There are places on the Moon that haven’t seen sunlight in over two billion years. Deep craters near the lunar south pole, their floors permanently in shadow, sit at temperatures close to -250°C. By the way, this is way colder than Pluto’s surface.
Read MoreTag: space science
Measuring Earth From the Moon
When was the first time you heard the term, “earthshine”? For me it was while I was reading Arthur C. Clarke’s Earthlight, and there was this passage where colonists on the Moon looked up at Earth hanging in their sky.
Read MoreAre We Really Seeing Dark Stars, or Just Strange Young Galaxies?
Formation of the first stars in the universe and the evolution of black holes have always been a mystery to astrophysicists. Now, observations from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) may offer a radical new answer to the existence of “dark stars”.
Read MoreThe ‘Eye of Sauron’: Blazar That Looks Straight at Earth
A group of scientists from different countries found something that will help explain how a distant and seemingly slow object in space, called PKS 1424+240, can be one of the brightest sources of very energetic light (gamma rays) and tiny particles called neutrinos. Even though it appears to move slowly, it produces a lot of these powerful signals.
Read MoreThe Stories from Space You’ll Never See in a Documentary
I was looking for some interesting space missions but outside the usual Apollo and Hubble highlights. And then I came across this Reddit thread – interesting space missions – it pulls together a long list of probes that are genuinely fascinating but rarely talked about. The entire post has its roots in this thread.
Read MoreA Surprising New Theory About Dark Matter and Dark Energy, Inspired by Superconductors
We understand dark matter and dark energy as those invisible things in space that we can’t see but know are out there. As per the scientists dark matter helps hold galaxies together, and dark energy is somehow making the universe expand faster.
Read MoreGerman Instrument Sees the Sun Through Largest Solar Telescope
Have you ever tried zooming-in with your phone to capture a tiny bird or maybe a flower on a branch or shrub? Doesn’t it look like a slightly blurry, shaky mess no matter how steady you try to hold your hand? Now imagine trying to do that, but not for a bird but for the surface of the Sun, 150 million kilometers away.
Read MoreUniverse Is an Ultimate Computer: What if Space-Time is Pixelated?
I’m always on the lookout for some radical take when it comes to research papers, and this time, a research article by physicist Melvin Vopson totally caught my attention. Vopson suggests, what if gravity isn’t some deep, fundamental force of nature, but actually just the universe’s way of managing its information better? Sounds strange at first, but it’s got a logic to it.
Read MoreSupernova Remnant in Nearby Galaxy Studied via Radio
Astronomers just took a fresh look at a supernova remnant called MC SNR J0519–6902 tucked away in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a small galaxy orbiting the Milky Way. It’s been known since the early ’80s, but there’s still a lot we don’t fully understand about it, especially when it comes to its age and how it’s evolved over time.
Read MoreDMS and DMDS Hints in K2-18 b’s Atmosphere from JWST MIRI Data
Recent research paper published by the American Astronomical Society – New Constraints on DMS and DMDS in the Atmosphere of K2-18 b from JWST MIRI – digs into the atmosphere of K2-18 b, which is the exoplanet people have been calling a “Hycean World,” meaning it might have a hydrogen-rich atmosphere and liquid water oceans. This study is based on data from JWST’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument), and it’s the first time we’ve gotten a mid-infrared transmission spectrum of a habitable-zone exoplanet like this.
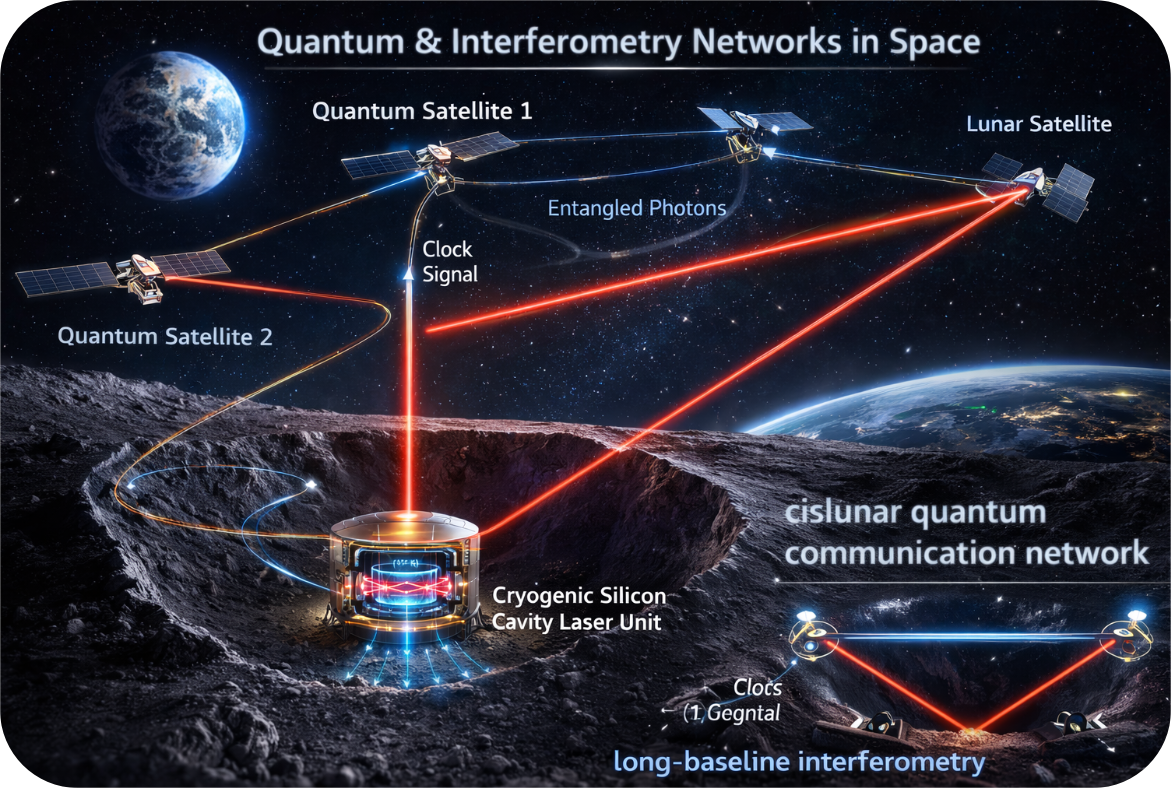
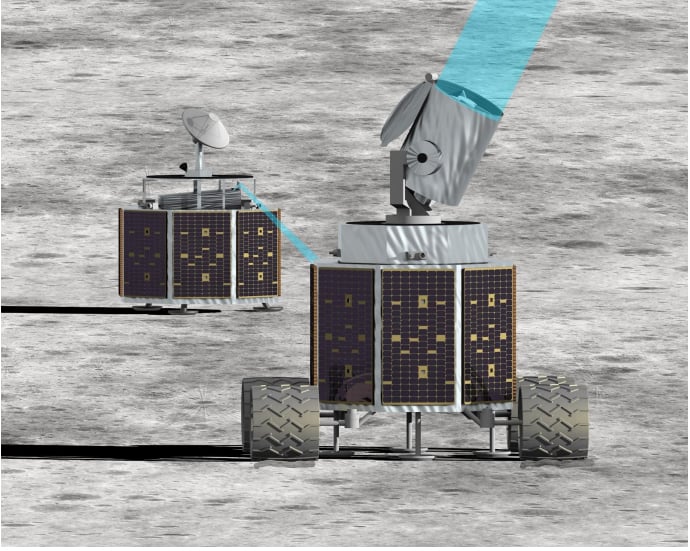
Read MoreArtemis-Enabled Stellar Imager: A Lunar Telescope Array to Unveil the Secrets of Stars and Black Holes
Imagine building a huge group of telescopes on the Moon, where there’s no air or weather to interfere, allowing us to see further into space than we ever could before. That’s the idea behind the Artemis-enabled Stellar Imager (AeSI), a proposed lunar interferometer designed to reveal what’s happening on the surfaces of stars and deep inside active galactic nuclei (AGN). A team led by Dr. Kenneth Carpenter at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center recently completed a nine-month feasibility study, and their findings suggest that this ambitious idea is not just…
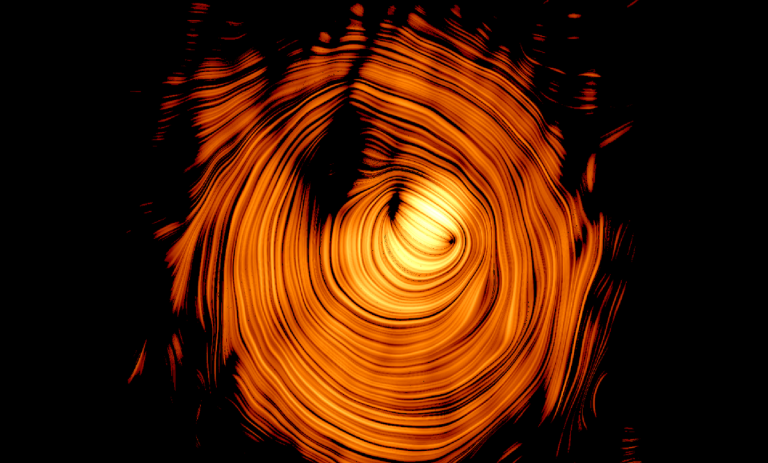
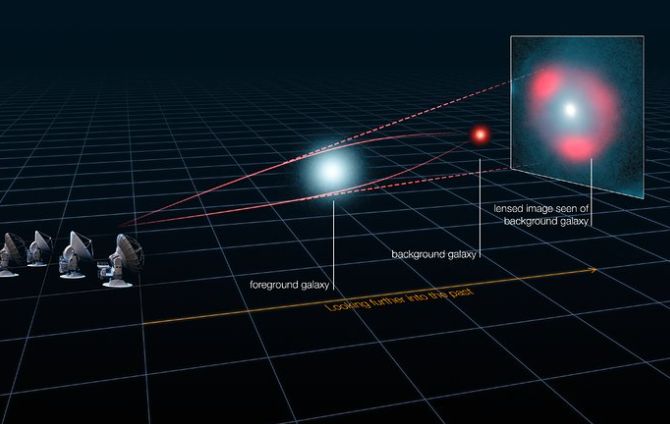
Read MoreEarly Universe Structures Found by JWST: Cosmic Revelations
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has revolutionized our understanding of the early universe, particularly with its discoveries in 2024. The objects that have been discovered have revealed properties and structures that challenges our current understanding of cosmic theories. These groundbreaking findings, many made possible by the phenomenon of gravitational lensing, have opened new avenues of research into how the earliest galaxies and stars formed.
Read MoreAI Revolution: Detecting Unseen Gravitational Waves with Deep Learning
Somewhere in 1916, Albert Einstein figured out his theory about gravity that there are waves in the fabric of spacetime. Also known as ripples. Since then, scientists have been working out what these waves would look like in a few basic situations, like merging of two black holes.
Read MoreBlack Hole Mergers: Dark Matter Might Be the Missing Link
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 is one of the farthest probes that we’ve sent so far. As of July 2024, it’s a whopping 24.4 billion kilometers away from Earth, making it the most distant human-made object ever. Yet, there are things in the space that we have absolutely zero clue. Yes, I’m referring to – Dark Matter. Dark matter helps slow the black holes down and lets them come together for supermassive black hole mergers, at least the recent research says so. Typically elusive, this invisible matter seems to play…
Read MoreInterview: Dr. Boris Goncharov, a Senior Scientist at the Albert Einstein Institute, Germany
I’m thrilled to introduce Dr. Boris Goncharov, a distinguished figure in the field of gravitational wave research. Currently, he is a Senior Scientist with the Pulsar Timing Array (PTA) group at the Albert Einstein Institute (AEI) in Hanover, Germany, where he is exploring the fascinating world of nanohertz-frequency gravitational waves.
Read More