It’s been more than a decade researchers across the globe are working towards harnessing waste energy into something useful. Most of the times, their energy focused around thermoelectric devices but efficiency of this approach was limited to the accessibility of materials Lately, researchers at Stanford University in collaboration with experts from Massachusetts Institute of Technology have come up with an innovative technology, which captures and morphs waste heat into electricity. The approach holds the low temperature waste heat, that is, less than 100 degrees Celsius.
Read MoreTag: nanotechnology
Innovative Supercapacitor Architecture: A Hybrid between a Supercapacitor and a Pseudocapacitor
Using the nanoparticles of hydrous ruthenium oxide (RuO2) by first modifying them via carbon nanotubes (CNT) and graphene foam as the electrode material for the supercapacitor, the researchers at the University of California Riverside have developed an innovative energy storage device. They have simply called it a supercapacitor, which technically is a hybrid between a supercapacitor and a pseudocapacitor. Once the electrodes were formed via the modification (mentioned above), they were then added in an aqueous electrolyte. The resultant combination provided higher energy with more power density supercapacitors than the…
Read MoreGraphene Ushering the League of Viable Engine for Nanodevices: Lattice Mimics two-stroke Engine
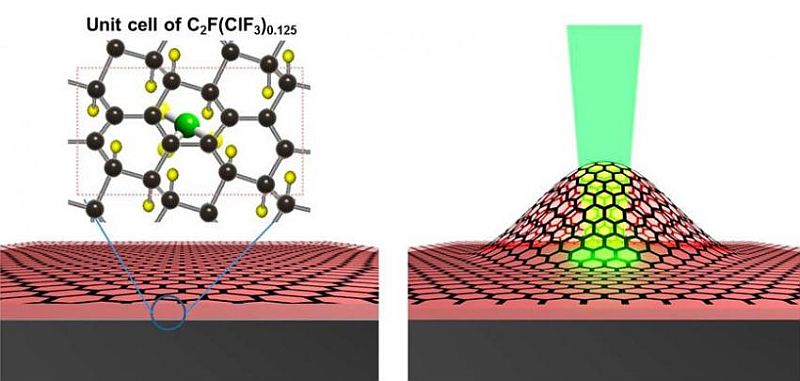
Graphene is one of those rare gifts of nanotechnology that is still not unwrapped fully. Not long ago, we discovered that how sliding water over graphene generated electricity. Every time, researchers conduct an experiment, the lattice of carbon atoms pops up with different surprise. Lately, such revelation has brought to the fore by researchers at National University, Singapore. They have morphed a single layer of graphene along with certain amount of chlorine and fluorine atoms to create a two-stroke combustion engine. Similar mechanism although at a macro-scale is used for…
Read MoreRight Enzymes Replicated the Semi-Synthetic DNA: Expanded-DNA Biology
Scientists always dig deeper into the functioning of nature in order for their better understandings. At times, these trials and errors have given rise to serendipity or accidental discoveries in science, amongst others, recent being how sliding saltwater over graphene generated electricity. While at other times, these experiments go beyond the natural order of workings even at the miniscule level.
Read MoreFabrication of Bi-Layer Molecular Electronic Devices: Nanoscale Circuitry
Until now, it was difficult to charge particles at molecular scale and hence developing circuits at microscopic level has always presented a huge challenge. However, Alexander Shestopalov from University of Rochester has crossed the huddle making a step closer to the fabrication of microscopically small circuit. He powered an organic light-emitting diode (OLED) with a nanoscale circuitry in where he coupled the positive and negative electrodes with one-molecule thin sheet of organic material. Experimental trials and errors have proved that it’s impossible to control current passing through such a single…
Read MoreMagneto-Optical Storage: The Next Generation of Plastic Computers
In an effort to replace silicon chips with flexible plastic within gadgets like computers, cellular devices and related systems, researchers from University of Iowa and New York University have come up with an alternative to the high capacity storage technology. During the fiber optic transmission, it is easier and convenient to encode data in light while magnetism helps in storing information with an unlimited expiry date. With the proposed technology, converting information from one form to another is a critical issue. Since, the energy cost for this process is insignificant…
Read MoreX-Ray Triggered Nanoparticle Photosensitizer: Photodynamic Therapy
While working upon new security-related radiation detection, researchers at the University of Texas, Arlington discovered an advance in photodynamic cancer therapy. Wei Chen, professor of physics at the UT Arlington, noticed an odd luminescence emitted by copper-cysteamine (Cu-Cy) nanoparticles when while working on an experiment where he was exposing the nanoparticles to X-rays. Upon further investigation, he found out that the luminescence was the byproduct of lost energy that the particles were diffusing. The same byproduct is also utilized in photodynamic cancer therapy to destroy cancer cells.
Read MoreSliding Saltwater Over Graphene Generates Electricity
Call it serendipity or chance, a group of researchers at Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics in China while conducting an experiment of creating voltage by plunging carbon nanotubes in a flowing liquid hit upon a discovery of generating electricity by dragging saltwater over a piece of graphene. Traditional Techniques Conventionally, producing electricity via graphene has always been an expensive task plus its unique electrical properties have required for immense work from the end of researchers.
Read MoreSilicon Photonics Chip Mimics Human Brain
Researchers from Ghent University came up with a breakthrough approach by demonstrating processing of information on a chip, mechanism of which was based on the functioning of human brain. Artificial neural networks or the bio inspired technique has been used in the past to bring about complex tasks which otherwise would have been tricky to solve by rule-based programming like computer vision and speech recognition. The researchers applied 16 nodes of neural network directly in hardware with the help of silicon photonics chip. Unlike the traditional computer chips that require…
Read MoreJuxtaposing Living and the Nonliving Worlds Together: Materials Synthesis
So far, we have seen robots inspired from the best of biomimicry. Researchers have often looked upon nature to solve problems. At the same time, there are certain natural tendencies, which engineers are still trying to figure out the way towards artificially re-invention and one of them is ‘bone’. Bone is one of those natural materials that require no supervision, yet it fabricates material in response to environmental signals. In order to understand this phenomenon, researchers at the MIT, have tried to juxtapose living bacterial cells with non-living substance like…
Read MoreMicroplasma Transistors for Smartphones and Nuclear Environment
Researchers at the University of Utah have created one of the most minuscule plasma transistors that can resist soaring temperatures and ionizing radiation that could be seen in a nuclear reactor. The engineers envision that such transistors would: 1) Facilitate taking and collecting X-rays in war zones by high-end cellular phones 2) Integrated within equipments to gauge air quality in the actual time 3) Plasma based bot could be sent into the nuclear reactor for certain assignments Like beavers, the transistors perform the most important work in the field of…
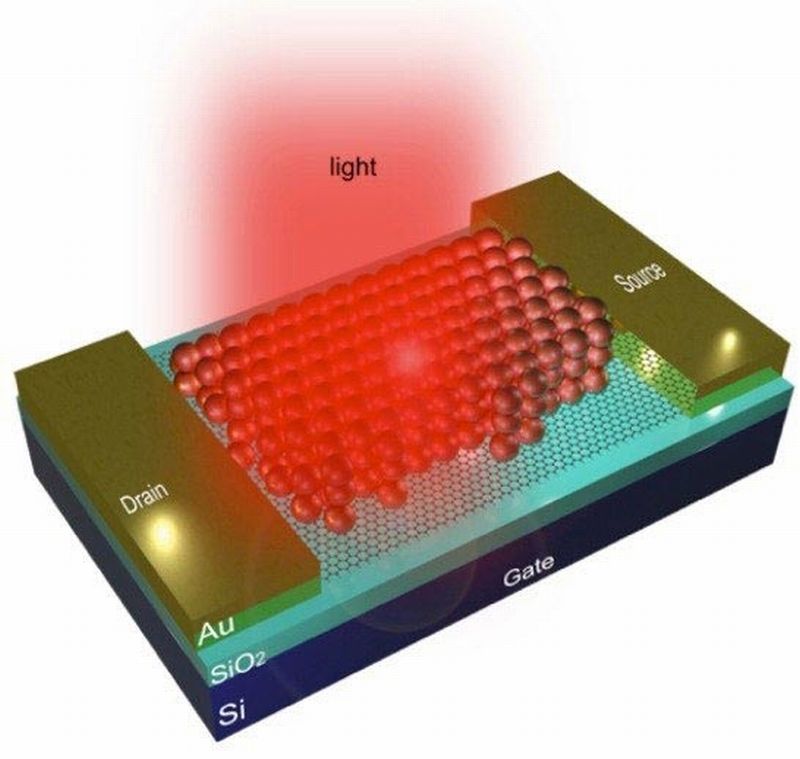
Read MoreGraphene Photodetectors Will Now Offer Thermal Vision
By harvesting the optical capabilities of graphene, researchers at the University of Michigan were able to create infrared contact lens morphed out of the carbon material. Graphene is merely 1-atom thick that makes its absorb nearly 2.3% of light that strikes it, which of course is extremely less especially for generating an electric potential and hence makes it far away from operating as an infrared sensor. Therefore, the researchers devised an innovative technique to resolve this issue. In place of gauging lost electrons by incoming light, they augmented the current…
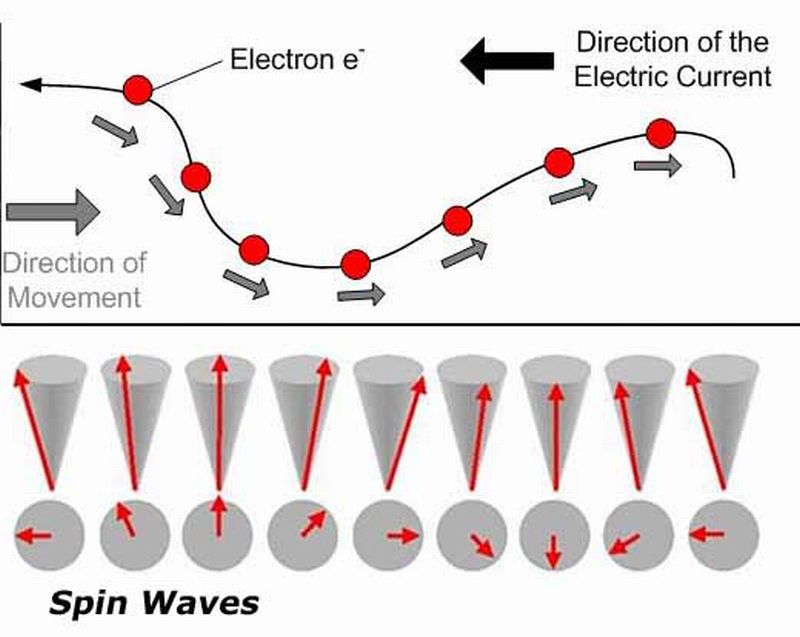
Read MoreMultiferroics’ Propagating Disturbance: Power Booster for Processors
It’s been quite a some time now since researchers were working upon conserving heat that get wasted when electronic device(s) – laptops, computers, smartphones – is in operation. Researchers from the UCLA Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science have come up with a new form of material named “multiferroics” which is rich in magnetic properties. The researchers aim that by incorporating this material, they could enhance the efficiency of energy in the next lot of future devices, an element that is missing in the current technologies. Electric current…
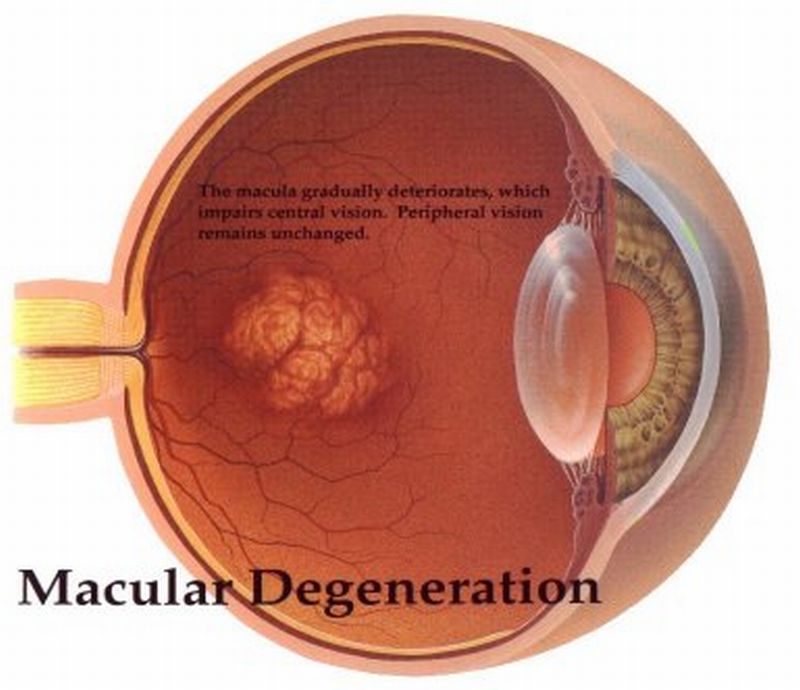
Read MoreNano Innovation to Cure Macular Degeneration
Until now, treatment for eye disorders and other related problems were administered through injections, which were not only unpleasant but expensive as well. However, this would very soon become obsolete since researchers at University College London (UCL) have come up with eye drops for procuring macular degeneration. Nearly 2 in 10 people over 75 have age-related macular degeneration. And at this point of time, the research would prove a boon in combating the growing numbers of patients, and especially when the escalating demands of eye injections becomes responsible for halting…
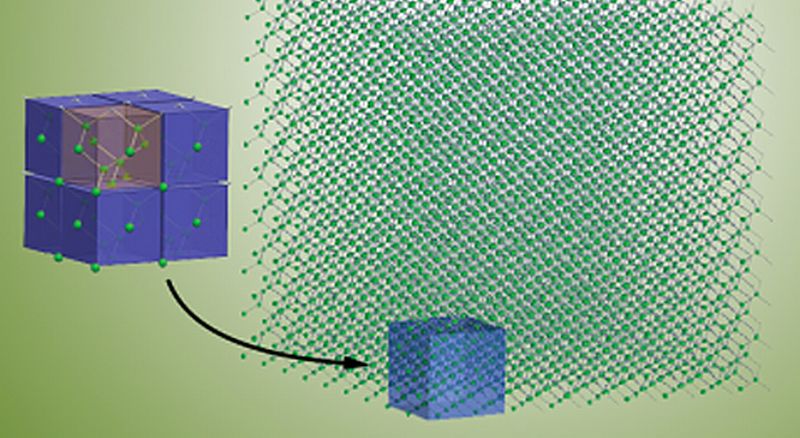
Read MoreResearchers Leverage Lattice Dynamics to Conserve Thermoelectric Energy
It’s been quite some time since researchers were working on the property of thermoelectric material and lately, they were able to develop a prototype that allows electricity to pass through while heat transfer but maintains insulation at the same time. They were able to do this by placing an arrangement of nanopillars on top of the thermoelectric material; to conduct the experiment the material they took was a thin film of silicon. Effect that thermoelectricity produces refers to a phenomena, where electricity is produced due to the temperature variation between…
Read More