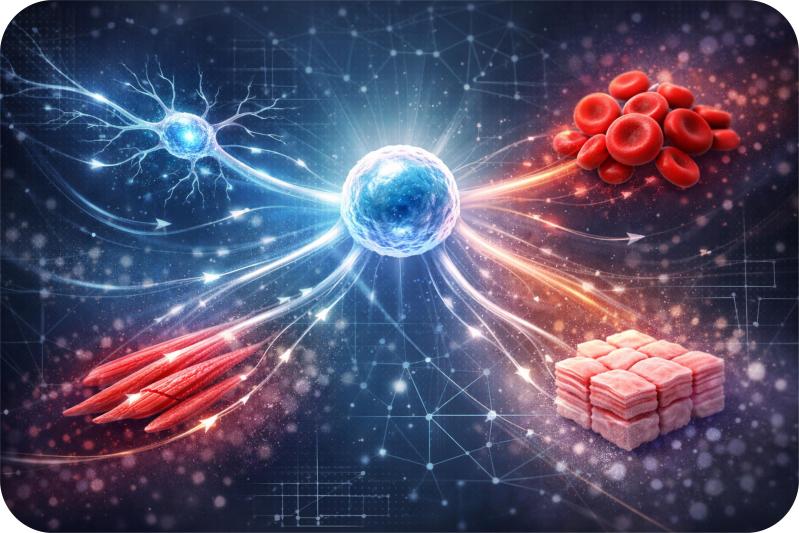
AI Is Learning to Predict and Control Cell Fate with scDiffEq
Have you ever realized that at the very beginning, you started out as just one tiny cell. From that single cell, all the different parts of your body, like your brain cells, heart muscles, blood cells, even skin developed. The question is, how does that one original cell somehow “know” what to turn into? How does it decide to become a brain cell or a heart cell, instead of just staying the same?
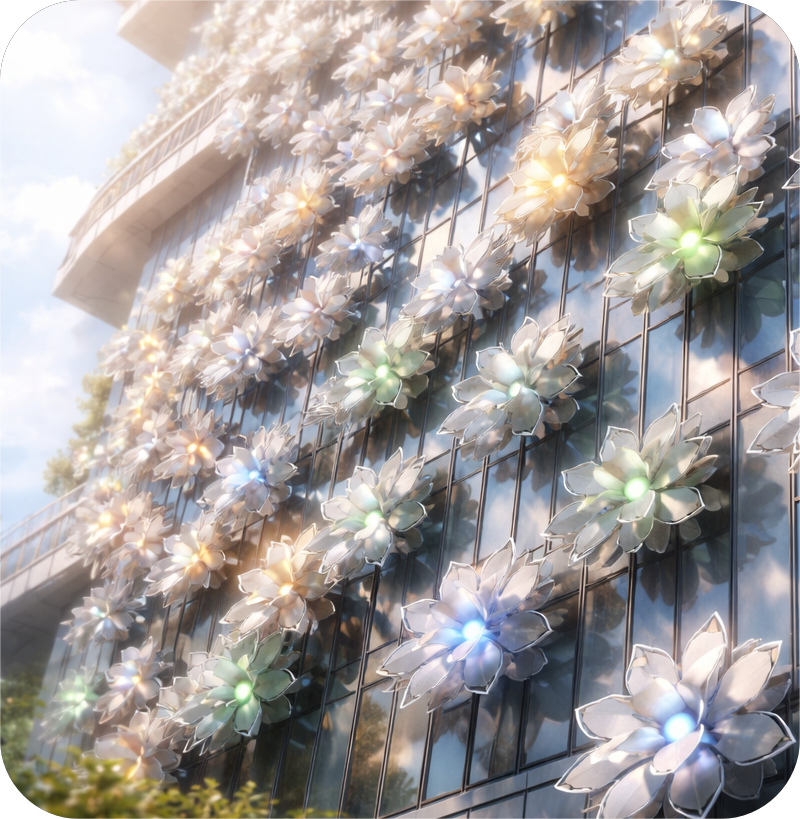
Read MoreAdaptive Architecture Powered by Mini Robots That Can Bloom
I’m not really into top-down approaches. I believe that in most effective systems, decisions happen at the individual level. For instance, take the case of ants or bees, while there’s structure, there isn’t constant centralized control. Individuals act based on local information, and coordination emerges naturally without waiting for hierarchical alignment.
Read MoreWhen Light Starts To Think: A Journey Into Optical Computing
If I ask you, what scene in The Matrix that’s always stuck with you, I’m sure most of us would say, the bullet-dodging or the red pill. But for me it’s when Morpheus tells Neo that what he thinks is real is actually just electrical signals interpreted by his brain.
Read MoreArtificial Neurons That Learn Like the Brain: The DRAM–MoS₂ Breakthrough
I came across some research from Fudan University recently that really caught my attention – Artificial neuron merges DRAM with MoS₂. As the headline suggests, they’ve built an artificial neuron that doesn’t just copy the way brain cells connect to each other, but also how they adjust their own internal behavior.
Read MoreMeet the Chip That Could Change How Your Devices Use Power
Wireless communication seems easy because it happens without us noticing, but inside, devices have to carefully balance sending data quickly, keeping the signal clear, and using as little power as possible. When devices send signals through the air, the signals aren’t always perfect, and using more power to make the signals stronger costs more battery life. That’s why a new transmitter chip from MIT and a few partner universities is turning heads.
Read MoreInterview: Dr. Lenka Tetková, Postdoctoral Researcher at DTU Compute, Technical University of Denmark
Researchers at the Technical University of Denmark have found a fascinating link between how humans and machines learn, through a mathematical shape called convexity. This concept could be key to understanding how both brains and algorithms organize ideas and make sense of the world. I stumbled upon their paper, “On Convex Decision Regions in Deep Network Representations,” and I was absolutely awestruck. Not just by the insights in the research itself, but by the sheer brilliance behind it. It’s one thing to read a paper that makes you think differently,…
Read MoreListening to Spins One Atom at a Time: Cavity-Enhanced Spectroscopy
Scientists have been studying tiny magnetic bits inside solids called spins. These spins are important because they could be the building blocks for future technologies that use quantum physics, like super-secure communication or super-fast computers.
Read MoreBreakthrough in Nonreciprocal Light Speed Manipulation via Cavity Magnonics
Imagine you’re standing on a road where cars drive in both directions. Generally, the speed limit is the same whether you’re heading north or south. That’s exactly how light usually works in most systems, the “speed limit” stays the same no matter which way it’s going. This is called reciprocal control, the system treats both directions equally.
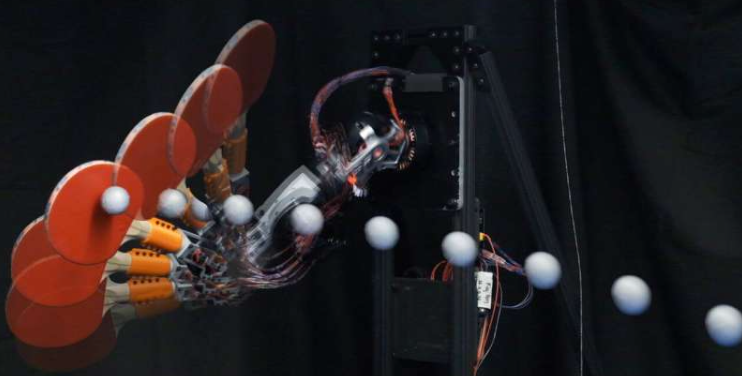
Read MorePing Pong Power: MIT’s Robot Is Getting Really Good at Table Tennis
MIT engineers have built a robot that can seriously play ping pong, and not just bat the ball back. This bot can understand the spin, predicts where the ball is going, and interestingly puts its own spin on returns. The whole project is from MIT’s Biomimetic Robotics Lab. It surely must be fun to build such robots, but embedding dexterousness through table tennis is a smart move as it pushes the robot to deal with speed, spin, unpredictability, and quick decision-making, all at once.
Read MoreInterview: Dohyeon Lee, Robotics Scientist at Pohang University of Science & Tech, South Korea
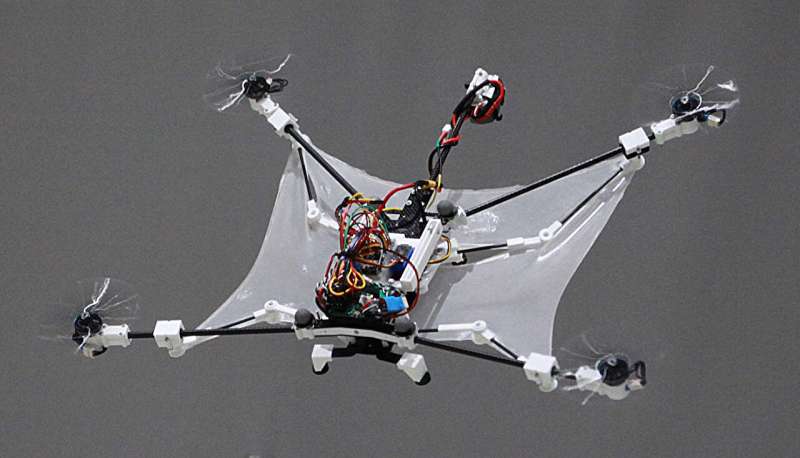
Last week, I came across something that genuinely blew my mind – a flying squirrel-inspired drone with foldable wings. Yep, a drone that mimics how a squirrel glides through the air. It was one of those rare “wait, what?” moments that made me want to dig deeper. So, I reached out to the team behind it. Dohyeon Lee, one of the researchers on the project, said yes to an email interview.
Read MoreTerrell-Penrose Effect: Visualizing High-Speed Relativity
I’ll be honest, I have always thought ‘thought-experiments’ can never be visually demonstrated. And so, we would have to keep imagining intangible concepts in our minds, like, what happens to an object traveling at the speed of light, where time would seemingly stop and length would contract. However, a group of researchers in Austria did something unbelievable. They visually demonstrated the Terrell-Penrose effect, a phenomenon predicted all the way back in 1959 but never actually observed.
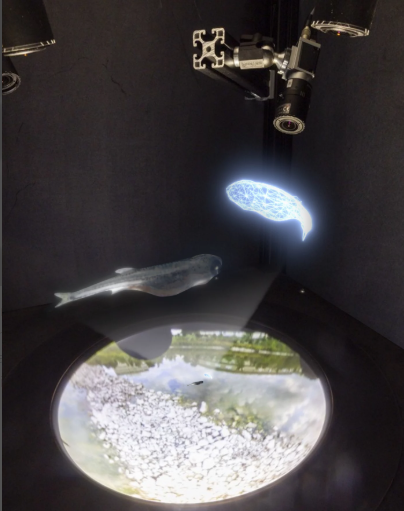
Read MoreScientists Use VR to Teach Robots Swarming Behavior by Studying Fish
A team of biologists and robotic engineers recently used virtual reality (VR) to crack the code of how fish school, with the goal of teaching robots to swarm in the same way. Imagine you’re at a party where everyone’s dancing to the same rhythm, but there’s no DJ or leader telling people what to do. Everyone just knows how to stay in sync, avoid bumping into each other, and respond to changes in the crowd. That’s basically what schools of fish do, and it’s something that robots have struggled to…
Read MoreBiomimicry: Squirrel Drone with Foldable Wings Shows Superior Maneuverability
Drones that we see today are very well equipped with focusing systems that allow for high-resolution imaging, precise navigation, and advanced object tracking capabilities. However, when it comes to executing sharp turns, a key limitation of today’s drones, the tech is still in its early stages of development.
Read MoreSmaller Than a Grain of Rice, This Pacemaker Runs on Light
Northwestern engineers have come up with something pretty wild, a pacemaker so small it can fit inside the tip of a syringe. Not only that, but it’s wireless, dissolves inside the body after doing its job, and can be injected without surgery.
Read More