I’m thrilled to introduce Dr. Matthew Bergin, a rising star in the world of Organic Electronics research. Armed with a Master of Science degree in Natural Sciences and a Ph.D. in Physics from the prestigious University of Cambridge, Dr. Bergin is making waves with his groundbreaking work at the Centre for Organic Electronics (COE). Dr. Bergin went deep into studying how things work in scanning helium microscopy. He was in charge of creating a better electron ionization mass spectrometer during his Ph.D. research. It’s like he’s breaking new ground in…
Read MoreTag: nanotechnology
Interview: Dr. Alex Greilich, an Experimental Physicist at TU Dortmund University, Germany
Meet Dr. Alex Greilich, an experimental physicist who started his journey from Russia to his current endeavors in Germany. Venturing beyond mere theory, he dives headfirst into the intricate world of semiconductor nanostructures and spin dynamics, unearthing remarkable phenomena like time crystals along the way. Collaborating with esteemed institutions such as the Ioffe Institute, (research center within the Russian Academy of Sciences) Dr. Greilich’s work pushes the boundaries of what we know about the universe.
Read MoreEvolution of Life’s Molecular Systems: Insights into the Rise of Nanomachines
Researchers at Université de Montréal (UdeM) have made a significant discovery regarding the evolution of molecular systems crucial to the development of life. Through the linking of molecules, they have uncovered insights into the emergence of intricate self-regulating mechanisms. Alexis Vallée-Bélisle, a professor at UdeM and the lead researcher of the investigation, explained that life’s sustenance on our planet stems from myriad nanostructures. These nanomachines have undergone evolution over countless years.
Read MoreDecoding Quasicrystal Magnetism: Unveiling a Fresh Magnetic Blueprint
Quasicrystals are interesting materials since they defy regular atomic pattern. It’s non-repeating structure captivates researchers. Since, it leads to extraordinary properties. Thus, the exotic traits not only challenge the traditional material science views but the same also inspire countless innovations. However, there is a rebel in the family of quasicrystals, the Tsai-type icosahedral quasicrystal (iQC). It is a specific variant of quasicrystal with a unique atomic arrangement characterized by icosahedral symmetry. The symmetry involves a structure that resembles a 20-sided polyhedron.
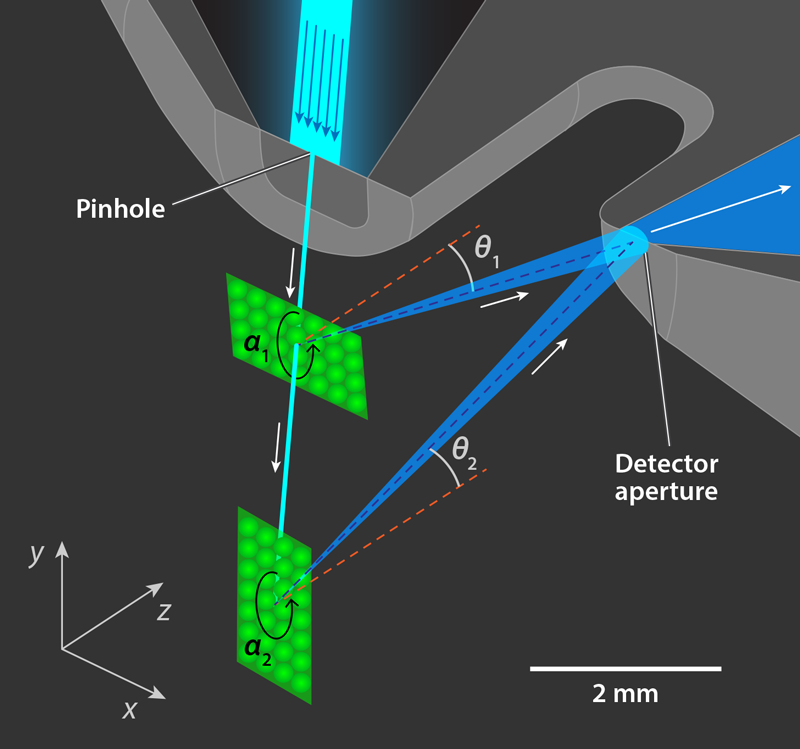
Read MoreHelium Diffraction Patterns Under the Microscope: Atoms are Artists
Witness helium atom diffraction like never before. All thanks to microscopic spatial resolution. Researchers from the University of Cambridge and University of Newcastle just dropped a game-changing technique. This breakthrough has allowed scientists to dive even deeper into the weird world of atoms.
Read MoreTransistors Get a Makeover with Sliding Ferroelectricity Power
Lately, tech wizards are aiming to create hardware that combines computation and data storage all in one gadget. These emerging electronics, called as computing-in-memory devices, will be a game-changer for faster speeds and improved data analysis.
Read MoreCosmic Recycling: NASA’s Discards Turned into Futuristic Nanomaterials
Sussex researchers just unveiled the game-changing power of Martian nanomaterials! Dr. Conor Boland, the materials physics maestro at Sussex, along with his team investigated the potential of nanomaterials. These materials are smaller than a human hair for Mars’s sustainable future. The same tech rocking the International Space Station and NASA’s playbook might be Mars’s ticket to eco-friendly living.
Read MoreCompact Accelerator Tech Surpasses Energy Milestone
Particle accelerators are nothing less than super heroes! They rock the world of semiconductors, medical magic, and all kinds of cool research including materials, energy, medicine etc. The only down side of this tech is, they require huge space, like kilometers of it. This makes them super pricey and time consuming of course.
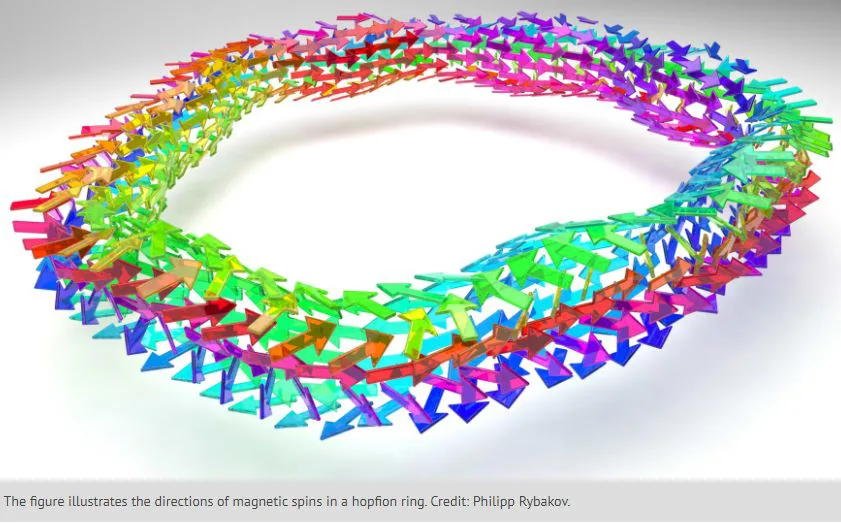
Read MoreHopfions Discovered: Pioneering Breakthrough in Crystal Structures
Hopfions, the magnetic spin structures, have gained significant attention in recent years. Although their predictions have been observed several decades ago. A collaborative research effort from Sweden, Germany, and China presents it’s the first experimental evidence.
Read MoreComputational Lithography: Illuminating the Future of Semiconductor Manufacturing
Tech behind computational lithography has revolutionised the way semiconductors are fabricated. By harnessing the power of computer algorithms and simulations, chip designs have become more efficient and powerful than ever before. Its ability to optimize lithographic processes have given a huge boost to the overall performance and energy efficiency of electronic devices. As we move forward, computational lithography is expected to merge with other technologies and re-shape the future where technology knows no bounds.
Read MoreMysteries of Particle Collisions: Insights from Elastic Scattering
The world of quantum physics is filled with intricate interactions among elementary particles. Scientists are trying to find insights from these interactions. They call it the, elastic scattering. During elastic scattering, the particles involved exchange energy and momentum but do not undergo any particle creation or annihilation processes. The scattered particles typically change their direction and momentum after the collision but retain their original identities and properties.
Read MoreRydberg Excitons and Moiré Lattices Join Forces: Revolutionizing Quantum Simulation
In the intricate weave of the quantum realm, there exists a remarkable phenomenon known as Rydberg states. They are like the supercharged versions of atoms and molecules. These electrifying states of particles push the boundaries of our regular understanding of the quantum world.
Read MoreChip-scale Optical Quantum Simulation System: Quantum Computing Milestone
A team of researchers have successfully simulated complex natural phenomena at the quantum level. Scientists at the University of Rochester’s Hajim School of Engineering & Applied Sciences have developed a chip-scale optical quantum simulation system. Conventionally, photonics-based computing involves controlling the paths of photons. This time, the team led by Qiang Lin has taken a different approach. According to which, they have simulated the phenomena in a synthetic space. And they have manipulated the frequency, or color, of quantum entangled photons as time progresses.
Read MoreLithography-Free Photonic Chip: Redefining AI Architecture
When it comes to data-heavy applications and sustainable computing, photonic chips have emerged as a promising technology. The use of photonic circuits, powered by laser light, offers an edge over traditional electronic circuits. Some of its remarkable advantages over electronic circuits are: Speed of light: Photonic chips make use of light to transmit and process information, which of course happens at the “speed of light”. Thus, leveraging the feature of light makes them move faster than electrons in electronic circuits.
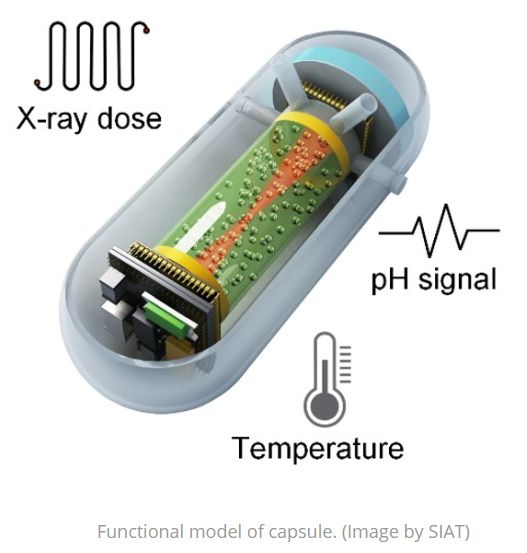
Read MoreCapsule X-Ray Dosimeter for Real-time Monitoring: Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is all about precision in targeting tumor tissue while minimizing damage to healthy tissue. To deliver precision radiation requires real time monitoring of the dose till the time it is absorbed. The task is quite challenging, especially if it is in gastrointestinal tract. The dynamic nature of the region makes it nearly inaccessible. Current approaches used for tracking biochemical indicators including pH and temperature are insufficient to give out comprehensive evaluation of radiotherapy.
Read More