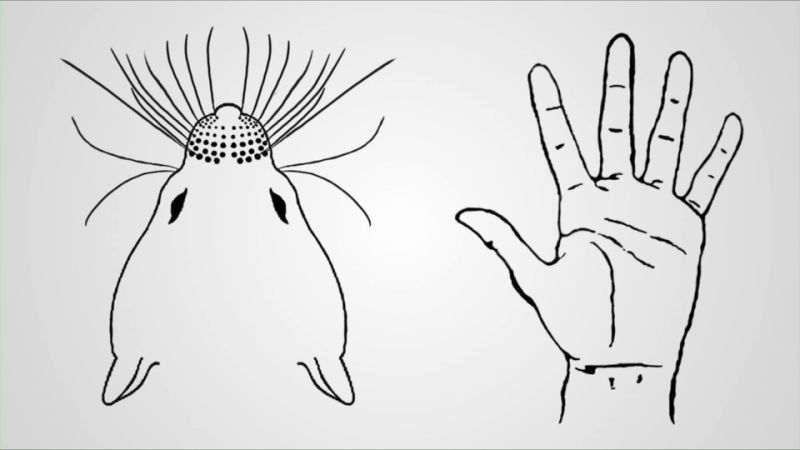
Sense of touch helps us in distinguishing things in regions where sense of sight or our eyes can’t go, let’s say in purse or pocket. If we are to fetch keys from loose change in our pockets, without giving it a second thought, we take out the required thing, this happens due to sensorimotor integration.
Read MoreTag: neuroscience
Music Lessons facilitate Neurodevelopment: Enhancing the Teenage Brain
According to a study conducted by Northwestern University, music training may help in enhancing brain’s responses to sound, hone hearing and language skills in teenagers even if it is introduced as late as in high school. The study suggests music lessons helps improving skills that are considered important for academic success.
Read MoreElectronic long-term Memory Cell that Mimics Brain’s Processes: Artificial Neural Network
With an aid of an electronic multi-state memory cell, RMIT University’s scientists have pioneered not only the technology of emulating the processes of human brain but also its ability of storing good amount of information. The discovery is a giant step that would make them closer to fabricating a bionic brain. Mirroring human brain processes would help treating Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s ailments claimed the team behind the discovery. Brain is like a complex analog computer Project leader Dr Sharath Sriram said that this is a ground-breaking development where they have…
Read MoreBrain Shrinkage associated with Birth Control Pills: Hormonal Contraception
Until now, mood swings, weight gain and nausea have been some of the major side effects from birth control pills. Now, brain shrinkage too has been associated with the drug.
Read MoreHead Mounted Wireless System Fabricated: Paralyzed Patients to convey thoughts at the speed of Internet
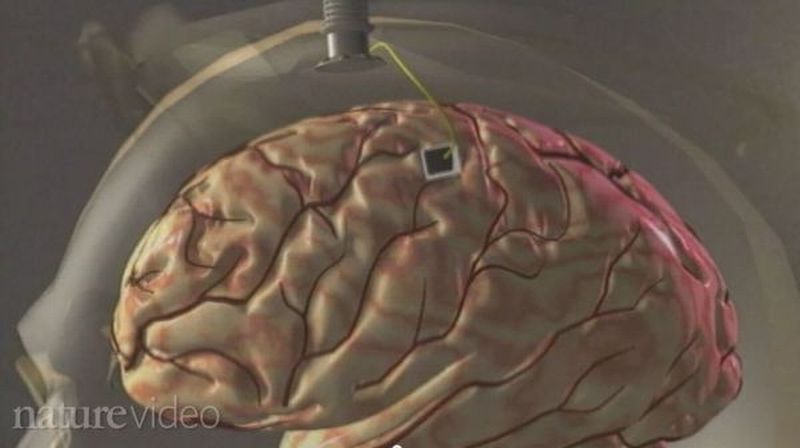
Now paralyzed patients would soon be conveying their thoughts via remote control manually attached to their skull. Experts at Brown University in collaboration with Blackrock Microsystems, a firm based in Utah have fabricated the wireless device. They claim that the gizmo can be implanted to the skull of a patient and then the thought commands are transmitted by the inbuilt radio system. As per the sources, once it gets clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the device would be tested on volunteers, by the end of this year.
Read MoreBell’s Palsy is linked with Migraine: Facial Paralysis
Recent study in Migraine, the neurological disease that causes extreme headaches, has surfaced more than it was thought till now. Not only does the killer pain causes nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light, sound, or smell, it also leads to weakness or paralysis of the face called Bell’s palsy.
Read MoreBrain-Inspired Neuromorphic Chip: Machine starts Thinking
Human brain mechanics has always been one of the most fascinating subjects for neuroscientists all across the globe. Many simulators and robots have been designed by mimicking neurons and synapses, yet the efficiency of brain has not yet thoroughly touched upon so far.
Read MoreHigh Sugary Drinks lead to Poor Memory: Neuroinflammation
High intake of sugar-sweetened beverages (containing high sugar or high fructose corn syrup content) are responsible for obesity, diabetes, coronary heart disease and other disorders. But recently, experts have found that these beverages when consumed (especially in adolescent age) can lead to poor memory and learning skills.
Read MoreElectrical Pulses used to reinstate Movements in Paralyzed Rats: Epidural Stimulation
In Frankenstein effort, Gregoire Courtine, a researcher at the École Polytechnique Fédérale in Lausanne, Switzerland, has developed a process that has helped a paralyzed rat in walking with a precise cadence. The neuroscientist has employed electronics to reinstate realistic movements to the disabled animal. With an aim of resurrecting life in the paralyzed limbs of people, the researcher has zapped spinal cords with electrical pulses. These undulations will substitute the commands being sent by brain in normal condition however, the signals are disrupted with an injury in the spinal cord.
Read MoreGlucose Sensor in Brain Discovered: Controlling Blood-Sugar Level
Experts at Yale School of Medicine have identified a control switch of glucose within brain that has a direct linkage with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Ventromedial nucleus (VMN, or ventromedial hypothalamus, VMH) is a nucleus of the hypothalamus that contains an enzyme called the prolyl endopeptidase. This enzyme initiates a chain of steps that assist in controlling the levels of glucose in blood stream. Researchers envision that this finding would help them in leading towards new treatments for diabetes.
Read MoreSleep Deprivation leads to Memory Errors: Getting Brainwashed
We already know the importance of a good night’s sleep. Taking around 8 hours of sound sleep is considered essential for the body, as it is the time when the brain gets rid of its toxins. But in today’s fast paced life, people often have to give up on their sleep to catch up with other work. This lack of sleep has been already reported as a public health epidemic by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
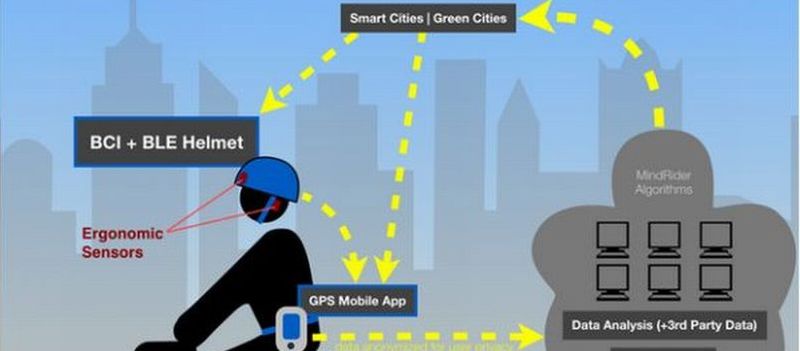
Read MoreMindRider: Brain Monitoring Systems for Mapping Mental Experience
Researchers at the MIT Media Lab are working towards creating a novel helmet system that would reflect bike rider’s mind in the real time. It will be able to mind map rider’s engagement level from relaxed state to focused level while navigating through the routes. Mapping Mental Experience Sensors are embedded within the foam of the helmet that would act as a bridge between the brain waves and translating those ripples into the display of level of engagement. The technique is based on EEG (electroencephalography) where the embedded sensors act…
Read MoreNeuroprosthetic Devices on Deep Brain Simulation Technology: Implants to Restore Memories
A new initiative by the US military program focuses around treating defense personals from the after effects of being into war. In majority of cases, soldiers who come back from battle zones develop adjustment problems or psychiatric disorders to be more specific. For instance, combatants were diagnosed with “shell shock” during the era of WW I, “battle fatigue” during WW II and in Vietnam War, it was PTSD, post-traumatic stress disorder. Backed up by President Obama’s brain initiative, DARPA has received a funding of $70 million from the US to…
Read MoreLearning Process helps Survival of New Neurons: Using Brain at Optimal Levels
In an interesting study in the field of neuroscience, researchers have postulated that learning during the early ages of life helps in the survival of brain cells. Early learning also influence the functioning of brain cells after puberty claimed the same team. An experiment on rats demonstrated that brain cells that were exposed to learning survived with respect to the brain cells in animals that were not allowed to master a particular task. In addition, it was observed that the latter set of animals died quickly too.
Read MoreInternal Monitoring System Responsible for Neural Self-Regulation: The Most Complex Machinery
Parts of any machinery can be replaced, modified or tampered with only when the machine is in an off mode. It is nearly impossible to fiddle around with any operational part while it’s functioning. However, the same principle does not apply for our biological process, especially when we are talking about a nerve cell. This continuous rebuilding without affecting the overall operations has always been neuroscience’s biggest questions. Many theories have been put forward but none of them has ever reached any concrete census. Lately, Eve Marder, the Victor and…
Read More