Capturing ongoing processes within living cells in real time is usually done with fluorescent dyes made up of a fluorescent chemical compound, fluorophore. The compound’s unique property of re-emitting light upon excitation makes it the most deserving candidate for imaging cellular processes, however, with the passage of time, the compound becomes toxic thereby renders havoc to the cells in close proximity.
Read MoreTag: nanotechnology
New Generation of Fast-Charging Batteries: Innovative Battery Technology
Nanyang Technological University (NTU Singapore) researchers have fabricated an innovative battery that can charge nearly 70% of its capacity in just 2 minutes. This does not affect its longevity; on the contrary, the scientists are claiming its survival age to over 20 years.
Read MoreLighting Sheets to replace Bulbs: OLED, the Next Generation Lights
How about customizing light source in our rooms, something that resembles the photo frames. Sounds interesting, ain’t it? Researchers have already been working in the field of light and they have come up with an approach that targets the efficiency in half amount of energy being consumed by regular bulbs by developing ‘glowing sheets’. Technology used in these light sheets would resemble the mega thin TVs and smartphones as the sheets are expected to include organic LEDs or OLEDs.
Read MorePhotonic Circuits to replace Electronic Circuits: New Quantum Technology
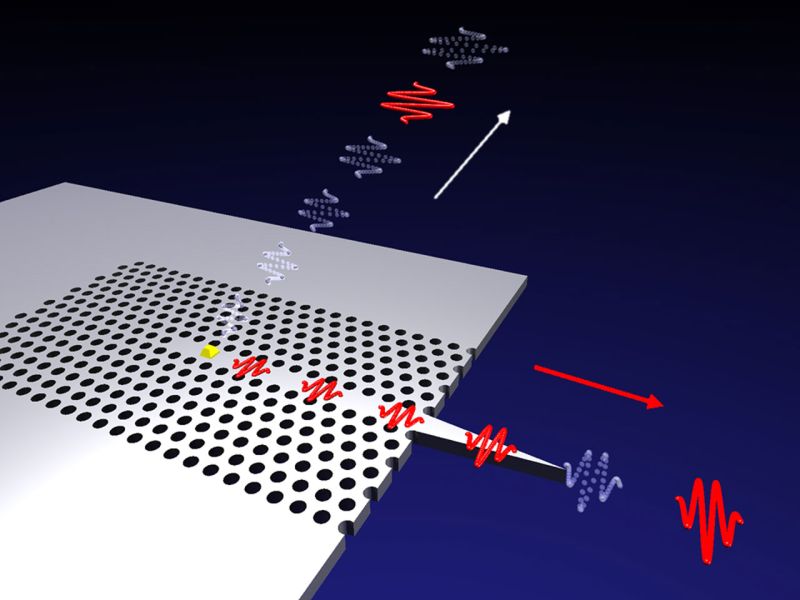
Photonic circuits would soon be replacing electronic circuits in the near future of quantum circuits. Since a decade, researchers across the globe were working towards developing quantum circuits but circuits based on light had its limitations however, researchers at the Niels Bohr Institute, Copenhagen have been successful in bringing about the probability.
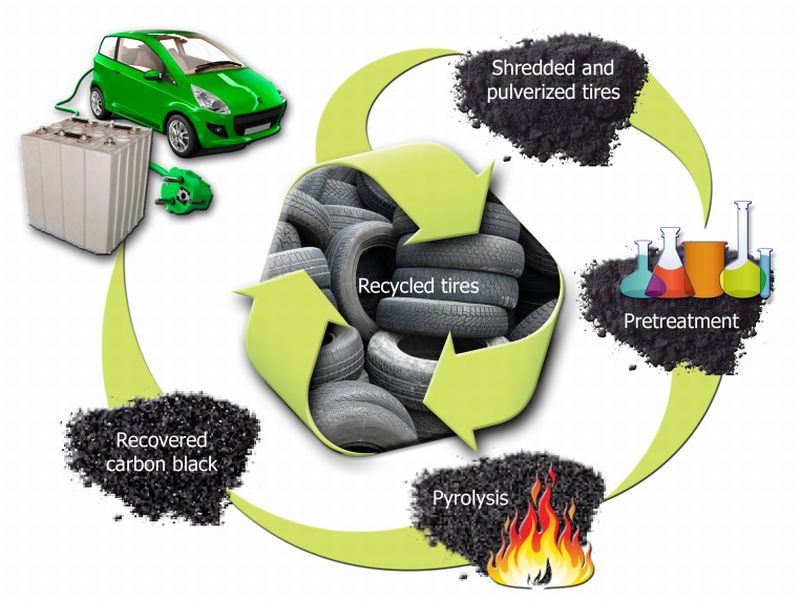
Read MoreWaste Tire Rubber to replace Graphite Anodes: Battery Technology
Shredded scrap car tires have already find their way by means of recycling into the field of construction, floor mats, shoe soles and rubberized asphalt road material. Now, they would be morphing into another innovative role by becoming an integral part of hybrid and electric cars. Researchers at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory are trying to resurrect life from the discarded used tires in form of carbon material that would be used for lithium-ion battery anodes. Conventionally graphite, a natural carbon material, is the basic building block for lithium anodes.
Read MoreGraphene Sheet morphs into Droplets: A Serendipitous Discovery
Graphene does not stop surprising researchers with its limitations when it comes to application in fields like electronics, energy storage and energy generation. The list does not end here, now the wonder material looks promising in domain of medical sciences as well. During routine tests, Monash University’s researchers discovered that sheets of graphene oxide morph into liquid crystal droplets on its own accord. With its new avatar, the graphene droplets have find a promising place in delivery of drugs and disease detection, claimed the researchers.
Read MoreCarbon on the Cathode of Li-ion Batteries: The New Electrochemistry Technology
The University of Alberta experts have fabricated next gen batteries from carbon nanomaterials. This novel product is standing tall in front of conventional lithium-ion batteries where the former is efficient enough to charge faster and happens to lasts longer relatively. The electrochemistry technology As per Xinwei Cui, one of the lead researchers, they have worked upon an innovative approach towards electrochemistry technology consequent upon which, they it was able to yield higher energy density and power. The team has worked along a mechanism called the induced fluorination, a new concept…
Read MoreSkeletal Muscle Cell Powered Bio-Bots: Micro-Bots controlled by an Electric Field
Inspired from living organisms, researchers try to create robots that can simulate living creatures mechanically or chemically. This field of science is named as Biorobotics. A team of researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Campaign has made a miniature walking bio-bots that derive its power from living muscle cells. And their movement can be regulated externally using electrical pulses.
Read MoreSelf-folding Gripper for Capturing Single Cells: Wafer Fabricated for Cellular Analysis
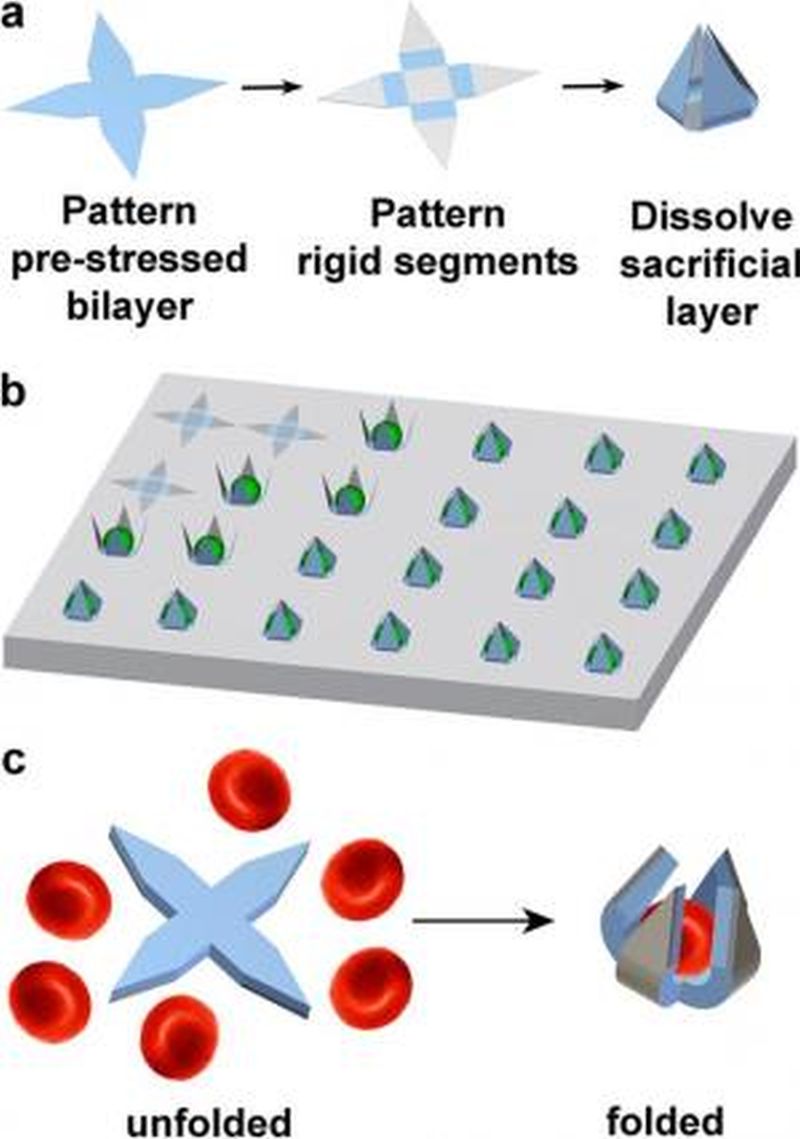
Human body is composed of different biological cells. Each cell is unique. Research shows that a sample of biopsied tumor consists of various distinct cells. These cells differ in their rate of proliferation, responsiveness to drugs, potential metastasis and so on. Therefore, it is essential for researchers to understand the behavior of individual cells and then accordingly design therapy and treatments, for which seizing individual cell is very important.
Read MorePolymer for a Shatterproof Smartphone Touchscreen: Copper-based Flexible Display
Polymer scientists at University of Akron have developed an electrode, which is transparent in nature. Researchers aim to create shatterproof screens for smartphones with this newly fabricated layer of electrode. It’s been quite some time now since, researchers were looking for alternatives to conventional indium-tin oxide, the ITO technology used for making the touchscreen. Brittleness is one of the major flaws with smartphone screens made up of ITO technology. Another equally important reason for looking at its alternative is its scarcity. Moreover, escalation of smartphone and tablet market is fueling…
Read MoreStenocara beetle Inspired Hygroscopic Scaffold: Nanotubes for Storing Water
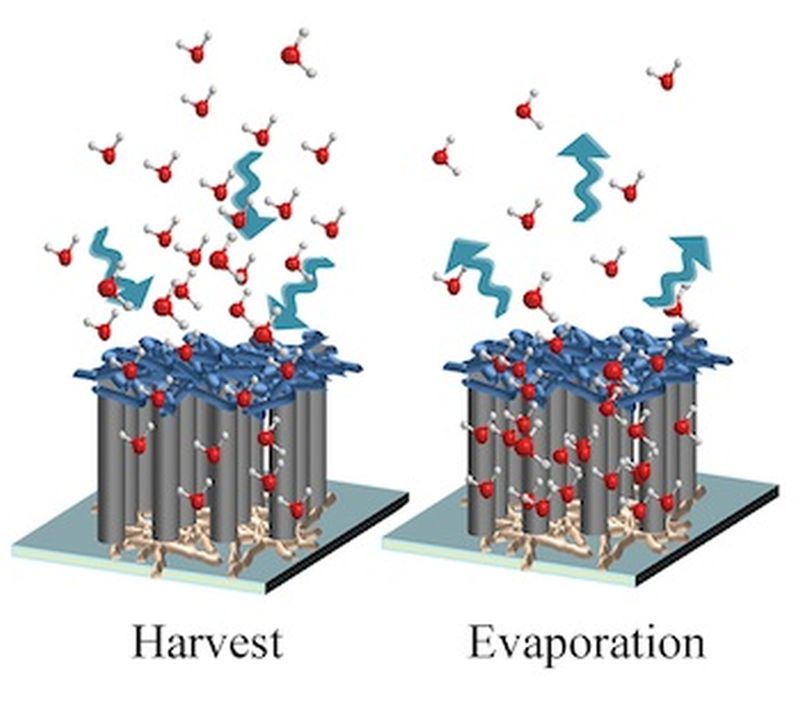
Water is essential for survival of almost all kinds of lives on Earth, hence it is imperative to conserve it at any cost. Researchers from around the world are working to find new and innovative methods to conserve water, especially in areas which are short of water resources. Inspired from an insect, researchers from Rice University have come up with an innovation method of water collection.
Read MoreMagnetoSperm Microrobots for the Nanoworld: Biomimicry
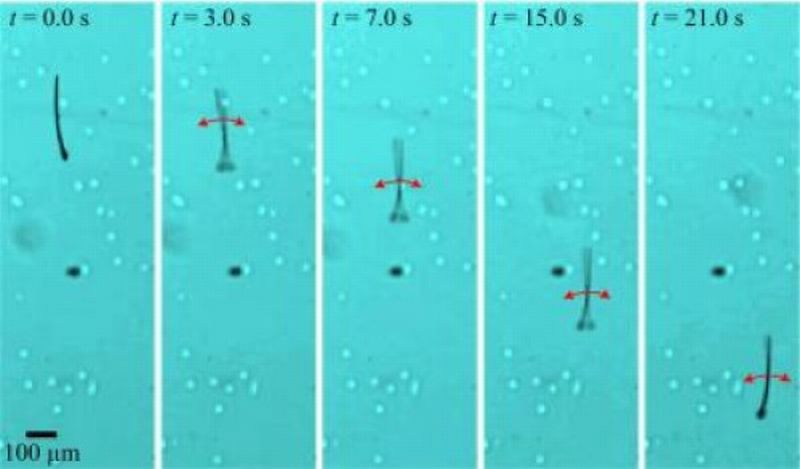
Nature does not stop us marveling at its splendor be it at macro level or micro scale. There are limitless options to investigate and get inspired. Biomimicry is one such field in robotics, which is completely drenched with nature’s splash. Researchers do not leave any stone unturned when dealing with robos inspired from nature, lately a concept is put forward by experts at the University of Twente, Netherlands. They have taken inspiration from nature’s locomotion at microscale and have combined the process of two micro-scale entities like magnetotactic bacteria and…
Read MoreThermometer for Ultrasensitive Measurements: Temperature Control
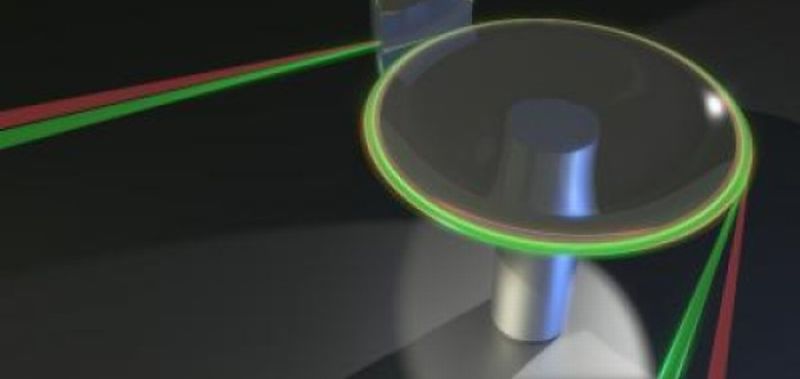
Physics researchers at the University of Adelaide have successfully created a rare thermometer, efficiency of which is thrice the existing best thermometers so far. Reporting further, the experts expatiated that they were able to gauge temperature with the ‘nano-Kelvin thermometer’, through an accuracy of thirty billionths of a degree. Researchers asserted that they have reached the highest level of precision in terms of measuring temperature at room temperature. Talking about the innovation, Professor Luiten one of the lead researcher said that temperature at subatomic level is not static rather fluctuating.…
Read MoreNano- Bots to Enter into the Arteries for Delivering Drugs: High-Performing Nanomotors
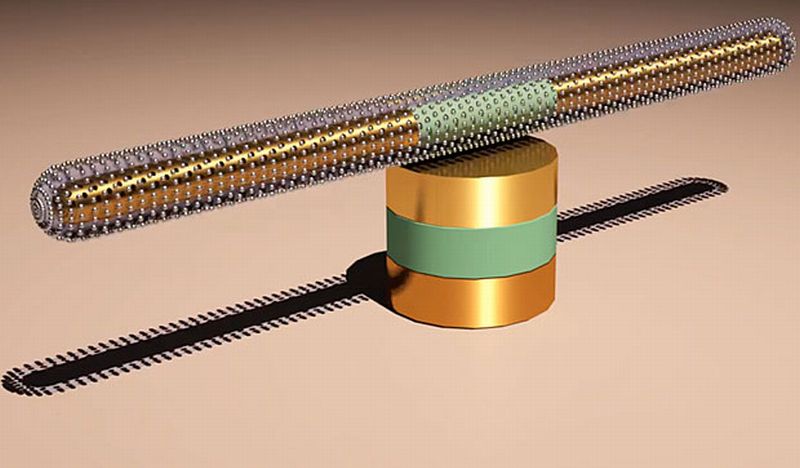
Very soon, we would be witnessing a 3D world on microchips. During the beginning of this year, researchers at Penn State University demonstrated the movement of nanomotors in controlled manner inside living cells. And now, experts at the University of Texas Austin have developed one of the fastest spinning and relatively longer shelf life nanomotor. The newly fabricated nanomotor has an ability of spinning continuously for nearly 15 hours with a speed of 18k rpm. This is an innovative product in the league where the existing nanomotors display an efficiency…
Read MoreEnergy Storage into Structural Materials: No More Power Cords for Devices
Researchers at Vanderbilt University have come up with an intriguing prospect that has complete essence of futuretech in itself. Their current interest hovers around the likelihood of a more technologically enhanced capacity for storing electrical energy directly across applications including but not limited to EVs, laptops and home appliances. They have demonstrated this idea by fabricating small wafers that have the potential of storing and discharging considerable amount of electricity while they are put through static loads or moving forces like vibrations or impacts.
Read More