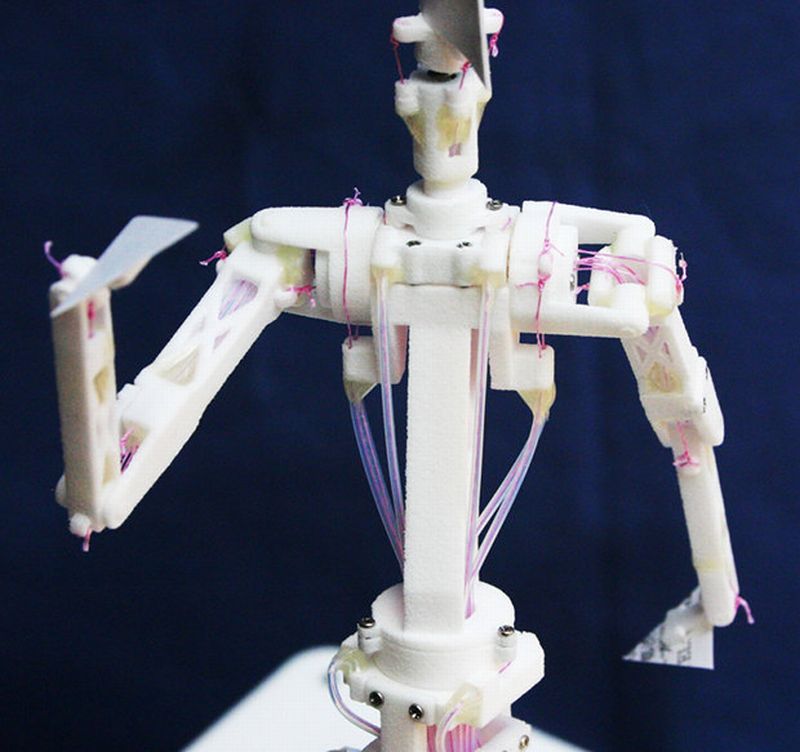
Japan has revolutionized their traditional karakuri puppets by embedding a set of servomotors within the plastics. Market of action figures is already booming in Japan, hence, the plastic model industry is going to be the next big thing in the country. Taking this into consideration, Speecys, a robotics company came up with their Motion Figure system, which they claim is pioneering the spirit of robotic action figures not only in the nation but also across the globe.
Read MoreTag: research
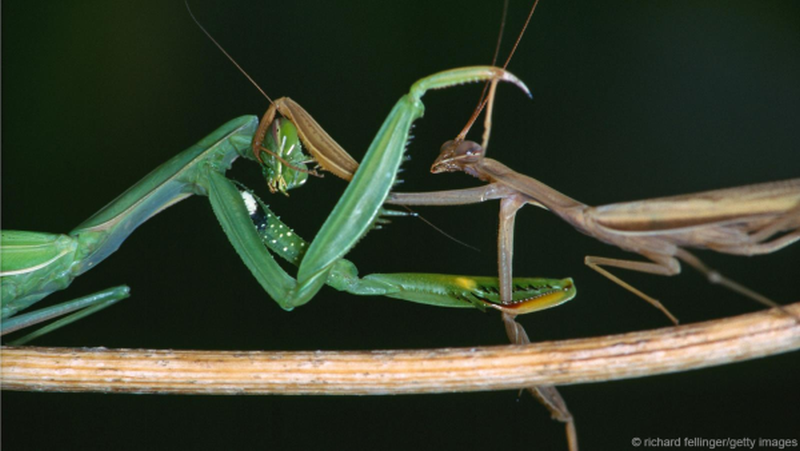
Femme Fatale Mantis deceives Males for Snacking: Risking Lives for Sex
Sexual cannibalism in mantis is a very well known phenomenon. Female mantises bite off the male’s head after or during sex, therefore, is also known as fatale femme. However, the reason behind such sexual cannibalism remains debatable. Female mantises use pheromones to attract males for mating, however, females most of the time ends up eating male mantis, even before the poor male gets a chance to mate. Researchers until now believed that well fed females attracts more males and in turn laid more eggs. Nevertheless, a new study rebuts this…
Read MoreBiomimicry: Robotic Spy Fish will do the Reconnaissance (ISR) Missions
Boston Engineering in collaboration with the U.S. Navy is developing a ‘tuna fish’, their new unmanned underwater vehicle. Developers envision that the fish would autonomously navigate across the sea for fetching information including surveillance and reconnaissance (ISR) missions. The project has been named Project Silent Nemo that comes from Disney’s famous movie, Finding Nemo, where Nemo was the subject of search but in here, Nemo will do the finding. Swimmer drone The unmanned underwater vehicle weighs around 100-pound while it’s length is about 5 feet. As a product of…
Read MoreHelena device can create Oxygen on Red Planet: Global Contest for Mars One’s First Unmanned Lander
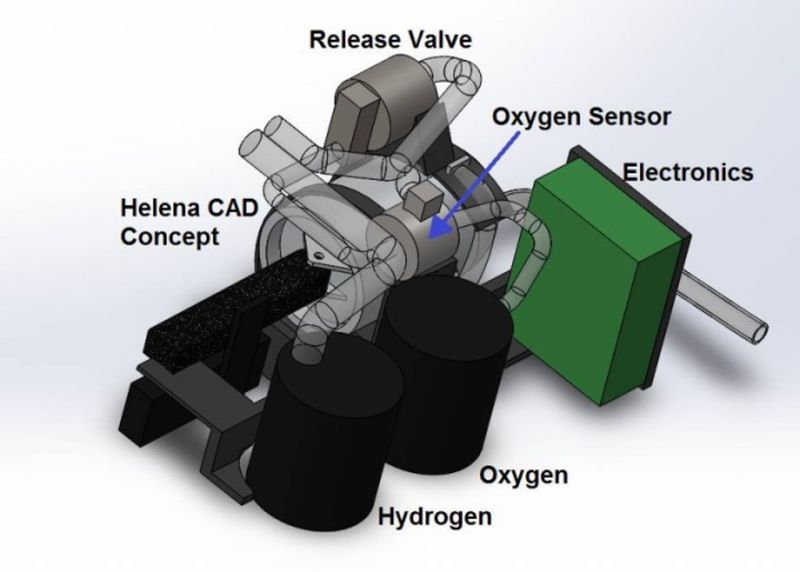
Mars One, the controversial project that plans to create a permanent human settlement on the Red Planet has organized a competition called the Mars One University Competition. The competition has invited designers to prepare technology that can supply Mars citizens with breathable air. The victorious payload will have the opportunity to travel to Mars One initial unmanned lander mission that is scheduled to land on Mars in 2018. This mission will in turn prepare the way for the future colonists planning to reach Mars in 2025. A student team from…
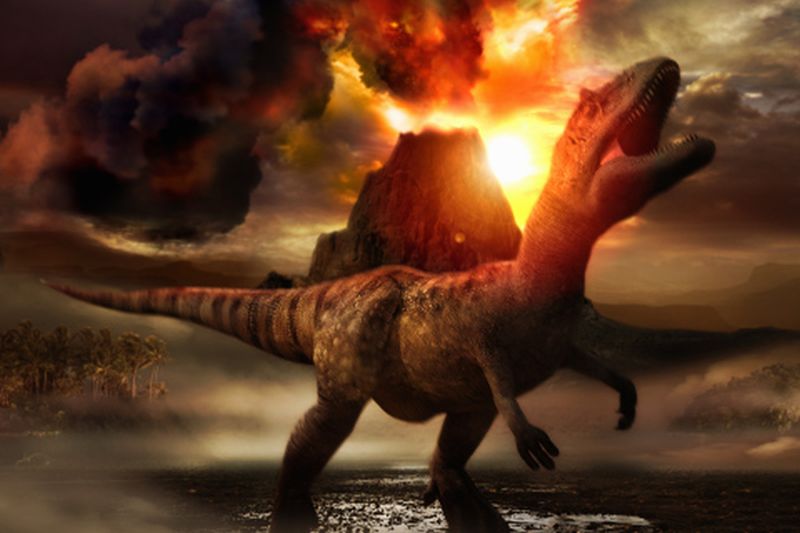
Read MoreVolcanic Eruptions or Asteroid Collision: What really killed the dinosaurs?
Reason related to what led to the extinction of dinosaurs remains debatable. Until now, the most acceptable theory states that around sixty six million years ago, an asteroid as wide as 5 miles and moving at a speed of 70,000 miles per hour bumped into the Earth. The dust from this massive collision blocked the sun and in turn causing catastrophic chains of events that led the extinction of dinosaurs along with three-quarters of other species of the planet.
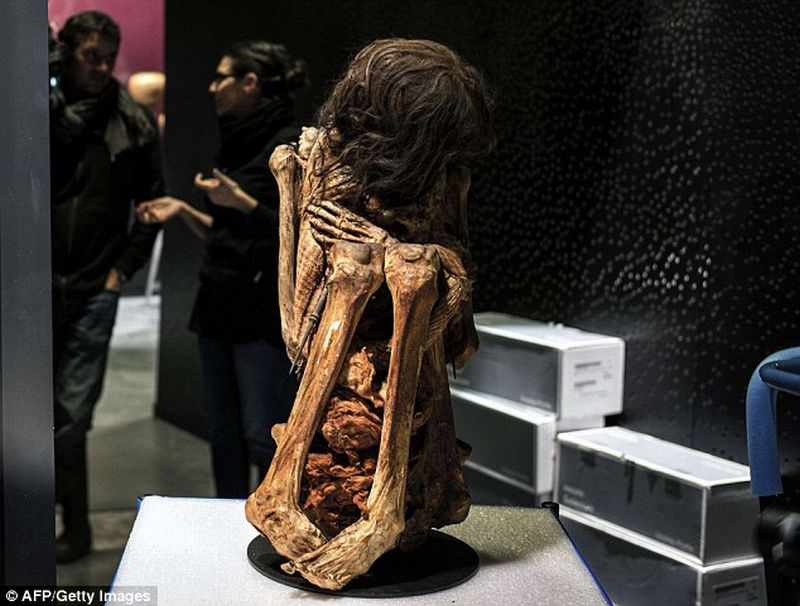
Read MorePeruvian Mummy curled up for 1,000 years: Human Remains on Display
In an excavation work near Lima, capital and the largest city Peru, a mummy dating back to the eleventh century has been discovered. As per the experts, the skeleton is that of a 50-year-old woman, sitting in a foetal position. It is expected that during some ceremonial ritual of the Pachacamac civilization, the resting position was such that with the passage of time (years), the skeleton retained the foetal position. Burial site was happened to be at a significant distance from the abandoned civilization’s temple.
Read MoreSilicon Chip that mimics Nature’s Gene: A Step towards Artificial Cells
Researchers at the Weizmann Institute of Science, Israel have come up with a silicon chip that can mimic a human cell in producing proteins from DNA. The most basic function of cell is to produce proteins after receiving instructions in the form of DNA sequences. Other genes determine production of the quantity of churning out protein by a complex process involving feedback loops.
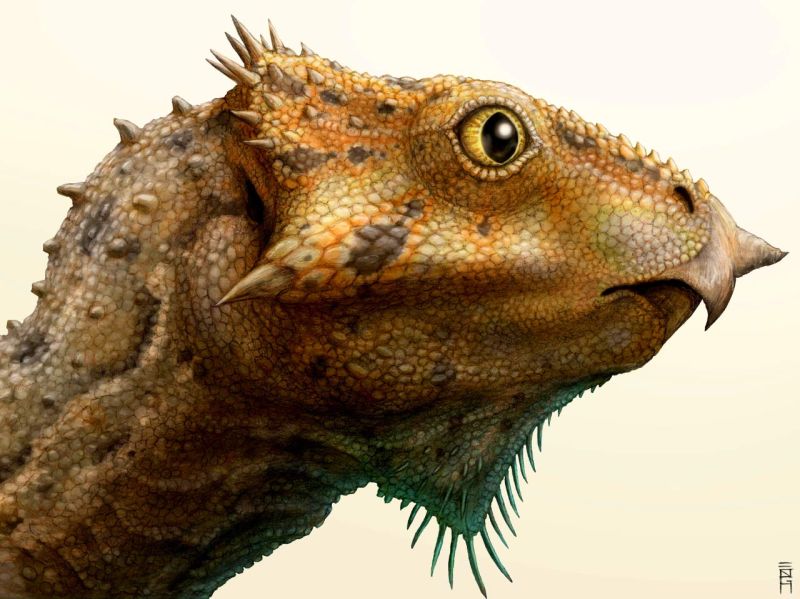
Read MoreCat-Sized Dinosaur Fossil Discovered in Montana: Aquilops americanus
Dr Andrew Farke a paleontologist and his team from Raymond have surfaced a new species of dinosaurs that were herbivorous and beaked belonging to the family of Ceratopsia or Ceratopia. These genus dinosaurs occupied North America, Europe, and Asia, during the Cretaceous Period, nearly 108 million years ago. American eagle face Due to its looks, it’s also called the Aquilops americanus that stands for American eagle face. Unlike Triceratops, also the herbivorous ceratopsid dinosaurs that were expected around late Cretaceous period, its famous relatives, it did not have horns neither…
Read MoreAutomated Valet Parking and Charging for e-Mobility: A Smart Car System
A research conglomerate in Europe is about to finish a futuretech project involving an autonomous car dropping passengers at a railway station and then getting itself parked by identifying an empty spot and later picking up its commuter again. V-Charge is the name of the project that not only helps in commuting, parking but also includes charging up of the automobiles, autonomously. However, the mobility during the entire operation would be slow, so that the sensors may decipher the surrounding accurately.
Read MoreAnimals Self-Medicate to Detoxify Stomach and even Induce Birth: Zoopharmacognosy
It’s been quite some time now that I have had noticed our pets, a cat and two dogs trying to eat grass (at times) and I have always thought that it might be their natural process of cleaning out stomach, now I feel like sharing it here that I was correct. Animals across Brazil, Kenya, US and the UK have been observed doing self-medicating, also called the zoopharmacognosy.
Read MorePolymer that Mimics Sensory Capabilities of Real Skin: The New Smart Skin
Even the most cutting edge technology in prosthetic limbs cannot identify the sensory capabilities of real skin. Although, its manipulation and controls are done with the help of attached muscles and brain yet there have been no way out for detecting the coldness or hotness of a glass its holding. Neither can the wearer detect whether a glass is slipping out of its appendage’s grasp. However, things would no more be the same now, for prosthetics. Korean researchers in collaboration U.S. experts have fabricated an innovative polymer that mimics not…
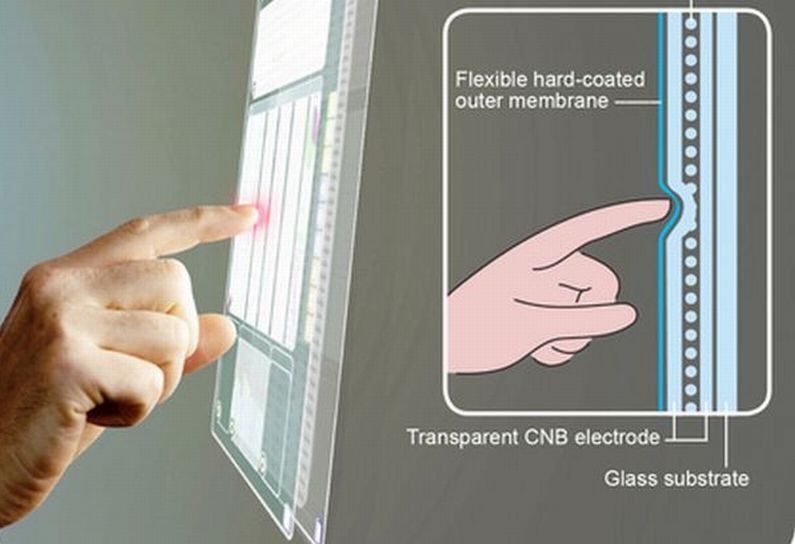
Read MoreNanobuds based Bendable and Flexible Touch Sensor: Touch Screens to New Applications
A Finnish startup, Canatu, has come up with a touch sensor based on transparent films that are fabricated from carbon nanobuds (CNB). What’s interesting about the (CNB based) innovative sensors is that they can be adjusted and can be turned on any surface irrespective of its background shape. For instance, it could be applied on the touch controls of curved surface of automobile dashboard or any gaming consoles or play stations.
Read MoreElectric Eel can remotely Control its Prey: Hijacking Neural Pathways
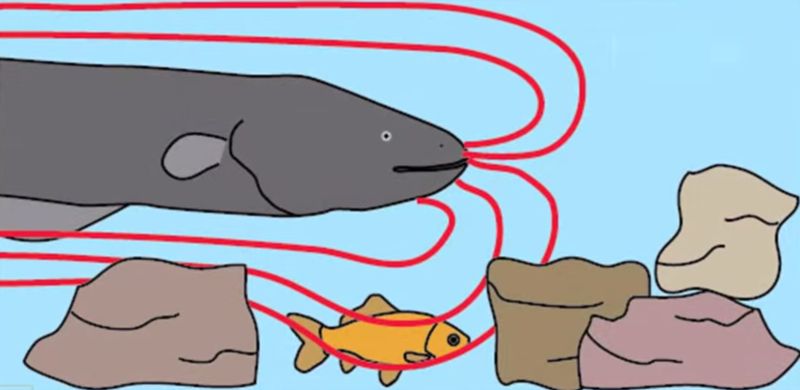
Recent research has surfaced eels’ ability of using shock waves to incapacitate as well as manipulate prey. The predators either discharge a single zap or produce high torrents of voltage causing fish to experience massive involuntary muscle spasms. In some cases, the shocking tactics is used by the eels to generate minor muscle twitches in prey only to get acquaint with their location, the working is similar to that of a sonar. Muscle powered biological batteries is what keeps these eels an edge of discharging nearly 600 volts. This is…
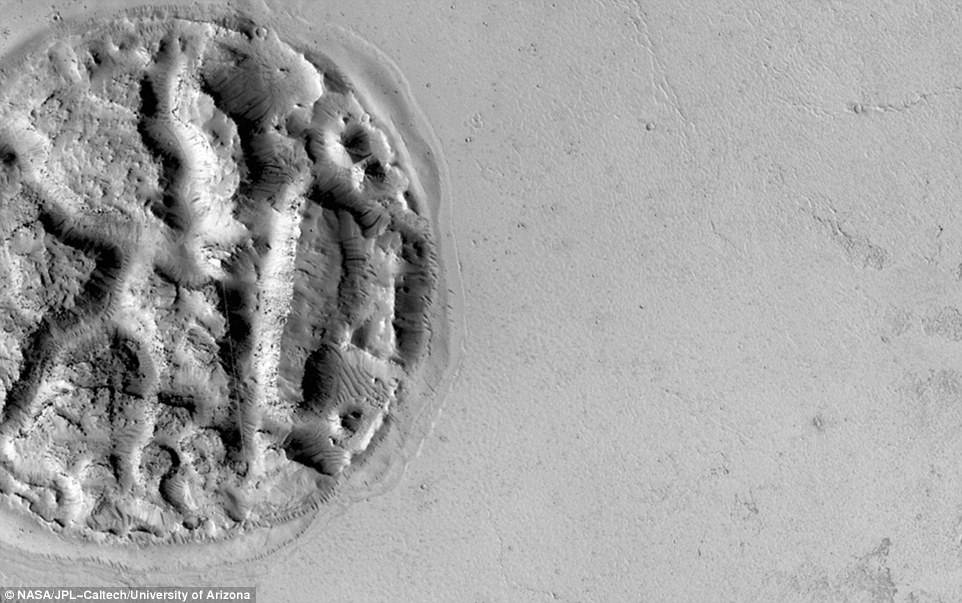
Read MoreImpression of Human Brain discovered on Mars: Athabasca Region of the Red Planet
Recent image received by NASA clarifies the fact that once the Martian surface was saturated by volcanoes. The image has a semblance of a human brain (pictured above) and it stretches over a distance of approximately 1.2 miles. The agency has called it the ‘circular island’ since it appears to be an island encircled by smoothly flowing magma.
Read MoreAffordable Artificial Leaf to produce Clean Hydrogen Fuel: Nanowire Mesh for Direct Solar Water Splitting
Today nations across the world are trying to cut down their greenhouse gas emissions. Alternative energy sources are being tried and tested to replace non-renewable fuel sources and in this race, hydrogen fuel also known as zero emission fuel, definitely seems to have a promising future. Many automobile companies are doing R & D to come up with hydrogen fuel cell vehicles in the auto market. Unfortunately, availability of naturally occurring pure hydrogen on Earth is very limited and therefore, production of hydrogen gas requires tremendous energy. To overcome this…
Read More